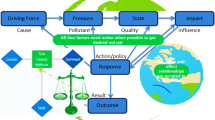
Abstract
The generation of municipal solid waste (MSW) in urban areas is rising globally and is having a negative impact on social, economic, and environmental situations. As a result, the environmental implications and resource recovery potential of MSW management systems are gaining traction. The major goal of this research is to evaluate Bahir Dar's solid waste management procedures by developing the Driver, Pressure, State, Impact, Response and Outcome (DPSIRO) framework indicators. Edraw Max and Cmap tools software were used to create DPSIRO framework indicators. Population increase, fast urbanization, and economic growth are all thought to be driving influences. The environmental state resulting from pressure was computed using the IPCC model and statistical analysis was done using SPSS software. The response indicators and respected outcomes are taken into account when the framework is conceptualized. In the years between 2007 and 2020, the population grew from 221,991 to 414,763. Driving force generates 73 tons of solid trash per day in 2007 and 148 tons per day in 2020. In 2020, the city's greenhouse gas emissions totaled 46 Gg/year. When the replies are implemented, the city may create around 47,772 tons of organic fertilizer, saving approximately 1,313,724 Ethiopian birr per year. According to the findings, Bahir Dar should begin implementing 3R solid waste management strategies to minimize potential environmental and human health risks while also maximizing economic benefits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Bank (2018) What a waste 2.0—a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. The World Bank 1818 H Street NW, Washington, DC 20433. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-1-4648-1329-0
Memon MA (2010) Integrated solid waste management based on the 3R approach. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-009-0274-0
Yirgalem M (2005) Landfill management, its impacts on the local environment and urban sustainability: the case of Repi landfill site, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Acta Geogr. Series B. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajee/2019/v9i230088
Teshome FB (2020) Municipal solid waste management in Ethiopia; the gaps and ways for improvement. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01118-y
Mohammed G (2015) Assessing the current status of solid waste management of gondar Town Ethiopia. Int J Sci Technol Res 4:28–36
Wegedie KT (2018) Households solid waste generation and management behavior in case of Bahir Dar City, Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia. Cogent Environ Sci 4:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2018.1471025
Elsaid E, Houssaine S (2017) A progress indicator—based assessment guide for integrated municipal solid—waste management systems. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-017-0647-8
Kazuva E, Zhang J, Tong Z, Si A, Na L (2018) The DPSIR model for environmental risk assessment of municipal solid waste in Dar es Salaam city, Tanzania. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081692
Levrel H, Kerbiriou C, Couvet D, Weber J (2009) OECD pressure—state—response indicators for managing biodiversity: a realistic perspective for a French biosphere reserve. Biodivers Conserv 18:1–12
Afrasiabi ZS (2015) Application of DPSIR framework for integrated environmental assessment of urban areas: a case study of Tehran. Int J Environ Res 9:445–456
Ramusch R, Obersteiner G (2009) Strategies for waste management in tourist cities. Urban-Waste 18(7):1719–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-008-9507-0
Carr ER, Wingard PM, Yorty SC, Thompson MC, Jensen NK, Justin R (2007) Applying DPSIR to sustainable development. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504500709469753
Kassahun E, Birara T (2018) Assessment of solid waste management practices in Bahir Dar. Pollution 4:251–261. https://doi.org/10.22059/poll.2017.240774.311
Tirusew AS, Ebistu A, Minal (2013) Solid waste dumping site suitability analysis using geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing for Bahir Dar Town, North Western Ethiopia. African J Environ Sci Technol 7:976–989. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJEST2013.1589
Lohri C, Riuji C, Ephraim J, Zurbrügg C (2014) Financial sustainability in municipal solid waste management—costs and revenues in Bahir Dar. Ethiopia, Waste Manag 34:542–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.10.014
Kassie KE (2016) The problem of solid waste management and people awareness on appropriate solid waste disposal in Bahir Dar city: Amhara region, Ethiopia. ISABB J Heal Environ Sci 3:1–8. https://doi.org/10.5897/ISAAB-JHE2016.0026
Seyoum S (2019) Institute of Ethiopian studies early history of Bahir Dar Town: c: 1900–1941. Inst Ethiop Stud 45:73–94
UNEP (2010) Solid waste characterization and quantification of Bahir Dar city for the development of integrated solid waste management. Int Environ Technol Cent. https://doi.org/10.21275/v5i6.NOV164799
Wegedie KT (2018) Advances in recycling and waste management household behavior and demand for better solid waste management services: a case of Bahir Dar City, Amhara national regional stat. Adv Recycl Waste Manag 3:1–14. https://doi.org/10.4172/2475-7675.1000152
Bairu A, Gesessew A, Jigar E (2014) Application of IPCC model for estimation of methane from municipal solid waste landfill. J Environ Sci Water Resour 164(1–4):249–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0889-6
Kaushal A, Sharma MP (2016) Methane emission from panki open dump site of Kanpur, India. Procedia Environ Sci 35:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.014
Biruk AF (2017) Waste management in the case of Bahir Dar city near Lake Tana shore in Northwestern Ethiopia: a review. African J Environ Sci Technol 11:393–412. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajest2017.2340
Srivastava V, Ismail SA, Singh P, Singh RP (2015) Urban solid waste management in the developing world with emphasis on India: challenges and opportunities. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:317–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-014-9352-4
Asmare M, Alelign B (2019) Bahir Dar city municipal solid waste potential assessment for clean energy. Am J Energy Eng 7:28–38. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajee.20190701.14
Kumar M, Prakash V (2020) A review on solid waste: its impact on air and water quality. J Pollut Eff Control 8:1–3. https://doi.org/10.35248/2375-4397.20.8.252.Copyright
Pandey K, Tiwari (2013) Impact of municipal solid waste on subsurface water quality near the landfill site. Int J Eng Res Technol 2:3767–3772
Adeolu AO, Ada OV, Gbenga AA, Adebayo OA (2011) Assessment of groundwater contamination by leachate near a municipal solid waste landfill. African J Environ Sci Technol 5:933–940. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJEST11.272
Feng H, Chen S, Zhang C, Xu T (2019) Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Landfills : A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Susteniablity. 1–15.https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082282
Hoang NH, Fogarassy C (2020) Sustainability evaluation of municipal solid waste management system for hanoi (Vietnam)—why to choose the “waste-to-energy” concept. Sustain 12:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082282
Polngam P, Chiemchaisri W, Kaewmanee A, Chiemchaisri C, Yamamoto K (2015) Chemical characterization in correlation to toxicity evaluation for water reuse of solid waste leachates in the itMBR-RO system. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 17:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-014-0310-6
Mekonnen B, Haddis A, Zeine W (2020) Assessment of the effect of solid waste dump site on surrounding soil and river water quality in Tepi Town, Southwest Ethiopia. J Environ Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5157046
Manfredi EC, Flury B, Viviano G, Thakuri S, Khanal SN, Jha PK, Maskey RK, Kayastha RB, Kafle KR, Bhochhibhoya S, Ghimire NP, Shrestha BB, Chaudhary G, Giannino F, Carten F, Mazzoleni S, Salerno F (2010) Solid waste and water quality management models for sagarmatha national park and buffer zone, Nepal. Mt Res Dev 30:127–142. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-10-00028.1
Sn C (2017) Solid waste pollution: a hazard to environment. Recent Adv Petrochem Sci 2:41–43. https://doi.org/10.19080/rapsci.2017.02.555586
Majumdar D, Srivastava A (2012) Volatile organic compound emissions from municipal solid waste disposal sites: a case study of Mumbai, India. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 62:398–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2012.655405
Navarro V, Torretta F (2019) Waste mismanagement in developing countries: a review of global issues. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061060
Biruk AF (2017) Waste management in the case of Bahir Dar city near Lake Tana shore in Northwestern Ethiopia: a review, African. J Environ Sci Technol 11:393–412. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJEST2017.2340
Kassahun T, Birara E (2018) Assessment of solid waste management practices in Bahir Dar city, Ethiopia. Pollution 4:251–261. https://doi.org/10.22059/poll.2017.240774.311
Wegedie KT (2018) Household behavior and demand for better solid waste management services: a case of Bahir Dar city, Amhara national regional stat, Ethiopia. Adv Recycl Waste Manag 03:1–15. https://doi.org/10.4172/2475-7675.1000152
Kinnaman TC (2009) The economics of municipal solid waste management. Waste Manag 29:2615–2617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2009.06.031
IoanaI I (2010) Clean technology from waste management. In: 4th WSEAS international conference on waste management, water pollution, air pollution, indoor climate, WWAI '10, pp 155–171
Kim J, Jeong S (2017) Economic and environmental cost analysis of incineration and recovery alternatives for flammable industrial waste: the case of South Korea. Sustain Adv Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9091638
Ghosh SK (2016) Sustainable SWM in developing countries focusing on faster growing economies, India and China. Proc Environ Sci 35:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.073
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misganaw, A., Teffera, B. Development of DPSIRO framework indicators for municipal solid waste management: a case of Bahir Dar city, Ethiopia. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 23, 2101–2111 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01266-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01266-9