Abstract
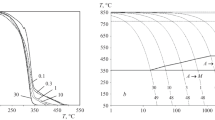
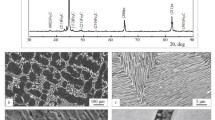
In this paper, we present the results of laboratory studies of the effect of the tempering temperature of hardened rolled structural steel with a carbon content of 0.18–0.20% on changes in the structure, the microstress level and dislocation density, mechanical properties and resistance to cracking in a hydrogen sulfide-containing environment. A metal structure with a microstress level of 0.08–0.075% and a dislocation density of 1.20 × 1013 m–2, a metal matrix hardness HV of less than 200, providing resistance against cracking in H2S environment, is shown to be formed after quenching at 920°C and tempering in the temperature range of 600–720°C.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Carneiro, R.A. and Ratnapuli, R.C., The influence of chemical composition and microstructure of API linepipe steels on hydrogen induced cracking and sulfide stress corrosion cracking, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, vol. 357, pp. 104–110.
Hara, T., Asahi, H., and Ogawa, H., Conditions of hydrogen-induced corrosion occurrence of X65 grade line pipe steels in sour environments, Corrosion, 2004, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 1113–1121.
Nayak, S.S., Misra, R.D.K., and Hartmann, J., Microstructure and properties of low manganese and niobium containing HIC pipeline steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vol. 494, pp. 456–463.
Shabalov, I.P., Matrosov, Yu.I., Kholodnyi, A.A., et al., Stal’ dlya gazonefteprovodnykh trub, stoikikh protiv razrusheniya v serovodorodsoderzhashchikh sredakh (Steel for Gas-Oil Pipes Resistant to Destruction in Hydrogen Sulfide-Containing Environments), Moscow: Metallurgizdat, 2017.
Zikeev, V.N., Construction steels resistant to hydrogen sulfide cracking and brittle fracture, Doctoral (Eng.) Dissertation, Moscow, 1984.
Ioffe, A.V., Development of high-strength and corrosion resistant steels for manufacturing of pipes for petroleum industry, Extended Abstract of Doctoral (Eng.) Dissertation, Penza, 2008.
Naumenko, V.V., Bagmet, O.A., and Mursenkov, E.S., Resistance of low-carbon microalloyed pipe steels to cracking in hydrogen sulfide media, Chern. Metall., Byull. Nauchno-Tekh. Ekon. Inf., 2018, no. 7, pp. 56–64.
Efron, L.I., Metallovedenie v bol’shoi metallurgiyi. Trubnye stali (Physical Metallurgy in Large-Scale Production: Pipe Steel), Moscow: Metallurgizdat, 2012.
Naumenko, V.V., Muntin, A.V., Baranova, O.A., et al., The effect of heat treatment on the mechanical properties and resistance to cracking of structural steel in the hydrogen sulfide environment, Chern. Met., 2020, no. 6, pp. 56–61.
Mursenkov, E.S., Kudashov, D.V., Kislitsa, V.V., et al., Features of technology for pipe steel modification with calcium and cerium with specification for resistance to H2S-media, Metallurgist, 2019, vol. 62, nos. 9–10, pp. 994–1005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by A. Ivanov
About this article
Cite this article
Naumenko, V.V., Muntin, A.V., Baranova, O.A. et al. Resistance to Hydrogen Cracking of Rolled Structural Steel after Heat Processing. Steel Transl. 51, 211–216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091221030086
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091221030086