Abstract
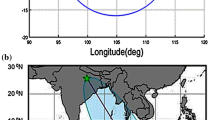
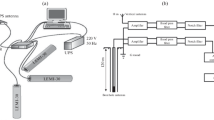
In this paper, we have analyzed TEC data obtained at Indian stations such as Agra, Lucknow, Hyderabad, Bangalore, and Port Blair and VLF amplitude data of NWC fixed frequency (f = 19.8 KHz) transmitter signals recorded at Agra for ±15 days from the day of occurrence of a strong earthquake of magnitude M = 8.5 on 11 April, 2012 in Indonesian region. The analysis is performed using well established statistical methods. We have found simultaneous seismogenic anomalies in TEC and VLF data prior and after the occurrence of the earthquake. Some of the anomalies occurring after the earthquake are identified as due to high solar activity. These anomalies are excluded from our analysis. Some on the VLF anomalies are simultaneous with TEC anomalies indicating that the effect of the earthquake from ground reaches to lower ionosphere and also penetrates up to upper ionosphere in a mechanism possibly involving atmospheric gravity waves (AGWs). These results are also supported by the ground based ULF measurements at Agra using a search coil magnetometer in which we found amplitude bursts in all the three components of the sensor on the day of earthquake after its occurrence. Finally, this multi-instruments and multi-stations data study has confirmed that the strong earthquake affects not only the epicenter area but also the adjoining region and the effect is larger away from the epicenter than that close to the epicenter. This is explained in terms of generation of AGWs from the epicenter.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
24 March 2022
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793222330015
REFERENCES
Akhoondzadeh, M., Anomalous TEC variations associated with the powerful Tohoku earthquake of 11 March 2011, Nat. Hazard Earth Syst., 2012, vol. 12, pp. 1453–1462.
Asada, T., Earthquake Prediction Techniques: Their Application in Japan, Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, 1982.
Cahyadi, M.N. and Heki, K., Coseismic ionospheric disturbance of the large strike-slip earthquakes in North Sumatra in 2012: Mw dependence of the disturbance amplitudes, Geophys. J. Int., 2015, vol. 200, pp. 116–129.
Calais, E., and Minster, J.B., GPS detection of ionospheric TEC perturbations following the January 17, 1994, Northridge earthquake, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1995, vol. 22, pp. 1045-1048.
Chapman, S., The equatorial electrojet as detected from the abnormal electric current distribution above Huancayo, Peru and elsewhere, Arch. Meteorol., Geophys. Bioklimatol.,Ser. A, 1951, vol. 4, pp. 368–390.
Choudhury, A., De, B.K., Guha, A., and Roy, R., Long-duration geomagnetic storm effects on the D region of the ionosphere: Some case studies using VLF signal, J. Geophys. Res: Space Phys., 2015, vol. 120, no. 1, pp. 778–787.
DasGupta, A., Das, A., Hui, D., Kumar, K.B., and Sivaraman, M.R., Ionospheric perturbations observed by the GPS following the December 26th 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake, Earth Planets Space, 2006, vol. 58, pp. 167–172.
Devi, M., Sarma, A. J.D., Kalita, S., Barbara, A.K., and Depueva, A., Adaptive techniques for extraction of pre-seismic parameters of Total Electron Content (TEC) at anomaly crest station, Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk, 2012, vol. 3, pp. 193–206.
Devi, M., Patgiri, S., Barbara, A.K., Oyama, K.I., Ryu, K., Depuev, V., and Depueva, A., Role of equatorial anomaly in earthquake time precursive features: A few strong events over West Pacific zone, J. Adv. Space Res., 2017, vol. 61, pp. 1444–1455.
Du, A., Huang, Q. and Yang, S., Epicenter location by abnormal ULF electromagnetic emissions, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2005, vol. 29, no. 10, pp. 94-1–94-3.
Garmash, S.V., Lin’kov, E.M., Petrova, L.N., and Shved, G.M., Generation of atmospheric oscillations by seismic gravitational vibrations of the Earth, Izv. Akad. Nauk: Fiz. Atmos. Okeana, 1989, vol. 25, pp. 1290–1299.
Ghaedi, K., and Ibrahim, Z., Earthquake prediction, in Earthquakes: Tectonics, Hazard and Risk Mitigation, Zouaghi, T., Ed., Rijeka, Croatia: IntechOpen, 2018, pp. 205–227.
Gokhberg, M.B., Gufeld, I.L., Rozhnoy, A.A., Marenko, V.F., Yampolsky, V.S., and Ponomarev, E.A., Study of seismic influence on the ionosphere by super long wave probing of the Earth–ionosphere waveguide, Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 1989, vol. 57, pp. 64–67.
Gonzalez, W.D., Joselyn, J.A., Kamide, Y., et al., What is a geomagnetic storm?, J. Geophys. Res., 1994, vol. 99, pp. 5771–5792.
Gufeld, I.L., Rozhnoy, A.A., Tyumentsev, S.N., Sherstyuk, S.V., and Yampolsky, V.S., Radio wave field disturbances prior to Rudbar and Rachinsk earthquakes, Izv.,Phys. Solid Earth, 1992, vol. 28, pp. 267–270.
Guo, J., Li, W., Liu, X., Wang, J., Chang, X., and Zhao, C., On TEC anomalies as precursor before MW 8.6 Sumatra earthquake and MW 6.7 Mexico earthquake on April 11, 2012, Geosci. J., 2015, vol. 19, pp. 721–730.
Gupta, S. and Upadhyaya, A.K., Pre-earthquake anomalous ionospheric signatures observed at low-mid latitude Indian station, Delhi, during the year 2015 to early 2016: Preliminary results, J. Geophys. Res., 2017, vol. 122, pp. 1–26.
Han, P., Hattori, K., Hirokawa, M., Zhuang, J., Chen, C.-H., Febriani, F., Yamaguchi, H., Yoshino, C., Liu, J.-Y., and Yoshida, S., Statistical analysis of ULF seismomagnetic phenomena at Kakioka, Japan, during 2001–2010, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2014, vol. 119, pp. 1–15.
Hasbi, A.M., Mohd Ali, M.A., and Mirran, N., Ionospheric variations before some large earthquakes over Sumatra, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2011, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 597–611.
Hattori, K., Akinaga, Y., Hayakawa, M., Yumoto, K., Nagao, T., and Uyeda, S., ULF magnetic anomaly preceding the 1997 Kagoshima earthquake, in Seismo-Electromagnetics: Lithosphere–Atmosphere–Ionosphere Coupling, Hayakawa, M., and Molchanov, O.A., Eds., Tokyo: Terra Scientific Publishing Company, 2002, pp. 19–28.
Hayakawa, M., Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena with Earthquakes, Tokyo: Terra Scientific Publishing Company, 1999.
Hayakawa, M., Lower ionospheric perturbations associated with earthquakes as detected by subionospheric VLF/LF radio waves, in Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes, Hayakawa, M., Ed., Trivandrum (India): Transworld Res. Net., 2009, ch. 6, pp. 137–185.
Hayakawa, M., Earthquake Prediction with Radio Techniques, Wiley, 2015.
Hayakawa, M., and Fujinawa, Y., Electromagnetic Phenomena Related to Earthquake Prediction, Tokyo: Terra Scientific Publishing Company, 1994.
Hayakawa, M., and Molchanov, O.A., Seismo Electromagnetics: Lithospheric–Atmospheric–Ionospheric Coupling, Tokyo: Terra Scientific Publishing Company, 2002.
Hayakawa, M., Molchanov, O.A., and NASDA/UEC team, Achievements of NASDA’s earthquake remote sensing frontier project, Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., 2004, vol. 15, pp. 311–328.
Hayakawa, M., Horie, T., Muto, F., Kasahara, Y., Ohta, K., Liu, J.Y., and Hobara, Y., Subionospheric VLF/LF probing of ionospheric perturbations associated with earthquakes: A possibility of earthquake prediction, SICE J. Control Meas. Syst. Int., 2010a, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 010–014.
Hayakawa, M., Kasahara, Y., Nakamura, T., Muto, F., Horie, T., Maekawa, S., Hobara, Y., Rozhnoi, A.A., Solovieva, M., and Molchanov, O.A., A statistical study on the correlation between lower ionospheric perturbations as seen by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation and earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res., 2010b, vol. 115, A09305.
Hayakawa, M., Raulin, J.P., Kasahara, Y., Bertoni, F.C.P., Hobara, Y., and Guevara, W., Day, Ionospheric perturbations in possible association with the 2010 Haiti earthquake, as based on medium-distance subionospheric VLF propagation data, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 513–518.
Hayakawa, M., Hobara, Y., Rozhnoi, A., Solovieva, M., Ohta, K., Izutsu, J., Nakamura, T., and Kasahara, Y., The ionospheric precursor to the 2011 March 11 earthquake based upon observations obtained from the Japan-Pacific subionospheric VLF/LF network, Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., 2013, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 393–408.
Heki, K., Otsuka, Y., Choosakul, N., Hemmakorn, N., Komolmis, T., and Maruyama, T., Detection of ruptures of Andaman fault segments in the 2004 great Sumatra earthquake with coseismic ionospheric disturbances, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, B09313, pp. 1–11.
Horie, T., Maekawa, S., Yamauchi, T., and Hayakawa, M., A possible effect of ionospheric perturbations associated with the Sumatra earthquake, as revealed from subionospheric very low-frequency (VLF) propagation (NWC-Japan). Int. J. Remote Sens., 2007, vol. 28, pp. 3133–3139.
Ismagulov, V. S., Kopytenko, Y. A., Hattori, K., and Hayakawa, M., Variations of phase and gradient values of ULF geomagnetic disturbances connected with the Izu strong earthquakes, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2003, vol. 3, pp. 211–215.
Jain, S.K., and Singh, B., Vertical motions of the low and equatorial-latitude F2 layers during prolonged and isolated magnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 1977, vol. 82, pp. 723–726.
Karia, S.P., and Pathak, K.N., Change in refractivity of the atmosphere and large variation in TEC associated with some earthquakes, observed from GPS receiver, Adv. Space Res., 2011, vol. 47, pp. 867–876.
Kasahara, Y., Muto, F., Horie, T., Yoshida, M., Hayakawa, M., Ohta, K., Rozhnoi, A., Solovieva, M., and Molchanov, O.A., On the statistical correlation between the ionospheric perturbations as detected by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation anomalies and earthquakes, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2008, vol. 8, pp. 653–656.
Kasahara, Y., Muto, F., Hobara, Y., and Hayakawa, M., The ionospheric perturbations associated with Asian earthquakes as seen from the subionospheric propagation from NWC to Japanese stations, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2010, vol. 10, pp. 581–588.
Kherani, E. A., Lognonne, P., Hebert, H., Rolland, L., Astafyeva, E., Occhipinti, G., Coïsson, P., Walwer, D., and dePaula,E. R., Modelling of the total electronic content and magnetic field anomalies generated by the 2011 Tohoku-Oki tsunami and associated acoustic-gravity waves, Geophys. J. Int., 2012, vol. 191, pp. 1049–1066.
Khilyuk, L.F., Chillingar, G.V., Robertson, J.O., Jr., and Endres, B., Gas Migration Events Preceding Earthquakes, Houston: Gulf Publishing Company, 2000.
Klimenko, M.V., Klimenko, V.V., Zakharenkova, I.E., and Pulinets, S.A., Variations of equatorial electrojet as possible seismo-ionospheric precursors at the occurrence of TEC anomalies before strong earthquake, Adv. Space Res., 2012, vol. 49, pp. 509–517.
Klotz, S. and Johnson, N.L., Eds., Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, John Wiley and Sons, 1983.
Kopytenko, Yu., Ismagilov, V., Hayakawa, M., Smirnova, N., Troyan, V., and Peterson, T., Investigation of the ULF electromagnetic phenomena related to earthquakes: Contemporary achievements and the perspectives, Ann. Geophys., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 325–334.
Lakshmi, D.R., Veenadhari, B., Dabas, R.S., and Reddy, B.M., Sudden post-midnight decreases in equatorial in F-region electron densities associated with severe magnetic storms, Ann. Geophys., 1997, vol. 15, pp. 306–313.
Laštovička, J., Monitoring and forecasting of ionospheric space weather-effects of geomagnetic storms, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2002, vol. 64, nos. 5–6, pp. 697–705.
Le, H., Liu J.Y., and Liu, L., A statistical analysis of ionospheric anomalies before 736 M6.0+ earthquakes during 2002–2010, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 116, A02303.
Liu J.Y., Chen, Y.I., Chuo, Y.J., and Tsai, H.F., Variations of ionospheric total electron content during the Chi-Chi earthquake, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2001, vol. 28, pp. 1383–1386.
Liu, J.Y., Chen, Y.I., Jhuang, H.K., and Lin, Y.H., Ionospheric foF2 and TEC anomalous days associated with M ≥ 5.0 earthquakes in Taiwan during 1997–1999, Terr. Atmos. Oceanic Sci., 2004a, vol. 15, pp. 371–383.
Liu, J.Y., Chuo, Y.J., Shan, S.J., Tsai, Y.B., Chen, Y.I., Pulinets, S.A., and Yu, S.B., Pre-earthquake ionospheric anomalies registered by continuous GPS TEC measurements, Ann. Geophys., 2004b, vol. 22, pp. 1585–1593.
Liu, J.Y., Chen, Y.I., Chuo, Y.J., and Chen, C.S., A statistical investigation of pre-earthquake ionospheric anomaly, J. Geophys. Res., 2006, vol. 111, no. A5.
Liu, J.Y., Chen, Y.I., Chen, C.H., Liu, C.Y., Chen, C.Y., Nishihashi, M., Li, J.Z., Xia, Y.Q., Oyama, K.I., Hattori, K., and Lin, C.H., Seismo-ionospheric GPS total electron content anomalies observed before the 12 May 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114, A04320, pp. 1–10.
Liu, J.Y., Chen, C.H., Chen, Y.I., Yang, W.H., Oyama, K.I., and Kuo, K.W., A statistical study of ionospheric earthquake precursors monitored by using equatorial ionization anomaly of GPS TEC in Taiwan during 2001–2007, J. Asian Earth Sci., 2010, vol. 39, pp. 76–80.
Liu, J.Y., Chen, Y.I., Chen, C.H., and Hattori, K., Temporal and spatial precursors in the ionospheric global positioning system (GPS) total electron content observed before the 26 December 2004 M9.3 Sumatra–Andaman Earthquake, J. Geophys. Res., 2011, vol. 115, A09312, pp. 1–13.
Maurya, A.K., Venkatesham, K., Tiwari, P., Vijaykumar, K., Singh, R., Singh, A.K., Ramesh, D.S., The 25 April 2015 Nepal Earthquake: investigation of precursor in VLF subionospheric signal, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2016, vol. 121, no. 10, pp. 10403–10416.
Miyaki, K., Hayakawa, M., Molchanov, O.A., The role of gravity waves in the lithosphere ionosphere coupling, as revealed from the subionospheric LF propagation data, in Seismo Electromagnetics: Lithosphere–Atmosphere–Ionosphere Coupling, Tokyo: Terra Sci. Pub. Co., 2002, pp. 229–232.
Molchanov, O.A. and Hayakawa, M., Subionospheric VLF signal perturbations possibly related to earthquakes, 1998, vol. 103, no. A8, pp. 17489–17504.
Molchanov, O.A. and Hayakawa, M., Seismo-Electromagnetics and Related Phenomena: History and Latest Results, Tokyo: TERRAPUB, 2008.
Molchanov, O.A., Mazhaeva, O.A., Golyavin, A.N., and Hayakawa, M., Observation by the Intercosmos-24 satellite of ELF-VLF electromagnetic emissions associated with earthquakes, Ann. Geophys., 1993, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 431–440.
Molchanov, O.A., Hayakawa, M., Miyaki, K., VLF/LF sounding of the lower ionosphere to study the role of atmospheric oscillations in the lithosphere–ionosphere coupling, Adv. Polar Upper Atmos. Res., 2001, vol. 15, pp. 146–158.
Muto, F., Kasahara, Y., Hobara, Y., Hayakawa, M., Rozhnoi, A., Solovieva, M., and Molchanov, O.A., Further study on the role of atmospheric gravity waves on the seismo-ionospheric perturbations as detected by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2009, vol. 9, pp. 1111–1118.
Naaman, S., Aplerovich, L.S., Wdowinski, S., Hayakawa, M., and Calais, E., Comparison of simultaneous variations of the ionospheric total electron content and geomagnetic field associated with strong earthquakes, Nat. Hazards and Earth Syst. Sci., 2001, vol. 1, pp. 53–59.
Oikonomou, C., Haralambous, H., and Muslim, B., Investigation of ionospheric TEC precursors related to the M7.8 Nepal and M8.3 Chile earthquakes in 2015 based on spectral and statistical analysis, Nat. Hazards, 2016, pp. 1–20.
Pandey, U., Singh, A.K., Kumar, S., and Singh, A.K., Seismogenic ionospheric anomalies associated with the strong Indonesian earthquake occurred on 11 April 2012 (M = 8.5), Adv. Space Res., 2018, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 1244–1253.
Ray, S., Chakrabarti, S.K., Mondal, S.K., and Sasmal, S., Ionospheric anomaly due to seismic activities. III: Correlation between nighttime VLF amplitude fluctuations and effective magnitudes of earthquakes in Indian sub-continent, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 2699–2704.
Rozhnoi, A., Shalimov, S., Solovieva, M., Levin, B., Hayakawa, M., and Walker, S., Tsunami-induced phase and amplitude perturbations of subionospheric VLF signals, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, A09313, pp. 1–8.
Rozhnoi, A., Hayakawa, M., Solovieva, M., Hobara, Y., and Fedun, V., Ionospheric effects of the Mt. Kirishima volcanic eruption as seen from subionospheric VLF observations, J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys., 2014, vol. 107, pp. 54–59.
Park, S.K., Johnson, M.J.S., Maddenm, T.R., Morgan, F.D., and Morrison, H.F., Electromagnetic precursors to earthquakes in ULF band: A review of observations and mechanism, Rev. Geophys., 1993, vol. 31, pp. 117–132.
Pulinets, S., Ionospheric precursors of earthquakes; recent advances in theory and practical applications, Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., 2004, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 413–435.
Pulinets, S. and Boyarchuk, K., Ionospheric Precursors of Earthquakes, Springer, 2004.
Pulinets, S., and Davidenko, D., Ionospheric precursors of earthquakes and global electric circuit, J. Adv. Space Res., 2014, vol. 53, no. 5, pp. 709–723.
Pulinets, S.A., and Liu, J.Y., Ionospheric variability unrelated to solar and geomagnetic activity, Adv. Space Res., 2004, vol. 34, no. 9, pp. 1926–1933.
Pulinets, S. and Ouzounov, D., Lithosphere–Atmosphere–Ionosphere Coupling (LAIC) model—An unified concept for earthquake precursors validation, J. Asian Earth Sci., 2011, vol. 41, pp. 371–382.
Pundhir, D., Singh, B., Singh, O.P., 2014. Anomalous TEC variations associated with the strong Pakistan-Iran border region earthquake of 16 April 2013 at a low latitude station Agra, India. Adv. Space Res. 53, pp. 226–232.
Pundhir, D., Singh, B. Lakshmi, D.R., and Reddy, B.M., A study of ionospheric precursors associated with the major earthquakes occurred in Pakistan region, J. Ind. Geophys. Union, 2015, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 71‒76.
Pundhir, D., Singh, B., Singh, O.P., and Gupta, S.K., A statistical study of TEC anomalies induced by major earthquakes occurred around Indian Subcontinent, J. Ind. Geophys. Union, 2016, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 325‒333.
Pundhir, D., Singh, B., Singh, O.P., and Gupta, S.K., A morphological study of low latitude ionosphere and its implication in identifying earthquake precursors, J. Ind. Geophys. Union, 2017a, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 214–222.
Pundhir, D., Singh, B., Singh, O.P., Gupta, S.K., Karia, S.P., and Pathak, K. N., Study of ionospheric precursors using GPS and GIM-TEC data related to earthquakes occurred on 16 April and 24 September, 2013 in Pakistan region, J. Adv. Space Res., 2017b, vol. 60, pp. 1978‒1987.
Rama Rao, P.V.S., Niranjan, K., Prasad, D.S.V.V.D., Seemala, G. K., and Uma, G., On the validity of the ionospheric pierce point (IPP) altitude of 350 km in the equatorial and low latitude sector, Ann. Geophys., 2006, vol. 24, pp. 2159–2168.
Rastogi, R.G., Chandra, H., James, M.E., Kitamura, K., and Yumoto, K., Characteristics of the equatorial electrojet current in the central region of South America, Earth Planets Space, 2008, vol. 60, pp. 623–632.
Sarita, S., Singh, R.P., Pundhir, D., Singh, B., A multi-experiment approach to ascertain electromagnetic precursors of Nepal earthquakes, J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys., 2020, vol. 197, pp. 1–11.
Shalimov, S.L., and Gokhberg, M.B., Lithosphere–ionosphere coupling mechanism and its application to the earthquake in Iran on June 20, 1990: A review of ionospheric measurements and basic assumptions, Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 1998, vol. 105, pp. 211–218.
Schekotov, A.Y., Molchanov, O.A., Hayakawa, M., Fedo-rov, E.N., Chebrov, V.N., Sinitsin, V.I., Gordeev, E.E., Andreevsky, S.E., Belyaev, G.G., Yagova, N.V., Gladishev, V.A., and Baransky, L.N., About possibility to locate an epicenter using parameters of ELF/ULF pre-seismic emissions, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 2008, vol. 8, pp. 1237–1242.
Singh, B., and Pundhir, D., Shift of effective lightning areas during pre to post period of solar cycle minimum of 2008–2009 as determined from Schumann resonance studies at Agra, India, Ann. Geophys., 2014, vol. 57, no. 6, A0657. https://doi.org/10.4401/ag-6596
Singh, O.P., and Singh, B., Ionization enhancements in sporadic E-layers prior to some major Indian earthquakes, J. Atmos. Elect., 2004, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 75–87.
Singh, B. and Singh, O. P, Simultaneous ionospheric E- and F-layer perturbations caused by some major earthquakes in India, Ann. Geophys., 2007, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 111–122.
Singh, B., Kushwah, V., Singh, O.P., Lakshmi D.R., and Reddy, B.M., Ionospheric perturbations caused by some major earthquakes in India, Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C, 2004, vol. 29, nos. 4–9, pp. 537–550.
Singh, D., Singh, B., and Pundhir, D., Ionospheric perturbations due to earthquakes as determined from VLF and GPS-TEC data analysis at Agra, India, Adv. Space Res., 2018, vol. 61, pp. 1952–1965.
Sorokin, V.M., Yashchenko, A.K., and Hayakawa, M., Electric field perturbation caused by an increase in conductivity related to seismicity-induced atmospheric radioactivity growth, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2007, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 644–648.
Swati, Singh, B., Pundhir, D., Hobara, Y., Fractal analysis of ultra low frequency magnetic field emissions observed at Agra associated with two major earthquakes occurred in Pakistan, J. Atmos. Electr., 2020, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 1–15.
Xiangxiang, Y., Tao, Y., Xinjian, S., and Chunliang, X., Ionospheric TEC disturbance study over seismically region in China, J. Adv. Space Res., 2017, pp. 2822–2835.
Yamazaki, Y., Richmond, A.D., Maute, A., Liu, H.L., Pedatella, N., and Sassi, F., On the day-to-day variation of the equatorial electrojet during quiet periods, J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys., 2014, vol. 119, pp. 6966–6980.
Yang, Y.M., Meng, X., Komjathy, A., Verkholyadova, O., Langley, R.B., Tsurutani, B.T., and Mannucci, A.J., Tohoku-Oki earthquake caused major ionospheric disturbances at 450 km altitude over Alaska, Rad. Sci., 2014, vol. 49, pp. 1206–1213.
Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Liu, J., Shen, X., Miao, Y., Du, X., and Quain, J., Ground-based and satellite DC-ULF electric field anomalies around Wenchuan M8.0 earthquake, Adv. Space Res., 2012, vol. 50, pp. 55–95.
Zhao, B., Wang, M., Yu, T., Wan, W., Lei, J., Liu, L., and Ning, B., Is an unusual large enhancement of ionospheric electron density linked with the 2008 great Wenchuan earthquake?, J Geophys. Res. A: Space Phys., 2008, vol. 113, A11304.
Zhu, F., Wu, Y., Zhou, Y., and Gao, Y., Temporal and spatial distribution of GPS TEC anomalies prior to the strong earthquakes, Astrophys. Space Sci., 2013, vol. 345, pp. 239–246.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors are thankful to editor for his polite and encouraging suggestions. Thanks are also due to esteemed referee for line to line reading of the paper and extending useful suggestions which enhanced the quality of the paper. Authors are also grateful to Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), Government of India, New Delhi to provide the earthquake data. Thanks are also due to NASA for the IGS-TEC, geomagnetic and solar activity data.
Funding
The authors are thankful to the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, New Delhi for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devbrat Pundhir, Singh, B., Singh, R. et al. Identification of Seismogenic Anomalies Induced by 11 April, 2012 Indonesian Earthquake (M = 8.5) at Indian Latitudes Using GPS-TEC and ULF/VLF Measurements. Geomagn. Aeron. 61, 449–463 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793221030129
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016793221030129