Abstract
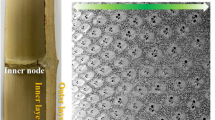
Bamboo is a biomass material, which is a great substitute for wood with the potential to reduce the demand for woody materials. However, there is still a huge challenge to obtain crack-free bamboo boards with an ideal width due to the hollow cylinder and large curvature of bamboo culms. Herein, a method is demonstrated that can flatten bamboo culms by high-pressure saturated steam (180 °C/6 min) under a compression force of 8–10 MPa by two rollers. The macro- and micro-mechanical properties of the flattened bamboo board were also characterized in this paper. Results indicated that the saturated steam had no significant effect on the microstructure of the bamboo, whereas it decreased its hygroscopicity due to the degradation of the hemicellulose. The mechanical properties of the cell walls bamboo samples treated by softening and flattening were elevated compared with those of the untreated ones. During the flattening process, the parenchymal cells became compact. The elastic modulus of bamboo fibers increased from 16.14 to 18.75 GPa, while the hardness increased from 0.58 to 0.77 GPa. The improved mechanical properties of cell walls and increased density had a positive effect on the modulus of elasticity of the bamboo board.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes HM, Lindsey GB, Hill JM (2009) Effect of copper xyligen treatment on bending properties of wood. Holzforschung. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2009.036
Cai S, Zhang N, Li K et al (2019) effect of pressurized hot water treatment on the mechanical properties, surface color, chemical composition and crystallinity of pine wood. Wood Res 64(3):389–400
Chen C, Wang Y, Wu Q et al (2020) Highly strong and flexible composite hydrogel reinforced by aligned wood cellulose skeleton via alkali treatment for muscle-like sensors. Chem Eng J 400:125876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125876
Chen J, Guagliano M, Shi M et al (2021) A comprehensive overview of bamboo scrimber and its new development in China. Eur J Wood Prod 79:363–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-020-01622-w
Chung MJ, Wang SY (2017) Effects of peeling and steam-heating treatment on basic properties of two types of bamboo culms (Phyllostachys makinoi and Phyllostachys pubescens). J Wood Sci 63:473–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-017-1647-y
Dong Y, Liu X, Liu J et al (2021) Evaluation of anti-mold, termite resistance and physical-mechanical properties of bamboo cross-linking modified by polycarboxylic acids. Constr Build Mater 272:121953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121953
García-Iruela A, Esteban LG, García Fernández F et al (2021) Changes in cell wall components and hygroscopic properties of Pinus radiata caused by heat treatment. Eur J Wood Prod 79:851–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-021-01678-2
Guan M, Tang X, Du K et al (2020) Fluorescence characterization of the precuring of impregnated fluffed veneers and bonding strength of scrimber in relation to drying conditions. Dry Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2020.1786109
Hao X, Wang Q, Wang Y et al (2021) The effect of oil heat treatment on biological, mechanical and physical properties of bamboo. J Wood Sci 67:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10086-021-01959-7
He Q, Zhan T, Zhang H et al (2018) The effect of high voltage electrostatic field (HVEF) treatment on bonding interphase characteristics among different wood sections of Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.). Holzforschung 72:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0168
He Q, Zhan T, Ju Z et al (2019a) Influence of high voltage electrostatic field (HVEF) on bonding characteristics of Masson (Pinus massoniana Lamb.) veneer composites. Eur J Wood Prod 77:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-018-1360-6
He Q, Zhan T, Zhang H et al (2019b) Variation of surface and bonding properties among four wood species induced by a high voltage electrostatic field (HVEF). Holzforschung 73:957–965. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2018-0190
Ju Z, Zhan T, Zhang H et al (2020) Preparation of functional bamboo by combining nano-copper with hemicellulose and lignin under high voltage electric field (HVEF). Carbohyd Polym 250:116936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116936
Ju Z, Zhan T, Zhang H et al (2021) Strong, durable, and aging-resistant bamboo composites fabricated by silver in situ impregnation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(44):16647–16658. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c06050
Li Y, Yin L, Huang C et al (2015) Quasi-static and dynamic nanoindentation to determine the influence of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of bamboo cell walls. Holzforschung 69:909–914. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2014-0112
Li Y, Huang C, Wang L et al (2016) The effects of thermal treatment on the nanomechanical behavior of bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens Mazel ex H de Lehaie) cell walls observed by nanoindentation, XRD, and wet chemistry. Holzforschung 71(2):129–135. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2016-0124
Li W-T, Long Y-L, Huang J, Lin Y (2017) Axial load behavior of structural bamboo filled with concrete and cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 148:273–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.061
Li X, Mou Q, Ren H et al (2020) Effects of moisture content and load orientation on dowel-bearing behavior of bamboo scrimber. Constr Build Mater 262:120864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120864
Lin Q, Huang Y, Li X, Yu W (2020) Effects of shape, location and quantity of the joint on bending properties of laminated bamboo lumber. Constr Build Mater 230:117023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117023
Liu X, Li Y (2020) Fabrication of crack-free flattened bamboo and its macro-/micro-morphological and mechanical properties. J Renew Mater 9(5):959–977. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2021.014285
Liu J, Zhang H, Chrusciel L et al (2013) Study on a bamboo stressed flattening process. Eur J Wood Prod 71:291–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-013-0670-y
Sundqvist B, Karlsson O, Westermark U (2006) Determination of formic-acid and acetic acid concentrations formed during hydrothermal treatment of birch wood and its relation to colour, strength and hardness. Wood Sci Technol 40:549–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-006-0071-z
Wang X, Chen X, Xie X et al (2018a) Effects of thermal modification on the physical, chemical and micromechanical properties of Masson pine wood (Pinus massoniana Lamb.). Holzforschung 72:1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0205
Wang X, Zhao L, Xu B et al (2018b) Effects of accelerated aging treatment on the microstructure and mechanics of wood-resin interphase. Holzforschung 72:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2017-0068
Wang X, Chen X, Xie X et al (2019) Effect of phenol formaldehyde resin penetration on the quasi-static and dynamic mechanics of wood cell walls using nanoindentation. Nanomaterials 9(10):1409–1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101409
Wang Q, Wu X, Yuan C et al (2020a) Effect of saturated steam heat treatment on physical and chemical properties of bamboo. Molecules 25:1999–2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081999
Wang X, Yuan Z, Zhan X et al (2020b) Multi-scale characterization of the thermal—mechanically isolated bamboo fiber bundles and its potential application on engineered composites. Constr Build Mater 262:120866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120866
Windeisen E, Strobel C, Wegener G (2007) Chemical changes during the production of thermo-treated beech wood. Wood Sci Technol 41(6):523–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-007-0146-5
Yang L, Lou Z, Han X et al (2020) Fabrication of a novel magnetic reconstituted bamboo with mildew resistance properties. Mater Today Commun 23:101086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101086
Yu H, Zheng H, Zhan M et al (2021) Surface characterization and biodegradability of sodium hydroxide-treated Moso bamboo substrates. Eur J Wood Prod. 79:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-020-01613-x
Yuan T, Liu J, Hu S et al (2021) Multi-scale characterization of the effect of saturated steam on the macroscale properties and surface changes of moso bamboo. Mater Express 11(5):740–748. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2021.1954
Zhang YM, Yu YL, Yu WJ (2013) Effect of thermal treatment on the physical and mechanical properties of phyllostachys pubescen bamboo. Eur J Wood Prod 71:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-012-0643-6
Zhang X, Yu Z, Yu Y et al (2019a) Axial compressive behavior of Moso Bamboo and its components with respect to fiber-reinforced composite structure. J for Res 30:2371–2377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0780-9
Zhang X, Zhou Z, Zhu Y et al (2019b) High-pressure steam: a facile strategy for the scalable fabrication of flattened bamboo biomass. Ind Crops Prod 129:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.061
Zhu W, Yao Y, Zhang Y et al (2020) Preparation of an amine-modified cellulose nanocrystal aerogel by chemical vapor deposition and its application in CO2 capture. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:16660–16668. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c02687
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank TopEdit (www.topeditsci.com) for linguistic assistance during preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31971740 and 31901374); Jiangsu Science and Technology Project (Grant No. BE2018391); A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD); A Project Funded by the National First-class Disciplines (PNFD) project of “13th Five-Year” National Key R&D Plan (2017YFD0600801); and Zhejiang province collaborative innovation center for bamboo resources and high-efficiency utilization (Grant No. 2017ZZY2-06) and forestry science and technology development project of national forestry and grassland administration (Grant No. KJZXZZ201900X), a key research and development project of Fujiang province (Grant No. 2019N3014). Zhejiang province Key R&D Project (Grant No. 2019C02037); Supported by the Doctorate Fellowship Foundation of Nanjing forestry university.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TY formal analysis, writing. HH conceptualization, design of the experiments, review, and editing. XH and ZW fabrication of the materials. ZW and FW investigation. TY, SEM characterization. FW data curation. YL conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, T., Han, X., Wu, Y. et al. A new approach for fabricating crack-free, flattened bamboo board and the study of its macro-/micro-properties. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 79, 1531–1540 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-021-01734-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-021-01734-x