Abstract
Ensuring safe water supply for communities across the United States is a growing challenge due to aging infrastructure, impaired source water, strained community finances, etc. In 2019, about 6% of public water utilities in the U.S. had a health-based violation. Due to the high risk of exposure to various contaminants in drinking water, point-of-use (POU) drinking water treatment is rapidly growing in popularity in the U.S. and beyond. POU treatment technologies include various combinations of string-wound sediment filters, activated carbon, modified carbon, ion exchange and redox media filters, reverse osmosis membranes, and ultraviolet lamps depending on the contaminants of concern. While the technologies are well-proven, highly commoditized, and cost-effective, most systems offer little in the way of real-time performance monitoring or interactive technology like other smart home appliances (e.g., thermostats, smoke detectors, doorbells, etc.). Herein, we review water quality regulations and violations in the U.S. as well as state-of-the-art POU technologies and systems with an emphasis on their effectiveness at removing the contaminants most frequently reported in notices of violations. We conclude by briefly reviewing emerging smart water technologies and the needs for advances in the state-of-the-art technologies. The smartness of commercially available POU water filters is critiqued and a definition of smart water filter is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
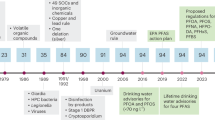
Access to clean water is of utmost importance for human health and society at large. References to water purification and filtration methods can be traced back to ancient Sanskrit and Egyptian writings—including descriptions of boiling, solar heating, and sand filtration1. Hippocrates, often referred to as the “father of medicine,” found that water could be made purer by filtering it and, in 500 BC, he designed a simple sediment filter by running water through cloth2. In modern times, sand filters were first documented as a water treatment device in 1804. By 1852, the Metropolis Water Act in London required the use of sand filters in part of the city3. The filters removed suspended solids, but did not address pathogenic microorganisms or chemical contaminants since microbiology and analytical chemistry were not yet adequately established4. In the United States, drinking water standards were gradually developed over the 20th century, culminating in the passage of the Clean Water Act (1972) and the Safe Drinking Water Act (1974), which were part of a landmark decade of promulgating new environmental regulations.
Water quality can be broken into numerous physical, biological, and chemical components5. Physical water quality descriptors include turbidity, total, settleable, filterable and dissolved solids, color, taste, odor, and temperature. Biological quality refers to protozoan, bacterial, and viral pathogens. Biological contamination is often an immediate health risk: crippling outbreaks of typhoid, cholera, salmonella, and other diseases have been spread through contaminated water supplies. Chemical components include trace organic and inorganic compounds, which may be toxic to humans and can also cause discoloration, poor taste, or odor6. Toxic chemicals may lead to both acute and chronic health effects. Water quality regulations in the U.S. were developed to address all three classes of contaminants. Primary drinking water standards are defined by maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)7. The standards focus on biological and chemical contaminants. The trace chemical contaminants are sometimes less than one part per billion and may be set at or near the limits of analytical detection methods7. Physical water quality components are mainly covered by the U.S. EPA’s secondary drinking water standards, which are unenforced unlike their primary counterparts8.
Although water quality is well-regulated in the U.S., there is considerable variation in contaminant levels by location. Consequently, consumers who are concerned about the quality of their water supply often purchase bottled water or various water-filtration devices to remove any remaining impurities. For instance, a recent set of studies conducted in Los Angeles, CA, USA has determined the following9,10:
-
Levels of distrust in tap water are high, especially among households of color (e.g., LA County had 2nd highest level of distrust among urban areas in the country before Flint).
-
Equating distrust with misperception in all cases (as many water systems and public health agencies do) is incorrect and generic “education” approaches to improve trust are neither effective nor respectful.
-
Much of distrust appears “rational” and stems from past/present experience of unclean, if not unsafe (we draw a distinction here) drinking water, much of it from premise plumbing.
-
Solutions to issues of premise plumbing are tough especially due to tenancy split-incentive issues, but legal and especially financial incentive approaches from other sectors can be brought to bear.
-
The consequences of distrust are severe for household health, finances, trust in the government, and the environment.
Since water quality degradation may occur in the distribution system, one solution could be widespread implementation of point-of-entry (POE) water treatment where a POE system is installed at a household’s or building’s water main intake ahead of the structure’s taps, faucets, or other dedicated outlets used to dispense water for drinking, cooking, and bathing. However, degradation can occur in premise plumbing (e.g., copper pipes) in older buildings, and hence, it may make the most sense to deploy point-of-use (POU) water treatment just ahead of the tap, faucet or dispensing outlet. In this review, we focus on POU water treatment.
Typical POU systems contain water treatment technologies such as media filtration, reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, UV disinfection, and remineralization (particularly after RO)11. Large particles, rust, and debris are first removed by filtration through string-wound sediment filters. Next, some form of selective separation may be employed such as redox media, activated carbon (AC), and/or ion exchange (IEX). Membrane technology, most commonly RO, removes nearly all suspended and dissolved contaminants such as dissolved organic chemicals, dissolved metals, minerals, and salts11. UV disinfection inactivates pathogenic microorganisms, rendering them non-infectious11. Remineralization after RO filtration is often used to add back the minerals removed by earlier stages to provide pH-buffered, better-tasting water11. In each step, there are various technologies available with different contaminant removal efficacies to satisfy a variety of situations and needs. In addition, emerging POU treatment technologies such as capacitive deionization (CDI) are attracting attention because of their selective contaminant removal12.
The rapid development of Internet technologies has encouraged many home-appliance manufacturers to provide “smart” products, including “smart” POU filters. There are various definitions of smart home appliances13,14. The consensus is that if a product is smart, it is one that can be remotely controlled by the user via a smart phone, tablet, or other device. Connectivity and interaction with the user via an “app” is achieved using WiFi or Bluetooth® technology. Smart filter systems take many forms and have differing levels of sensor integration, but information on which filter media and sensors are included in home water treatment systems has been lacking. Moreover, different manufacturers seem to have different views on the smartness of water filters. Some products claim themselves to be “smart” because they can provide water with better quality, which does not satisfy the connectivity requirement of other smart home appliances.
This study reviews U.S. federal and (several) state regulations, the frequency and nature of water quality violations in the U.S., state-of-the-art POU water treatment technologies and their contaminant removal capabilities, especially emerging contaminants. Further, representative commercially available POU systems are compared, making note of filter types, any sensors employed, expected service life, and other details. Finally, the smartness of commercially available POU water filters is critiqued and a definition of smart water filter is proposed.
Water quality regulations, violations, and hazards in the US
Access to clean drinking water is imperative because of the potential for both acute and chronic health risks associated with drinking contaminated water. Federal regulations serve the purpose of reducing the likelihood of becoming ill from drinking the tap water. The EPA regulates contaminants by establishing MCLs for microbiological, organic, and inorganic contaminants based on health guidelines, research, and feasibility15. These standards delineate the maximum amount of a contaminant that can be allowed in drinking water to minimize exposure. States may build on the EPA’s standards by adding additional contaminants not regulated at the federal level and by further reducing MCLs for federally regulated contaminants.
Federal drinking water regulations
To regulate drinking water, the EPA establishes primary and secondary drinking water standards. Primary standards are enforceable by law and apply to all the U.S. public water systems; their goal is to limit levels of harmful contaminants in drinking water. The EPA15 has a list of 88 contaminants regulated in the primary standards with the following contaminant categories and numbers: 3 disinfectants, 4 disinfection byproducts (DBPs), 16 inorganic chemicals, 8 microorganism categories, 53 organic chemicals, and 4 radionuclides. The EPA regulates most of these contaminants by establishing MCLs that can be present in the effluent of drinking water treatment plants. These MCLs are intended to keep people safe, but they are not necessarily safe. The maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG) is the amount of a contaminant in drinking water at which there is no known or expected risk. MCLs are determined by feasibility of measurement, removal, and enforcement in combination with MCLGs, so there may be some health risks even with MCLs in place.
To supplement the enforced primary standards, the EPA sets unenforced secondary drinking water standards. They are intended to improve aesthetic qualities of water such as taste, color, and odor. According to the EPA, these standards are important because if water looks, tastes, or smells bad, people may not drink it even if it is perfectly safe. Some other secondary standards help control scaling, which restricts water flow and corrosion, which can cause pipes to wear out or dissolve harmful contaminants previously fixed within the mineral scale8.
The EPA also maintains a contaminant candidate list (CCL) for compounds that are not currently regulated but are expected to be found in public water systems and may require regulation in the future16. The CCL serves an essential purpose in the process of enacting water quality regulations. Every 5 years, the EPA decides if it will regulate or not regulate at least five contaminants on the CCL. In February 2020, the EPA made preliminary decisions to regulate perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), but not to regulate six other chemicals including dichloroethane and acetochlor17. They make these decisions using data collected about these contaminants and compare it to the criteria for regulation under the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). The CCL must be updated every 5 years, and the contaminants with the greatest potential health risks in drinking water shall be placed on the list16. Once the EPA decides to regulate a contaminant, it can take years before a regulation is enacted. For example, the EPA decided to regulate perchlorate in 2011, but as of 2020, the EPA still has not set a MCL for perchlorate18. Because it takes many years to regulate a chemical that it deems to be unsafe for human consumption19, there may be chemicals present in drinking water for which negative healthy effects are known, but no action has yet been taken.
State drinking water regulations
States are required to have standards at least as strict as EPA standards for primary drinking water treatment20. Yet, state standards may vary from the EPA standards, providing room for states to regulate certain contaminants more strictly or address contaminants that are not yet federally regulated21,22. For example, in California, contaminants are regulated because of determinations made by the California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, which sets public health goals based on the health impacts of individual contaminants23,24. For carcinogenic contaminants, they create regulations based on the risk of cancer from exposure to different amounts of the contaminant. Typically, the acceptable risk is for—at most—one person in a million to get cancer upon exposure over 70 years. After proposing a standard based on current research, they consult a group of scientific experts, make further revisions, and finally allow public comment. After setting a goal, they can establish an enforceable standard that is as close as possible to the goal while considering economic and technical feasibility. This process is similar to how the EPA sets its MCLs, but because it is separate from the EPA, they can regulate chemicals of local concern such as agricultural contaminants25.
Table S17,26,27,28 compares the EPA’s primary drinking water standards to the drinking water regulations of several states; it also displays the health effects of exposure and the origins of these contaminants. Alaska, Texas, and California exhibit an exemplary range of different state’s approaches to regulations, with California being the most stringent29. Exposure to regulated contaminants can cause a variety of health issues including cancer, kidney problems, nervous system problems and more, which is why these chemicals are regulated by the EPA and states. In addition, one clear commonality amongst the origins of these contaminants is that they frequently come from industrial operations that discharge waste into the environment.
Violations of standards
Even though regulations exist to limit exposure to toxic contaminants, sometimes public water utilities violate existing standards. Public water utilities are categorized by the EPA as community water systems (CWSs), transient non-community water systems (TNCWSs), or non-transient non-community water systems (NTNCWSs) (Fig. S1). The EPA then classifies the size of these public water systems in categories of very small, small, medium, large, and very large (Table 1)30. Fig. S230 displays the amount of each type of public water system by size. It can be seen that CWSs represent a larger percentage of public water systems as the size of the population served increases, which means they end up serving residential communities, whereas smaller public water systems tend to be TNCWSs.
The EPA publishes a database with information about the types and sizes of public water systems and the violations that occur within these public water systems. Violations required to be reported under SDWA of EPA are grouped into the following categories31:
-
1.
Health-based, including 3 categories: (1) exceedances of the maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) which specify the highest allowable contaminant concentrations in drinking water, (2) exceedances of the maximum residual disinfectant levels (MRDLs), which specify the highest concentrations of disinfectants allowed in drinking water, and (3) treatment technique requirements, which specify certain processes intended to reduce the level of a contaminant31.
-
2.
Monitoring and reporting: failure to conduct regular monitoring of drinking water quality, or to submit monitoring in time, as required by SDWA31.
-
3.
Public notice: systems are required to alert consumers if there is a serious problem with their drinking water or if there have been other violations of system requirements, as required by SDWA31.
-
4.
Others: violations of other requirements of SDWA, such as failing to issue annual consumer confidence reports31.
Table 2 shows the number of serious violations by treatment plant size. A serious violation is when a public water system has unresolved serious, multiple, and/or continuing violations, which need to be returned to compliance or the system will be faced with formal enforcement action30. Many serious violators have violated monitoring and reporting guidelines; they fail to regularly monitor drinking water quality or promptly submit monitoring results to the EPA or a public health agency32. These violations indicate mismanagement or neglectful monitoring rather than an immediate health hazard.
However, some violations are health-based violations where public water systems exceed MCLs, maximum residual disinfectant levels, or have an incorrect treatment technique that is put in place to remove certain contaminants30. Especially, those violations that can pose immediate health effects are called acute health-based violations. There were over 6.5 million people affected by health-based violations in the United States in 2019. Violations including exceeding monthly allowed turbidity levels, treatment technique violations, Escherichia coli present in treated water, and nitrate violations have been reported30.
Allaire et al.33. evaluated spatial and temporal patterns in health-related violations of the SDWA using a panel dataset of 17,900 CWSs from 1982 to 2015. About 21 million people are affected by health-based water quality standard violations in the year 2015, according to the study33.
During each year between 1982 and 2015, 9–45 million people, up to 28% of US population, were affected33. Health-based violation was observed in about 8.0% of the 608,600 utility-year observations, while total coliform violation is observed in about 4.6% of all observations33. In total, 95,754 health-based violations were observed, and 37% of all violations are the total coliform type (Fig. 1a). About 36% of violations are categorized as “other” contaminants, primarily DBPs. While violations of treatment rules and nitrate are less commonly observed (21% of total)33.
a Number of health-based violations, and b total violations per water system. In total, 95,754 health-based violations were observed from 1982 to 2015, affecting up to 28% of US population. Rural areas have a larger compliance gap than suburban and urban areas; however, fewer violations with DBP violations were observed in rural areas with higher incomes (reprinted with permission from33; Copyright© PNAS, 2018).
The number of violations per CWS (Fig. 1b) differs between rural and urban areas. Rural areas have a larger compliance gap than suburban and urban areas, however, fewer violations with DBP violations were observed in rural areas with higher incomes33. Differences between rural and suburban areas were exaggerated after new DBP rules in the early 2000s33, corresponding to the spike in Fig. 1b. Due to limited financial resources and technical expertise, regulatory compliance is a challenge for rural systems33. In contrast to large systems, small systems face restricted access to loans and outside financing34. Moreover, smaller customer base has less revenue for infrastructure improvements, repayment of debt, and salaries to attract technically skilled operators34. All these factors make the rural system operations and development challenging, and eventually may trigger the violations.
Violations also vary geographically. The distribution of the total number of violations, from 1982 to 2015, per CWS in a given county is shown in Fig. 2A. The majority of violations are observed in rural areas, located in Texas, Oklahoma, and Idaho. Total coliform violations, as shown in Fig. 2B, are primarily observed in the West and Midwest. Differences of violations across counties can be attributed to the difference of quality of source water as well as the state-level enforcement33. Other factors such as different temperatures at different seasons can also contribute to the regional difference of violations across the U.S. For instance, high summer temperatures might cause the Southwest region to be particularly susceptible to DBP violations. SDWA violations are mostly identified in Oklahoma and parts of Texas, based on local spatial autocorrelation, shown in Fig. 2C. 11% of the CWSs have repeat violations, including two or more subsequent years of a violation33. The states with the greatest proportion of CWSs with repeat violations are Oklahoma (43% of CWSs in the state), Nebraska (35%), and Idaho (33%)33.
A Total violations. B Total coliform violations. C Spatial clusters (hot spots) of health-based violations, 1982–2015. Violations also vary considerably across geographic locations. Some of the counties with the highest prevalence of violations are rural, located in Texas, Oklahoma, and Idaho (reprinted with permission from33, Copyright© PNAS, 2018).
Table S4 shows the breakdown of the size of treatment plants and the source of water. Larger treatment plants tend to use surface water, whereas smaller treatment plants predominantly use groundwater. From the above table and information about the different types and sources of violations of drinking water treatment plants, the percentage of violations by water source can be determined. The values in Table S5 were computed using the number of surface water and groundwater violations by size and comparing that to the total number of treatment plants using either surface water or groundwater as a source by size (data from Table S4). The percentages of CWSs, NTNCWSs, and TNCWSs were computed as well, using the number of violations of those types by size and comparing that to the total numbers of treatment plants by type and size (data from Table S4). Table S5 shows that with every type of violation, treatment plants that use surface water as a source tend to have a higher percentage of violations than treatment plants that use groundwater as a source. As the size of the treatment plant increases, the percent of violations amongst public water systems that use surface water tends to decrease. The only exception seen here is for treatment plants of very large size. In addition, CWSs typically have slightly higher percentages of violations (Table S5). This analysis, presented in Table 3, shows that CWSs tend to have a higher percentage of surface water sources compared to NTNCWSs and TNCWSs.
Non-grid-tied water resources
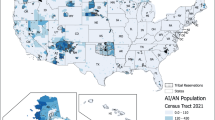
Domestic wells (private or homeowner wells) are the dominant source of drinking water for people living in rural parts of the United States35. Population distribution using domestic supply wells per square kilometer is shown in Fig. 3a. Over 43 million people, 15% of the U.S. population, rely on domestic (private) wells as their source of drinking water36. These private wells are not regularly tested for known contaminants, and thus, may pose unknown health risks. The water safety of domestic wells is not regulated by the Federal Safe Drinking Water Act or, in most cases, by state laws. Instead, individual homeowners are responsible for maintaining and monitoring their own wells36.
a Population using domestic wells, and b domestic wells affected by arsenic. Over 43 million people, 15% of the U.S. population, rely on domestic (private) wells as their source of drinking water. About 2.1 million people in the conterminous U.S. were using water from private wells with predicted arsenic concentration >10 μg/L (reprinted with permissions from35,36; Copyright© Elsevier, 2017; Copyright© ACS, 2017).
In a study of 2100 domestic wells, water in about 20% of the wells is contaminated with one or more contaminants at a concentration greater than MCLs35,36. Table 4 summarized some common contaminants in domestic wells which frequently exceeding health standards (MCLs regulated by USEPA or U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Health-Based Screening Levels) in tests. The most common contaminants that were found to exceed health standards were metals including lead and arsenic, radionuclides, and nitrates37. Nitrates in drinking water supplies can cause harm such as methemoglobinemia in young children, but nitrates rarely cause direct harm to adults36. Microbial contaminants (for example, bacteria) were found in about 30% of wells tested, about 400 wells in total36. Ayotte et al.35. developed a logistic regression model of the probability of having arsenic >10 μg/L (“high arsenic”) from 20,450 domestic wells in the U.S. As shown in Fig. 3b, approximately 2.1 million people in the conterminous U.S. were using water from private wells with predicted arsenic concentration >10 μg/L35. Some states have both relatively large population, over 1 million people, and high percentages, over 1%, of total state populations with arsenic >10 μg/L. It is noteworthy that 60% of all counties with the largest population with high-arsenic wells are located in New England; other top-10 counties are located in Ohio, North Carolina, California, and Idaho, respectivly35. Considering the high risk of exposure to the various contaminations, it is therefore imperative to apply additional treatments, such as POU, before using the well water in households.
Contaminants of emerging concern with no regulations
Contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) are chemicals or microorganisms that are not commonly monitored in drinking water because they do not have established MCLs38. A USGS study found that over 80% of streams in the U.S. contained some form of emerging contaminant including pharmaceuticals, hormones, detergents, plasticizers, fire retardants, pesticides, and more. Although these were generally found at low concentrations, a growing number of research report their close relationships with some human diseases39,40. In addition, a more recent study found that about 8% of groundwater sources used for drinking water contain hormones and pharmaceuticals41. The unregulated status of these contaminants makes them unmonitored by treatment plants in many cases. It is also unknown how much of them end up in drinking water after drinking water treatment. Thus, there is potential health risk for people consuming these contaminants in drinking water.
Table 5 shows the features of several typical CEC types in drinking water. N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) is a semi-volatile organic compound used to help produce liquid rocket fuel, antioxidants, and additives for lubricants. Animal studies have found that NDMA causes cancer in the liver, respiratory tract, kidneys, and blood vessels39. NDMA is also expected to be carcinogenic to humans42, while EPA has not set a MCL for NDMA yet. However, it has been placed on the fourth contaminant candidate list (CCL4). Also, several states have guidelines (not regulations) for levels of NDMA that could exist in water. In California, several nitrosamines have guidelines set that were above a specified level (in the instance of NDMA, 300 ng/L), and a response is recommended. Potential treatments for NDMA include photolysis with UV radiation43, biological treatment, microfiltration, and RO treatment. Despite these treatments, it may still be present in water because it is a byproduct of chlorination, which occurs after treatment39.
Pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) are commonly found in sources of drinking water and enter these sources through domestic wastewater, hospital discharges, improper manufacturer disposal, and wastewater treatment plants44. PPCPs typically enter wastewater through human excrement or bathing and washing activities45. The amounts of PCCPs found in these treatment plants is low with concentrations between ng/L and μg/L. However, their long-term health effects are unknown and they can cause health issues through accumulation in the food chain46. In addition, some PPCPs containing amine groups demonstrate the potential to react with chloramines in the disinfection process to form toxic nitrosamines such as NDMA, which is not federally regulated and can cause adverse health effects as stated before47.
1,4-dioxane is another concerning contaminant given its classification as a probable human carcinogen. Approximately 30 million people in the U.S. have levels of 1,4-dioxane exceeding the health reference level for cancer, which indicates that it poses a serious risk to human health48. It is currently on the EPA’s CCL4 and has been on prior CCLs, which indicates 1,4-dioxane’s recognition as an emerging contaminant39. The problems with 1,4-dioxane include that it is highly soluble in water and does not react easily with other chemicals. In addition, AC filters do not absorb it. The best-known removal method appears to be RO48.
Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) is an additive used in gasoline, designed for more efficient fuel combustion thus to improve overall air quality. It can cause liver, kidney, immune system, testicular, central nervous system, uterine, headache, and lung problems40. Like other CECs, no regulations have been established for MTBE by the EPA. In California, an established MCL for drinking water is 13 μg/L and a secondary maximum contaminant level (SMCL) is 5 μg/L49. The SMCL was established for water quality aesthetic properties such as taste and odor42.
Perfluorinated compounds such as PFOS are extremely hazardous emerging contaminants that enter the environment through their applications in the metal industry, firefighting foam, coatings on paper and textiles, and semiconductor production50. They can also occur due to biotransformation of dipolyfluoroalkyl, phosphates, fluorotelomer alcohols, and other chemicals51. They are persistent in the environment and tend to accumulate in red blood cells48. PFCs can cause pancreatic, liver, and Leydig cell cancers40. They are frequently found in treated drinking water with levels of up to 1000 ng/L, and over 6 million people receive water from systems that exceed health advisory levels for PFAS48. Studies have concluded that people who drink water with PFAS in it have higher levels of PFAS in their blood, indicating the contaminant’s health risk48. PFOS are easily removed by using granular activated carbon (GAC) filters which can remove over 90% of them and ROMs which can remove more than 99% of them44. The EPA decided in 2020 to regulate PFOA and PFOS in drinking water, but it may take many years before a MCL can be established as was the case with other contaminants taking over 10 years between the decision to be regulated and actual regulation44.
Antibiotics are another concerning contaminants that can be found in water. Antibiotics in water can cause the rise of antibiotic-resistant genes and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This can make the use of antibiotics less effective against human and animal pathogens. As of now, there are approximately 2 million people who die in the U.S. from antibiotic-resistant bacteria per year, which is why it is important for them not to end up in aquatic environments48. Antibiotics can be detected at very low levels across the United States in the sources of drinking water (levels of between 20 and 60 ng/L)52. They are rarely detected in treated drinking water, and if they are detected, the levels are even lower (5–20 ng/L), and thus present little risk to human consumption themselves53.
Another concerning area of emerging contaminants is DBPs which are produced when chemical oxidants (e.g., chlorine, ozone, chloramine, etc.) are used for disinfecting microbes in drinking water. Over 700 DBPs have been identified by EPA, while only 11 types are regulated48. DBPs have been known to cause cancer and birth defects48. Thus, they too pose a risk to human health despite regulations that exist.
In summary, although well-intended and well-developed, the U.S.’s drinking water regulations do not fully assure the quality of tap water to prevent either short-term or long-term illness from drinking it. Improving upon water treatment technologies and moving them closer to the POU is a way to help remove contaminants that are not regulated yet or are introduced during distribution from the treatment plant to the tap. GAC, RO, UV radiation, and combinations of the above are all advanced water treatment technologies that remove emerging contaminants effectively. Although there has been much research on the mechanics and removal efficacies of these water treatment technologies, little information is available on their application in POU water treatment.
POU water treatment technologies
POU drinking water treatment systems are installed on the water supply lines ahead of water taps, showers, and dispensers to provide on-site purification of water for drinking, bathing, or cooking. A wide range of POU technologies have emerged in the past two decades including AC, redox media, ROMs, UV disinfection, CDI, and others. They are usually combined in a specific sequence to form a POU system (Fig. 4). The systems are thus expected to remove hazardous contaminants exceeding regulation limits while keeping those substances that are healthy and essential for human health.
Media filtration
Sediment filters
The most basic type of POU filter is the sediment filter, a form of physical filtration. It removes suspended solids from water, such as insoluble iron and manganese, and reduces water turbidity. In Fig. 5, we present a schematic of the flow configuration and a photo of typical string-wound sediment filter54. Suspended solids from untreated water will accumulate throughout the depth of the filter material, while dissolved contaminants are not retained. Therefore, the classification and removal efficacy of sediment filters is highly dependent on the pore size of the filter media. For example, a “5 μm” filter is able to capture sediments as small as about 5 μm55. In addition, the filter rating is commonly described as either “nominal” or “absolute.” Nominal filters are expected to trap >90% of particles larger than the pore size ranting, while absolute filters should trap about >99%.
Suspended solids from untreated water will accumulate throughout the depth of the filter material, while dissolved contaminants are not retained. Therefore, the classification and removal efficacy of sediment filters is highly dependent on the pore size of the filter media (reprinted with permissions from54,57; Copyright© Filters Fast LLC, 2020; Copyright© UNISUN, 2020).
The string-wound sediment cartridge filter is a common type of POU sediment filter, which is made from a central cartridge wrapped in string (Fig. 5). This type of filter typically has a micron-rating from 0.5 to 200 depending on the diameter of the string. The filter functions by mechanically trapping particles that are larger than the characteristic space between strings; sometimes thinner string is used near the core center and thicker string on the outside. In this way, the string-wound sediment filter can capture particles not only on the cartridge surface, but also through its depth and at the core surface.
The first string-wound filter cartridge entered the U.S. market around the mid-1930s. It was made of a woven wire mesh core surrounded by cotton yarn56. Today, this type of cartridge filter has evolved considerably by improving the filter material and the media arrangement. For example, by adding silver ions to the polypropylene yarn, the string-wound filter inhibits the growth of microbes. Also, to be compatible with corrosive solutions or high-temperature fluids, stainless-steel can be used as the core material to enhance the polypropylene stability and prevent it from swelling or softening57.
Ion exchange resins
Ion exchange (IEX) is a reversible chemical reaction between compounds in the aqueous phase and fixed charged functional groups on and within a solid phase. Polymeric resins are the most common IEX materials, widely used not only in POU filtration, but also in large-scale water and wastewater treatment, hydrometallurgy, chromatography, and sensors58. Although there seem to be a variety of IEX resins for water treatment in the market, they can be roughly categorized into five groups based on their framework (Table 6): strong-acid cation (SAC) resins, weak-acid cation (WAC) resins, strong-base anion (SBA) resins, weak-base anion (WBA) resins, and metal-selective chelating (MSC) resins59. Cation resins are extensively used in the water softening process, removing hardness ions (e.g., Ca2+, Mg2+, and other divalent cations). WAC resins are more effective for treating feed waters containing a high concentration of hydrogen peroxide or chlorine than SAC resin because they have a higher resistance to corrosive oxidants and are more stable. It is worth noting that different anion resins have a varied affinity to different acids, and WBA resins cannot remove weak acids such as carbon dioxide and silica60.
For POU applications, IEX resins meet the needs of water softening and demineralization. An acidic environment with high lead concentration might occur when solders and/or pipes corrode61. Cation softening resin is used to adsorb positively charged lead and many other metal ions. With a high molecular weight and a 2+ valence, lead has a high affinity towards the cation resin, MSC resin62. In addition, perchlorate can be removed to a very low level by SBA resin63. The major concerns for POU versions of the IEX resin involve its regeneration process. Even under strong acids, lead-laden cation resin cannot fully strip lead from the resin61. Similarly, perchlorate attaches strongly to the anion resin. The safe and economical disposal of high-concentration regenerant brines is also an environmental concern.
Activated carbon
Activated carbon (AC) is the most commonly employed commercial POU filter in the United States64. AC is created from charcoal by treating it with extremely hot gases, leaving pure carbon with many microscopic pores. Granular activated carbon (GAC) is a ubiquitous form of AC water filters in residential water filter systems. The carbon particles repel water and strongly attract nonpolar organic compounds via intermolecular Van der Waal’s and hydrophobic interactions. Van der Waal’s interactions are almost universally attractive and based on permanent, temporary, and induced dipole interactions between the atoms of the GAC and chemical compounds; hydrophobic attraction occurs between nonpolar compounds or nonpolar moieties within complex molecules. Highly polar and charged compounds can experience electrostatic and hydrophilic repulsion, which makes them less likely to be well removed by GAC. The surface area available for adsorption is extremely large due to the large quantity of micropores in the carbon. GAC is thus used to remove organic contaminants, some heavy metals65, and DBPs such as trihalomethanes (THMs).
In addition to bare GAC, several surface modification methods have been researched to enhance the affinity to different impurities, including chemical treatment, impregnation, and plasma treatment66 (Fig. S3). AC can be chemically modified to have an acidic or basic surface. In most cases, an acidic surface has typical functional groups of carboxylic acid, lactone, phenol, or lactol groups, while a basic surface is represented by the existence of chromene, ketone, pyrone, and nitrogen groups67. AC can also be impregnated with metals and metal oxides. These additive crystallites will disperse in carbon pores and become active sites for contaminant adsorption66. Silver-impregnated activated carbon (SIAC) is one promising POU filter medium based on this removal mechanism. Another class of surface modification is plasma treatment. Under vacuum or atmospheric conditions, AC is treated with air or oxygen plasma to create oxygen functional groups, which makes AC more active66.
The novel SIAC has extensive use in POU water treatment. This filter type has high removal efficiency towards the natural organic matter (NOM), disinfection byproducts (DBPs), trihalomethanes (THMs), and many other key drinking water contaminants. Rajaeian et al. discussed the silver leaching mechanism of SIAC (Fig. S4). Their research reported that if the solution pH is properly controlled, additional bromide removal can be achieved, while minimizing silver leaching68. With preconditioning at pH 10.4, the release of silver is only 3%, which makes SIAC more competitive with longer service life68. Watson et al. found that combined with an enhanced coagulation pre-treatment, SIAC (0.1% Ag) can reduce tTHMs by over 98%, bromide by 95 ± 4%, and total dihaloacetonitriles (tDHANs) by 97 ± 3% (tDHANs = sum of dichloroacetonitrile (DCAN), bromochloroacetonitrile (BCAN), and dibromoacetonitrile (DBAN) concentrations)69. The enhanced removal rate for Cr6+ has also been studied, over 94% Cr6+ removal by SIAC can be achieved by cost-effective H2SO4 pre-treatment70.
KDF redox media
Kinetic degradation fluxion (KDF), a type of copper-zinc filtration, relies on the redox potential between these two metals to remove certain contaminants. Figure 6 diagrams the removal mechanism of KDF for various contaminants. Heavy metals dissolved in the water are reduced into an insoluble form and thus precipitate out so they can be retained in the filter medium71. KDF filters also reduce free chlorine and inhibit bacterial growth. Experiments showed that the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) rapidly drops from 200 mV to −500 mV when feedwater passes through KDF72. This sharp decrease makes the environment unsuitable for bacteria to survive. However, KDF filters do not remove organic contaminants. For this reason, KDF is often used as a prefilter or combined stage with GAC (Fig. S573).
Heavy metals dissolved in the water are reduced into an insoluble form and thus precipitate out so they can be retained in the filter medium (reprinted with permission from180; Copyright© Elsevier, 2019).
There are two primary types of KDF filters in the market for POU applications: KDF55 and KDF85 (see Table 7 for a comparison). Based on their differing composition, KDF55 is more suitable for chlorine, heavy metal, and bacteria removal, while KDF85 is a better choice for eliminating iron and hydrogen sulfide74. A higher portion of zinc in the material enhances the reduction ability of KDF55. Thus, it is more effective for free chlorine removal. However, in large-scale applications, maintaining high performance of the KDF filter requires a backwashing procedure with a high flow rate, about 30 gallons per minute per square foot of bed surface area75. The backwash rate is also supposed to be tunable to the environment temperature. Fouling problems and poor efficacy might result if backwashing procedures are not properly followed. Innovative modification of KDF process media is thus expected to improve the filter. Nano-KDF is a pioneering nano-sized filter medium which originated from KDF76,77. Its specific surface area is over 100 times larger than the conventional type. Even under high initial chlorine concentration of 3 mg/L, the removal efficiency can be over 99.9%77.
Novel green filter media
In residential water filtration systems, cheaper and greener alternatives are often preferred by consumers. Many companies have developed such eco-friendly water filters in recent years. By using recyclable raw materials, the carbon footprint and manufacturing cost is greatly reduced. For example, Glanris (https://www.glanris.com) is a 100% green product made from rice hulls, reducing 98% of carbon emissions during the manufacturing process; hence, the “green” aspect of their filter media78. The biodegradable raw material makes it non-toxic and easy to dispose. At the same time, the widespread availability of its raw material lowers the price to $3–6 per lb for specialty metal removal and $3–10 per lb for nutritional/vitamin grade. By combining features of both GAC and IEX resins, this hybrid technology achieves in a single step removal of a wide range of organics and heavy metals79. High chlorine removal capacity is developed with fast kinetics and color in drinking water can be eliminated as well. Another example is Swift Green Filters (https://swiftgreenfilters.com) who makes AC from renewable coconut shells, which has the advantage of 50% more micropores than other plant-based shells80. Since the global consumption of coconuts has rapidly increased in recent years, the massive amount of coconut husk waste can be sustainably reused, providing a steady and environmentally friendly raw material source for the company. Key water impurities like turbidity, lead, mercury, chlorine (taste and odor), and asbestos can all be effectively reduced81. Swift’s green water filters are categorized into refrigerator filters, under the sink systems, tap filters, alkaline water filters, etc.
Membrane filtration
Compared with media filtration, membrane filters require no chemical additives to achieve a target separation, and act as absolute barriers82. Pressure-driven membranes are divided into 4 categories83 (Fig. S7): microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF), and reverse osmosis (RO)84. Most of MF/UF membrane products are made of commodity polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyvinylidinefluoride (PVDF), polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polysulfone (PSU), and polyethersulfone (PES), although ceramic analogs are also widely available85,86. Both NF and ROMs are most often composite (multi-layered) structures where a denser film coats over a MF/UF-type membrane to provide enhanced selectivity towards dissolved substances. Depending on the pore size, membranes have distinct target pollutants and removal efficiencies (Table 8).
Among the four types, RO is the most popular membrane type in POU systems. Unlike MF, UF, and NF membranes, RO membranes are the “tightest,” allowing water to pass, but virtually everything else in water is retained down to simple salts (e.g., NaCl) and small organic molecules >100 Da87. It is thus highly efficient in rejecting dissolved organic and inorganic contaminants (Table 9). Even for pollutants with low molecular weight, only trace concentrations exist after RO filtration, and the values are typically below health limits88. ROMs also completely reject pathogens, with no E. coli or viruses detectable in RO permeate89. Moreover, with the feedwater concentration ranging from 0.5 to 1500 mg/L, over 99% of PFOS can be rejected by ROMs90. However, ROMs may not be as effective for carcinogenic nitrogen DBPs, as only 50–65% or less NDMA may be removed by RO91. Currently, UV treatment is an effective method for removal of NDMA. NDMA in aqueous solutions undergoes direct photolysis upon UV exposure, which further leads to dimethylamine, and nitrite and nitrate ions as the major degradation products92. A combination of RO and UV disinfection is thus preferred to improve efficiency to 59–75%91. The previously mentioned emerging carcinogen 1,4-dioxane can also be reduced by nearly 96% by a removal system combining RO and GAC93.
While ROMs are common in POU water filters, they are more expensive than GAC and sediment filters. Many consumers find less expensive filters sufficient for their needs. However, RO units produce purer water than other commercially available technologies. Also, pre-treatment is necessary during this process; otherwise, membrane fouling or damage can quickly occur. Given sufficient pressure, nearly all dissolved solutes can theoretically be removed, but realistic removal rates on the order of 90–99% are possible for contaminants that cannot be removed by other filtration methods. RO systems are thus in demand among those with a high standard for water quality. Some water filter companies address differing customer standards by selling versions of systems that differ only in the inclusion of a ROM.
UV disinfection
UV irradiation has been increasingly used in water disinfection to inactivate microorganisms because it adds no chemicals, does not produce harmful DBPs, and does not cause disinfectant resistance in bacteria94. The radiation penetrates the microorganisms and results in photochemical damage by impairing nucleic acids (DNA or RNA). Such damage further disables microorganisms from replication and infection. In this way, microorganisms are rendered unable to function or reproduce and might even be killed95,96.
Mercury-based lamps are often used as the UV emission source for the disinfection system. After the excitation of mercury vapors in the lamp, UV rays are generated. UV mercury lamps are mainly categorized into two types: low pressure and medium pressure. With pressure under 10 torr, the emission of conventional low-pressure mercury lamps is monochromatic at 254 nm97; often used at low flow rates where the exposure time to UV can be longer. Medium pressure (approximately 1000 torr) UV lamps have higher emission intensity and cover a broader range of wavelengths (200–400 nm)97. Because of the high energy demand for emission, medium-pressure UV lamps are exclusively used in more commercial or regulatory contexts such as drinking water or wastewater treatment plants.
UV-LED has emerged as a viable alternative over the past decade to achieve a more sustainable, low-energy UV disinfection (Fig. S6)94,98. Its small size (5–9 mm diameter) enables easy transport and disposal in POU application99. As LED does not need warm-up time, it saves energy and allows intermittent use, thus leading to lower system cost. The germicidal efficiency of UV-LEDs is reported to be at least as good as low-pressure UV disinfection lamps100. In most cases, the germicidal effect of UV-LEDs is enhanced compared to conventional UV mercury lamps as they can incorporate an LED array of differing UV wavelengths. UV radiation with different wavelengths have varied microorganism inactivation efficiencies101; thus, UV-LED can maximize its combined germicidal effect. Pulsed irradiation by UV-LEDs can also be used to improve germicidal effects102. At 272 nm under pulsed UVC, the log inactivation rate for E. coli is 3.8 higher than continuous illumination with the same UV dose103.
Remineralizing media filters
Remineralization aims to adjust the alkalinity of RO-filtered water by re-introducing healthy minerals; tap water RO permeate is deficient in healthy minerals, has a slightly dry, burning feeling to the tongue, and is slightly corrosive with pH < 6.0104. Product water after remineralization not only makes RO-treated water more palatable, but also non-corrosive105, fulfilling the following water quality criteria: pH between 6.5 and 8.5; alkalinity >80 mg/L as CaCO3, and calcium carbonate precipitation potential (CCPP) range of 80 < CCPP < 120 mg/L as CaCO3106,107.
Figure 7 gives an example of a 5-in-1 alkaline, remineralization, and far-infrared filter108. There is a bit of marketing mythology surrounding some remineralization filters with statements such as “Like the flow of a mountain spring, water passes through mineral rocks in sequence.” For other media, such as the Maifan Mineral stone (a.k.a., “Japanese & Chinese Medicine Stone”), product claims include “releasing beneficial microelements, stabilizing water pH, and absorbing chlorine and heavy metals, Maifan stone is widely used in traditional Chinese treatments of many conditions like digestive problems and high blood pressure”84. The “alkaline ceramic ball” claims a “capacity to break down a big water molecule groups into smaller ones” and to “activate water”100. Another claim is that ceramics can generate far-infrared rays (FIR), and hence, the alkaline ceramic ball offers enhanced filter performance in antibacterial, activation, absorption, and water purification100. We find no scientific evidence supporting any of the above claims and assume they are largely marketing stories; however, such 5-in-1 remineralizing filters appear popular following ROMs in high-end POU filtration systems.
Remineralization aims to adjust the alkalinity of RO-filtered water by re-introducing healthy minerals; tap water RO permeate is deficient in healthy minerals, has a slightly dry, burning feeling to the tongue, and is slightly corrosive with pH < 6.0 (reprinted with permission from108; Copyright© EZFILTER, 2020).
Emerging technologies: an example of CDI
Apart from the above technologies, a growing number of novel water treatment technologies have emerged to meet the increasing removal needs for emerging contaminants and from higher regulatory requirements. Water treatment based on electrochemical principles is one promising technology, which is presently emerging. Electrochemical water treatment technologies include electro-oxidation, electro-reduction, electro-coagulation, electro-flotation, electro-decantation, capacitive deionization (CDI), and others109. In this section, CDI is chosen as an exemplar electrochemical water treatment technology. Its working principles, developing history, and comparison between different types are discussed.
CDI, and its various derivatives, are promising POU water treatment technologies that use applied electric fields to separate dissolved ions by various mechanisms. Ions in feed water can be immobilized to two paired porous electrodes by applying a low-voltage electric field between the electrodes110. This process generally follows electric double layer theory where the charge on the electrode surfaces (from the applied potential) is neutralized by the accumulation of counterions from solution111. Positively charged ions such as Ca2+, Mg2+, and Na+ will be adsorbed to the negative cathode, while negatively charged ions such as Cl− and SO42− will be adsorbed to the positive anode. The electrodes are regenerated (e.g., ions released) by reversing the applied potential releasing electrosorbed ions.
After years of research and development, different architectures of the CDI module have been developed with various advantages and disadvantages (Table 10). Flow between electrodes is the most conventional format of CDI designed by Blair and Murphy in 1960112. The desalination efficiency of CDI was improved through an innovation by Johnson et al.113. by pumping feed water through the porous electrodes rather than between the solid electrodes. Researchers are devoted to combining CDI with existing filtration technologies such as membranes114,115 or modifying the surface and material for the electrodes116,117,118. However, high manufacturing cost limits widespread deployment of CDI-based POU water treatment products.
More recently, a form of CDI called “capacitive coagulation” has emerged as an electrically driven alternative to chemical coagulation with the advantages of no chemical use, no sludge production, and higher energy-efficiency than conventional chemical adsorption (https://electramet.com). A wide range of heavy metals like lead, copper, manganese, iron, zinc, nickel, and cobalt have been removed with over 99% selectivity119.
Summary of POU technology efficacy
A summary of available peer-reviewed studies on POU water treatment technologies is provided in Table 11, where we compare contaminant types, specific contaminants, treatment technologies, and removal rates. The reported removals for nearly all of the technologies are over 90% and, in many cases, >99%. It is fair to assume that the reported removals can be expected from the technologies as tested and reported. What is not known from peer-reviewed studies and from for-profit companies’ product performance claims, is how long a given technology maintains the reported level of performance in terms of time, volumetric throughput, or contaminant mass loading. This is difficult to evaluate due to the lack of data from published scientific studies or company claims.
Commercially available POU systems
Here we consider the filtration and purification components most commonly employed, in what formats (e.g., under the sink, countertop, etc.), and how they are combined to create various POU water filtration systems. Mass-produced water filters need to be effective at removing contaminants, and also, must be compact, low-cost, and easy to maintain. These constraints place some limits on the purification technologies that consumers can access, which drives most consumer products to use highly commoditized filter media. We compiled data from 11 POU water filter companies’ websites, and the configurations of their systems are summarized below. Individual filters and system components are listed in order when they could be determined. Price ranges are listed where available; the range of products were selected to reflect the lowest and highest priced products within the category. The prices shown were listed on the companies’ websites, including discounts, as of December 2020. Many available products were not included in this analysis as the one’s shown are simply indicative of industry norms.
Under-the-sink water filters
One of the most popular POU locations is under the kitchen sink, for filtering water just before it comes out of the tap. Most households with these systems use untreated tap water for most of their water needs (such as showers and washing machines) and a small amount of filtered water for drinking and cooking. Under-the-sink filters are designed to purify only a few hundred gallons of water before needing replacement of filter media. They may be further divided based on the number of filtering stages or the presence of a ROM. There is considerable flexibility in the number of stages depending on the needs of customers, but may comprise up to seven stages including a sediment prefilter (SED), ion exchange (IEX), KDF or GAC media filters, activated carbon block (ACB) filters, RO membrane (ROM), remineralization media filters (ALK), UV sterilization (UVS) and/or postfiltration activated carbon (PAC) (Fig. 8).
There is considerable flexibility in the number of stages depending on the needs of customers, which may contain up to seven stages including a sediment prefilter (SED), ion exchange (IEX), KDF or GAC media filters, activated carbon block (ACB) filters, RO membrane (ROM), remineralization media filters (ALK), UV sterilization (UVS) and/or postfiltration activated carbon (PAC) (reprinted with permission from181; Copyright© Express Water Inc., 2020).
Table 12 summarizes the abundance of under-the-sink water filter media across several brands. Among the units including an ROM, APEC Water offers the most models. It has three five-stage models with sediment, two carbon blocks, RO, and GAC postfilter ($190–280), two models with added remineralization ($230–320), two models with added UV before postfilter ($280–290), one model with added UV and remineralization ($310), two models with added pumps for low-pressure households ($370–400), and one compact four-stage model with sediment, GAC, RO, and GAC ($250)120. Similarly, Aquasana has one model with four stages: sediment, AC, RO, and “Claryum”, which is a special design consisting of AC, sediment, and IEX ($200)121. Culligan has one tankless model with RO only122 and two models with storage tank and four stages: sediment, AC, RO, and specialized carbon block123,124. Whirlpool has three models with three stages and a tank: sediment/AC combined prefilter, RO, and AC postfilter125,126. Pelican has one six-stage model with 20 μm SED, GAC prefilter, RO, two GAC postfilters, and calcite remineralization ($220)127,128. GE and Kinetico provide comparatively limited choices, with one model for each brand. The former brand provides a model with GAC pre- and postfilters and tank ($180)129,130, while the latter has four stages: prefilter, RO, storage tank, and AC postfilter.
There are also many under-the-sink water filters without an ROM. For example, Aquasana has two models with SED and two “Claryum” stages ($142–175) and one model with two Claryum stages ($99)131,132. GE has one parallel-flow dual GAC model ($130)133 and two single-stage GAC filters ($70–80)134,135. Products from iSpring are more complicated. This brand provides one four-stage system with sediment, UF membrane, hybrid KDF/GAC, and carbon postfilter ($170)136; one similar compact model, but with UF as the final filter ($130)136; one three-stage model with sediment and two AC blocks ($120)136; and one two-stage system with GAC and AC block ($194)137. Similarly, Pelican has one single-stage GAC ($74)138 and one three-stage system with SED and two catalytic GAC filters ($154)139. Finally, Whirlpool has one model with two AC stages (the first might have a combined sediment stage)140, one three-stage system designed for microbiological purification containing AC, and one single-stage AC system designed for kitchen and bath use ($90)141.
Countertop and pitcher water filters
Table 13 summarizes configuration details of available countertop and pitcher water filters. Countertop systems, among the cheapest of home water filters, often include only one or two stages which may combine multiple filter media (e.g., sediment and GAC). Some are pressurized and are essentially compact versions of under-the-sink systems. However, many are not pressurized: tap water is poured in and gravity alone moves the water through a small filter. Gravity-only filters are very popular and sold in retail hardware, grocery, and mega-stores; water filtration can be slow and most are designed to improve water taste (with some health protection benefits) removing residual chlorine, dissolved organics, and some metals like lead and copper. For some pitcher filters, the filtration process takes only around 30 s. Customers can simply pour water into the pitcher, then get clean drinking water in the pitcher reservoir as feedwater passing through the filter cartridge. In addition, the price of a common water filter pitcher is relatively lower than other filter types, typically less than $40. However, since most pitcher filters only contain GAC, IEX, and/or KDF media, not all contaminants are removed, especially some heavy metals, volatile organic compounds, and hormones.
Refrigerator water filters
Many refrigerators are designed to deliver filtered cold water and ice. All water that passes through a refrigerator is filtered first using a replaceable filter cartridge. This cartridge may be any combination of GAC/ACB, WAC, SBA, KDF, and/or media, but most often is solely some form of GAC or ACB. For example, GE142 and Whirlpool143 have numerous GAC/ACB models for refrigerators, while iSpring has one single-stage GAC ($39) model (Fig. S8)144,145,146,147,148 and one two-stage model with GAC and remineralization ($40)149.
Faucet-mounted water filters
By design, faucet head filters are among the smallest filters available. They usually consist of a single stage with a granular filter medium, which may consist of a couple components mixed in one housing (e.g., KDF and GAC). For example, Brita has two POU models with sediment filter and carbon block filter ($19–30) and PUR has four models with slightly more expensive prices ($20–35)150. iSpring has two models with what appears to be KDF, GAC, and calcium sulfite remineralization according to a picture on their website ($29–35) (Fig. S8)147.
Showerhead water filters
These filters are designed to filter shower water, so drinking water purity is not strictly required; however, many volatile organics could be inhaled while showering and other contaminants could be taken up by dermal absorption from showering or bathing. Many shower filters are designed to remove chlorine (which dries out some people’s skin) and may include one or more remineralization stages for adding minerals deemed to be beneficial to the skin. Both GE and Pelican only have one model for showerhead water filters. The model from GE is similar to a KDF filter ($23)151, while Pelican’s model is more complex with copper-zinc, GAC, and remineralization media ($42)152. Aquasana has three two-stage models which are KDF followed by AC ($55–65)49,51. Models from iSpring are even more complicated (Fig. S8), with three models of 15 stages each. In order, the stages are sand, stainless-steel mesh, particulate, many remineralization and ion exchange stages, KDF, GAC, particulate, stainless-steel mesh, and finally sand ($19–26).
Smart POU water filters
Definition of “Smart Water Filter”
One definition of “smart” originates from computer science, where SMART is a fault detection and monitoring system short for Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology153. The expectation about “smart” is higher now with the expansion of Internet coverage and WiFi technology. Nonliving things are becoming animate and “smart” through artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) by interacting with human beings. Therefore, the present study proposes a new, expanded definition for “smart” with the following equation: Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting + Interaction with Human through Internet = SMART. In recent years, “smart” is an increasingly attractive product description for home equipment and appliances, including water filters. According to Investopedia.com14, “smart home” refers to a convenient home setup where appliances and devices can be automatically controlled remotely from anywhere with an Internet connection using a mobile or other networked device. Devices in a smart home are interconnected through the Internet, allowing the user to control functions such as home security systems, access to the home, temperature, lighting, music, and home theater equipment. Here are a few key takeaways about smart home technology.
-
A smart home allows homeowners to control appliances, thermostats, lights, and other devices remotely using a smartphone or tablet through an Internet connection.
-
Smart homes can be set up through wireless or hardwired systems.
-
Smart home technology provides homeowners with convenience and cost savings.
-
Security risks and bugs continue to plague makers and users of smart home technology.
Further, “smart products” include features such as context awareness through data collection, autonomous operation via AI/ML algorithms, and WiFi or Bluetooth connectivity and connection to other devices and/or the Internet154. For example, one smart air filter can not only actively track the filter life, but also provide environmental air quality information and tips for the user through a convenient mobile app155. Similar to a smart air filter, a smart water filter could allow the user to control the appliance remotely and keep track of important details such as filter lifespan and filtered-water quality. However, there is little consensus on what constitutes a smart water filter. Moreover, current smart water filters are not actually smart based on the fact that they can neither be remotely controlled nor provide necessary water quality information to the consumers.
Most “smart” water filter systems in the U.S. market only have a timer, flow counter, or “# of times used” counter to remind the user when to replace a filter. These rely on preset assumptions of filter usage and water quality, and do not directly measure the quality or quantity of water consumed. Water filter companies which use a battery-powered timed replacement feature include GE, Pelican, and Whirlpool. Kinetico claims to use a smart reminder, but its products simply use a flow counter to shut off the system when a prespecified number of gallons have been used156. Flow sensors record the rotation of an impeller wheel as water moves through the device157. Brita pitchers use a different method: a sensor in the lid counts how many times the lid has been opened to fill the pitcher, approximating the output of a flow sensor. Some sensors, such as those used in PUR faucets158, track both time and water flow. While more sophisticated than a time-based reminder, a flow-based reminder still does not use actual water quality information to assess filter performance or treated-water quality. Moreover, water quality can vary considerably between different households in different regions with different water quality and based on the age of premise plumbing. Pre-programmed filter change reminders have limited ability to adapt to local water quality or assess whether a system is functioning as designed.
It seems obvious to incorporate smart technology and elements into POU water filters, in particular, to reliably notify the user when to replace the filter. Conductivity, pH, and ORP sensors are widely available and some for less than $10 (presumably even less when purchased in bulk). However, we find limited evidence of such technologies in any commercially available POU products. A filter’s ability to remove lead, arsenic, and other harmful contaminants may be well-advertised, but it is not clear for how long that performance persists in a given household installation. A time- or flow-based change reminder is consistent in that a manufacturer can expect attentive customers to buy a replacement at predictable time intervals. This increases the ability of the manufacturer to plan their production and finances. Many customers may never replace their filter cartridges due to inconvenience or switching to a different filter brand. Customers in this group would also be unlikely to benefit from a more intelligent reminder system.
It seems likely that most consumers who will eventually replace their filters would prefer to do so when their system wears out or breaks rather than at a predefined time interval. If a product is developed which includes this feature, perhaps including sensors more sophisticated than TDS (total dissolved solids) (conductivity), then these capabilities could prove attractive. Users could be warned that contaminants have reached unacceptably high levels at the filtration system’s output, providing a more compelling reason to replace one or more components. The availability of in-line TDS sensors which can be plugged into existing water supplies indicates that measurement capabilities are in demand159,160. Given the trend towards an Internet of Things, a smart water filter with electronics which accurately measures water quality would be a fitting contribution to the idea of a smart home.
Sensors that could make water filters smarter
In a smart water filter, evaluation of various parameters using sensors is necessary to monitor water quality. Many sensors have been developed to measure physical qualities of water or the presence of chemical contaminants. These include sensors for electrical conductivity (EC)—a surrogate for TDS, ORP, pH, turbidity, ion-selective electrodes as well as emerging optical, fluorescent, and spectrophotometric devices. Adding these sensors to water filter systems could allow users to check the quality of their water without worrying about silent product expiry. Moreover, the widespread use of sensors could push manufacturers to improve removal efficacy and address more diverse contaminants. Moreover, even if sensors like those described below were to be deployed in POU water treatment systems, they would not be truly SMART until they communicate to the system owner directly through some smart device like an Internet connected phone, tablet, or PC.
TDS sensors
One of the most common sensors is an EC sensor, which requires only a pair of electrical contacts to measure the resistance of water by applying a small current. EC can be closely correlated with TDS because dissolved ions in water allow electricity to flow more freely between the contacts161,162. For instance, there is a fairly robust conversion factor from EC to TDS for fresh water, namely 1 mS/cm EC = 640 ppm TDS163. However, this is a crude measurement because conductivity fails to account for the specific ionic composition of the water. The TDS sensor is small and cheap, with simple versions available for close to $10164. The least expensive sensors can measure TDS within 10% accuracy164, while more expensive ones can achieve 1% accuracy or better165. Multiple forms of the sensor are available; Fig. S9160,166 depicts one sensor with exposed metal contacts and one in-line sensor which covers the contacts in a way that allows them to be placed in series with a water supply159. Due to their simplicity and adaptability, TDS sensors are one of the most common devices for measuring water quality. HM DigitalTM TDS Meter can achieve EC-to-TDS conversion easily, and some meters can even have selectable conversion factors. The Dual Inline TDS Meter is different from the first one as it can measure two different water lines together. As a result, customers can get TDS information about both tap water and filtered water at the same time.
Uncharged contaminants such as soluble hydrocarbons, DBPs, and some pharmaceuticals and pesticides cannot be detected by conductivity sensors because they do not change the ability of water to conduct electrical current. Some charged contaminants such as lead, chromium (VI), and arsenic—while they can be ionic—are toxic at levels in the parts-per-billion range, too small to be detected by all but the most precise conductivity sensors167. Despite limitations, an EC/TDS sensor’s measurements could be used to evaluate whether a filter system is working. If an ROM is breached, downstream EC/TDS sensors would register an increase in the measured EC, which would indicate system performance has declined or failed168. Other filter stages such as WAC/SAC or SBA/WBA IEX resins may become less effective at removing ions from water when nearing saturation, and this difference may be indicated in conductivity measurements. Conductivity thus provides useful information on the status of a filtration system in the absence of more comprehensive water quality data.
pH and ORP sensors
Other types of water quality sensors, which do not appear to be implemented in any commercial POU systems, include pH169 and ORP170 sensors. Several types of pH sensors are available, of which the most common variation is the combination pH sensor. Two electrodes measure either side of a specially designed glass membrane, which contains a reference solution. The measured electrical potential is proportional to the pH of the test solution171. Like conductivity measurements, pH measurements can also indicate the successful operation of a RO Or IEX system172. Like pH probes, ORP probes consist of a test and reference electrode. The test electrode either gains or loses electrons from the solution, resulting in a measurable potential across the two electrodes. ORP is measured in millivolts and depends on the substances present in the solution as well as their concentrations173. These sensors are more complex and correspondingly more expensive, starting at around $30 for the cheapest pH sensors169 and $90 for the cheapest ORP sensors170. Although not present in water filters due to their cost, the combination of pH and ORP measurements can provide significant insight into the chemical makeup of water such as speciation of metals (e.g., Fe2+/Fe3+), oxyanions (e.g., H2AsO4−/HAsO42−), and multi-protic anions (e.g., HCO3−/CO32−) as well as corrosivity (e.g., Langlier saturation index).
Future smart POU system using nanotechnology-enabled sensors
Nanomaterial-enabled sensors, also called nanosensors, are invented for high-efficacy, multiplex-functionality, and high-flexibility sensing applications174. Interest in developing these sensors in POU applications origins from their potentials on facile, in-field contaminant detection. Many existing nanosensors are capable of sensing and monitoring the water safety. However, these sensors require further development into consumer- and operator-friendly products with the high compatibility of POU systems174. While monitoring the water safety, nanosensors have ultralow multiplex detection and rapid analysis times, due to their novel properties175,176. However, the great achievements in the laboratory and in the literature about nanosensors have seldom been translated to successfully commercialized products174.
In principle, nanosensor is comprised of (1) a nanomaterial, (2) a recognition element, and (3) a mechanism for signal transduction177. The interaction between the analytes and the recognition element will induce a detectable signal174. The specificity of the nanosensor is endowed by detecting an intrinsic signal from the analyte or by employing highly specific recognition elements that ideally bind only to a given target177. Moreover, the properties of the nanomaterial and the transduction method determine the sensitivity of the nanosensor174.
Electrically based nanosensor typically employs nanomaterials such as silicon, noble metal nanoparticles (Pt, Ag, Au), carbonaceous nanomaterials (graphene, carbon nanotubes), and inorganic two-dimensional nanosheets due to their high conductivity and electrochemical stability174. The electrically based nanosensors have enabled sensitive detection of waterborne contaminants such as E. coli174. Figure 9 illustrates representative electrically based nanosensor architecture for environmental analyte detection. A glassy carbon electrode was functionalized via multiple steps, including the treatment with reduced graphene oxide, electro polymerization of pyrrole, electrodeposition of gold, and the co-deposition of silica and acetylcholinesterase174. This nanosensor is capable of sensing organophosphorus pesticides.
A glassy carbon electrode was functionalized via multiple steps, including the treatment with reduced graphene oxide, electro polymerization of pyrrole, electrodeposition of gold, and the co-deposition of silica and acetylcholinesterase (reprinted with permission from182; Copyright© RSC, 2014).
In contrast to the electrochemical method, magnetic transduction shows less background signal and therefore can detect contaminants with low concentrations177. The analytes that can then be detected are magnetically isolated via the functionalization of nanomaterials with analyte-specific biomolecules174,178. Figure 10 illustrates representative magnetically based nanosensor architecture for environmental analyte detection. Combined magneto-fluorescence approach is applied to sense and detect bacteria via fluorophore labeled magnetic nanoparticles. Fluorescence and magnetic bacterial sensing are achieved by functionalizing specific antibodies of E. coli with magneto-fluorescent nanosensors.
Combined magneto-fluorescence approach is applied to sense and detect bacteria via fluorophore labeled magnetic nanoparticles. Fluorescence and magnetic bacterial sensing are achieved by functionalizing specific antibodies of E. coli with magneto-fluorescent nanosensors (reprinted with permission from183; Copyright© ACS, 2016).
Compared to traditional conductivity sensors or ORP sensors, nanosensors can be capable of detecting and monitoring a wider spectrum of contaminants by tailoring the sensor compositions174,179. However, the challenges associated with transitioning novel nanosensors into POU system are particularly vexing due to the lack of capital sources powering product research, development, and marketing. In general, if a novel technology is to gain a foothold then the potential profits associated with it have to be considerable, while the risks of adoption must be acceptable174.
Concluding remarks
Current household tap water quality in the United States is as good as anywhere else where drinking water is treated to regulated quality. That said, violations for a wide array of regulated contaminants by public water systems, unregulated non-grid-tied groundwater wells, and unregulated emerging contaminants still pose serious acute and chronic health risks. For example, some very-high-profile cases of impaired municipal drinking water have occurred in recent years (e.g., lead in Flint, Michigan and Newark, New Jersey). Moreover, long timelines for implementing new regulations in the U.S. cause some concern over the purity and healthfulness of municipal drinking water, especially with so many toxic, carcinogenic, endocrine disrupting, and pharmaceutically active chemicals known to be in drinking water’s source waters. Treatment plants that use surface water as a source tend to have a higher frequency of violations compared to those using groundwater. For smaller systems, many of the violations are for lack of reporting versus reports of known violations, so the potential risk to the populations served is difficult to assess. As the size of treatment plants increase, the percent of violations and, in particular, those that use surface water both tend to decrease; however, the number of people potentially at risk is quite high due to the large populations served.
These well-documented drinking water violations, unregulated off-grid groundwater wells, and emerging contaminants all give rise to consumers’ lack of confidence in drinking water quality and justify the use of POU drinking water treatment systems. Although there has been much research on the mechanisms and removal efficacies of the types of water treatment technologies employed in POU applications, most peer-reviewed studies are framed in the context of large-scale municipal or industrial treatment applications and few independent studies have evaluated their efficacy in POU water treatment applications. Components in commercially available POU water filter systems are highly commoditized and standardized across the industry. Sediment, KDF, AC (either GAC or ACB), RO, remineralization, and UVS are the most commonly employed technologies. This level of homogeneity in the production of filter systems is good in that it drives down costs to the consumer making POU water treatment widely accessible; however, the lack of regulations, monitoring and control of POU systems make it difficult to know if and when a POU system stops working as it was designed.
The smartness of POU water filters may be defined as their ability to perform tasks such as monitoring and reporting water quality, monitoring filter performance and expected lifetime, controlling filtration remotely, and connecting with consumers through personal smart devices. By this definition, currently there are no commercially available SMART POU water filtration products. Sensors providing water quality information is an essential feature for a water filter to become SMART. However, a SMART water filter is also expected to be connected to WiFi or Bluetooth and deliver the information to a mobile app. Interaction and control through the use of Internet is a key characteristic of any smart home technology. Future design and production of SMART POU water treatment systems should consider moving beyond timers and counters to flow meters and (at least) basic water quality sensors (e.g., EC/pH/ORP) along with Internet connectivity and interactive consumer apps. Finally, these technological innovations must be accomplished at very low cost to assure widespread accessibility for the most vulnerable and underprivileged populations.
Data availability
The authors declare that no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Change history
06 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00159-0
References
Blake, N. M. Water for the Cities: A History of the Urban Water Supply Problem in the United States Vol. 3 (Syracuse University Press, 1956).
Aziz, H. A. & Amr, S. S. A. (eds). Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Water and Wastewater Treatment (IGI Global, 2019).
Tynan, N. Nineteenth century London water supply: processes of innovation and improvement. Rev. Austrian Econ. 26, 73–91 (2013).
Huisman, L. & Wood, W. E. Slow Sand Filtration 1–89 (WHO, 1974).
Crittenden, J. C., Trussell, R. R., Hand, D. W., Howe, K. J. & Tchobanoglous, G. MWH’s Water Treatment: Principles and Design (John Wiley & Sons, 2012).
Crittenden, J. C., Trussell, R. R., Hand, D. W., Howe, K. J. & Tchobanoglous, G. Water Treatment: Principles and Design (John Wiley & Sons, 2005).
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (2020).
EPA. Secondary Drinking Water Standards: Guidance for Nuisance Chemicals https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/secondary-drinking-water-standards-guidance-nuisance-chemicals (2020).
Javidi, A. & Pierce, G. US households’ perception of drinking water as unsafe and its consequences: examining alternative choices to the tap. Water Resour. Res. 54, 6100–6113 (2018).
Pierce, G. & Gonzalez, S. Mistrust at the tap? Factors contributing to public drinking water (mis) perception across US households. Water Policy 19, 1–12 (2017).
Eric M.V. Hoek, David Jassby, Richard B. Kaner, Jishan Wu, Jingbo Wang, Yiming Liu, Unnati Rao. Unnati Rao Sustainable Desalination and Water Reuse (Morgan & Claypool, 2021).
Oren, Y. Capacitive deionization (CDI) for desalination and water treatment—past, present and future (a review). Desalination 228, 10–29 (2008).
Hunker. Definition of Smart Appliances https://www.hunker.com/13409415/definition-of-smart-appliances (2020).
Webopedia. Smart Home https://www.webopedia.com/TERM/S/smart-home.html (2020).
EPA. Drinking Water Regulations and Contaminants https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/drinking-water-regulations-and-contaminants (2020).
EPA. Basic Information on the CCL and Regulatory Determination https://www.epa.gov/ccl/basic-information-ccl-and-regulatory-determination#how-ccl1ccl2-developed (2020).
EPA. Regulatory Determination 4 https://www.epa.gov/ccl/regulatory-determination-4 (2020).
EPA. Perchlorate in Drinking Water https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/perchlorate-drinking-water (2020).
Hoek, E. M. V. Reverse Osmosis Membrane Biofouling: Causes, Consequences and Countermeasures http://www.aquamem.com/publications/WPI_RO-Biofouling_WhitePaper_v1_4-24-17.pdf (2017).
EPA. How EPA Regulates Drinking Water Contaminants www.epa.gov/sdwa/how-epa-regulates-drinking-water-contaminants (2020).
Toupin, L. U.S. Federal vs. State Environmental Regulations: What to Follow https://enablon.com/blog/u-s-federal-vs-state-environmental-regulations-what-to-follow/ (2020).
US EPA. Enhancing Effective Partnerships Between the EPA and the States in Civil Enforcement and Compliance Assurance Work https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-07/documents/memoenhancingeffectivepartnerships.pdf (2019).
California Legislative Information. CHAPTER 6.6. Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986. (2020).
OEHHA. Proposition 65 Law and Regulations https://oehha.ca.gov/proposition-65/law/proposition-65-law-and-regulations (2020).
How Drinking Water Standards are Created in California https://www.cleanwateraction.org/features/how-drinking-water-standards-are-created-california (2020).
Boards, C. W. Maximum contaminant levels and regulatory dates for drinking water: U.S. EPA vs California. 6–9 https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/drinking_water/certlic/drinkingwater/documents/ccr/mcls_epa_vs_dwp.pdf (US EPA, 2018).
Duffour, C. et al. Texas Administrative Code. Summary of Maximum Contaminant Levels, Maximum Residual Disinfectant Levels, Treatment Techniques, and Action Levels. https://www.tceq.texas.gov/assets/public/legal/rules/rules/pdflib/290f.pdf (2017).
Scott, R. & Jones, J. L. State of Alaska. Department of environmental conservation, 18 AAC 70, Water Quality Standards. https://dec.alaska.gov/media/1046/18-aac-70.pdf.
Guidance Values and Standards for Contaminants in Drinking Water https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/risk/guidance/gw/index.html (2020).
EPA. Analyze Trends: Drinking Water Dashboard https://echo.epa.gov/trends/comparative-maps-dashboards/drinking-water-dashboard (2020).
EPA. Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) Resources and FAQs https://echo.epa.gov/help/sdwa-faqs (2020).
EPA. Drinking Water Dashboard Help https://echo.epa.gov/help/drinking-water-dashboard-help (2020).
Allaire, M., Wu, H. & Lall, U. National trends in drinking water quality violations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, 2078–2083 (2018).
VanDerslice, J. Drinking water infrastructure and environmental disparities: evidence and methodological considerations. Am. J. Public Health 101, S109–S114 (2011).
Ayotte, J. D., Medalie, L., Qi, S. L., Backer, L. C. & Nolan, B. T. Estimating the high-arsenic domestic-well population in the conterminous United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 12443–12454 (2017).
Johnson, T. D. & Belitz, K. Domestic well locations and populations served in the contiguous U.S.: 1990. Sci. Total Environ, 607–608, 658–668 (2017).
DeSimone, L. A. & Hamilton, P. A. Quality of Water from Domestic Wells in Principal Aquifers of the United States, 1991–2004 (US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, 2009).
Rosenfeld, P. E. & Feng, L. G. H. in Risks of Hazardous Wastes (eds Paul E. Rosenfeld & Lydia G. H. Feng) 215–222 (William Andrew Publishing, 2011).
Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Facilities Restoration and Reuse Office. Technical Fact Sheet – 1,4-Dioxane (EPA, 2017).
Bilal, M., Adeel, M., Rasheed, T., Zhao, Y. & Iqbal, H. M. N. Emerging contaminants of high concern and their enzyme-assisted biodegradation–a review. Environ. Int. 124, 336–353 (2019).
Bexfield, L. M., Toccalino, P. L., Belitz, K., Foreman, W. T. & Furlong, E. T. Hormones and pharmaceuticals in groundwater used as a source of drinking water across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 2950–2960 (2019).
NDMA and Other Nitrosamines - Drinking Water Issues https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/drinking_water/certlic/drinkingwater/NDMA.html (2020).
EPA. Technical Fact Sheet – N-Nitroso-dimethylamine (NDMA) https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/201403/documents/ffrrofactsheet_contaminant_ndma_january2014_final.pdf (2014).
Yang, Y., Ok, Y. S., Kim, K.-H., Kwon, E. E. & Tsang, Y. F. Occurrences and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in drinking water and water/sewage treatment plants: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 596, 303–320 (2017).
Wang, Y. et al. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from municipal waste water with integrated membrane systems, MBR-RO/NF. Int J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15, 269 (2018).
Hao, J. et al. Bioaccessibility evaluation of pharmaceuticals in market fish with in vitro simulated digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 411, 125039 (2021).
Shen, R. & Andrews, S. A. Demonstration of 20 pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) as nitrosamine precursors during chloramine disinfection. Water Res. 45, 944–952 (2011).
Richardson, S. D. Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal. Chem. 81, 4645–4677 (2009).
Premium Shower Filter | Massaging Shower Head https://www.aquasana.com/shower-head-water-filters/premium-shower-filter/no-shower-head (2020).
Arias Espana, V. A., Mallavarapu, M. & Naidu, R. Treatment technologies for aqueous perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA): a critical review with an emphasis on field testing. Environ. Technol. Innov. 4, 168–181 (2015).
Shower Filters for Chlorine https://www.aquasana.com/shower-head-water-filters (2020).
Ye, Z., Weinberg, H. S. & Meyer, M. T. Occurrence of antibiotics in drinking water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 387, 1365–1377 (2007).
Ye, Z., Weinberg, H. & Meyer, M. Occurrence of Antibiotics in Drinking Water (IATP, 2004).
A Simple Guide to Water Filtration https://www.filtersfast.com/blog/guide-to-water-purification/ (2020).
Fresh Water System. What is a Sediment Filter and How Does It Work? https://www.freshwatersystems.com/blogs/blog/what-is-a-sediment-filter-and-how-does-it-work (2020).
McNamara, P. What Are String Wound Water Filters and How Are They Used? https://www.waterfiltersfast.com/What-Are-String-Wound-Water-Filters-and-How-Are-They-Used_b_74.html (2017).
UNISUN. 5um PP Yarn String Wound Filter Cartridges with stainless steel Core or PP Core http://zeusfilter-com.sell.everychina.com/p-107966081-5um-pp-yarn-string-wound-filter-cartridges-with-stainless-steel-core-or-pp-core.html (2020).
Alexandratos, S. D. Ion-exchange resins: a retrospective from industrial and engineering chemistry research. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48, 388–398 (2009).
Levchuk, I., Marquez, J. J. R. & Sillanpaa, M. Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) from water by ion exchange - a review. Chemosphere 192, 90–104 (2018).
SAMCO. What Is the Difference Between Cation and Anion Exchange Resins? https://www.samcotech.com/difference-cation-anion-exchange-resins/ (2018).
Basic Ion Exchange for Residential Water Treatment—Part 3 http://wcponline.com/2005/07/15/basic-ion-exchange-residential-water-treatment-part-3/ (2005).
Lalmi, A., Bouhidel, K.-E., Sahraoui, B. & Anfif, C. E. H. Removal of lead from polluted waters using ion exchange resin with Ca(NO3)2 for elution. Hydrometallurgy 178, 287–293 (2018).
Batista J.R., M. F. X., Vieira A. R. in Perchlorate in the Environment. Environmental Science Research Vol. 57 (ed. Urbansky E.T.) (Springer, 2000).
Wu, C. C. et al. The microbial colonization of activated carbon block point-of-use (PoU) filters with and without chlorinated phenol disinfection by-products. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 3, 830–843 (2017).
Karnib, M., Kabbani, A., Holail, H. & Olama, Z. Heavy metals removal using activated carbon, silica and silica activated carbon composite. Energy Procedia 50, 113–120 (2014).
Gaur, V. Adsorption on activated carbon: role of surface chemistry in water purification. In Aqueous Phase Adsorption: Theory, Simulations and Experiments (eds Singh, J. K. & Verma, N.) (CRC Press, 2018).
Pego, M., Carvalho, J. & Guedes, D. Surface modifications of activated carbon and its impact on application.Surf. Rev. Lett. 26, 1830006 (2019).
Rajaeian, B., Allard, S., Joll, C. & Heitz, A. Effect of preconditioning on silver leaching and bromide removal properties of silver-impregnated activated carbon (SIAC). Water Res. 138, 152–159 (2018).
Watson, K., Farre, M. J. & Knight, N. Comparing a silver-impregnated activated carbon with an unmodified activated carbon for disinfection by-product minimisation and precursor removal. Sci. Total Environ. 542, 672–684 (2016).
Mishra, S. P. & Ghosh, M. R. Use of silver impregnated activated carbon (SAC) for Cr(VI) removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 103641 (2020).
Lenntech. KDF Process Media https://www.lenntech.com/kdf-filter-media.htm (2020).
Zhang, F. & Liu, X. Experimental study on removal of phenol from water by KDF metal filter. China Water Wastewater 17, 70–71 (2001).
CrystalClear. KDF/GAC Water Filter Replacement Cartridge https://www.crystalclearsupply.com/KDF_GAC_Water_Filter_Cartridge_p/cf.htm (2020).
KDF Fluid Treatment, I. KDF Process Media Aid in Chlorine, Algae, Bacteria and Iron Removal from Water http://www.kdfft.com/products.htm (2020).
KDF Fluid Treatment, I. KDF®55 and 85 Process Media in Point-of-Entry Water Treatment Systems – Chlorine, Iron and Hydrogen Sulfide Reduction http://www.kdfft.com/pdfs/kdf55_85Sheet.pdf (2020).
Xiong, R. J., P., L. W., Xi,X. M. & Xiao, S. W. Application and amelioration prospect of copper-zinc alloy in water treatment. Ind. Saf. Environ. Prot. 30, 5–8 (2004).
Zhai, Y. J., Tian, X. J., He, G. H. & Zhang, M. An experimental study on removal of residual chlorine in water by using nano-metal clusters media. Tianjin Chem. Ind. 24, 56–59 (2010).
Glanris. 100% Green Filtration Media, at Ultra-Low Cost https://www.glanris.com/glanris-features (2020).
Glanris. BETTER, FASTER, MORE AFFORDABLE WATER FILTRATION MEDIA SOLUTION https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5c7ed0eb7d0c9159f879a61f/t/5db995c88650c07fab772463/1572443592570/Glanris+water+filtration+media_data+sheet.pdf (2020).
Swift. We are Providing Eco-Friendly Water Filtration Products http://www.swiftgreenfilters.com/about-us/ (2020).
Swift. Home Page for Swift Green Filter http://www.swiftgreenfilters.com/ (2020).
Asadollahi, M., Bastani, D. & Musavi, S. A. Enhancement of surface properties and performance of reverse osmosis membranes after surface modification: a review. Desalination 420, 330–383 (2017).
Different water filtration methods explained https://www.freedrinkingwater.com/water-education/quality-water-filtration-method-page3.htm (2020).
Madsen, H. T. Membrane filtration in water treatment - removalof micropollutants. In Chemistry of Advanced Environmental Purification Processes of Water (ed. Søgaard, E.G.) 199–248 (Elsevier, 2014).
Ramesh, A. et al. Biofouling in membrane bioreactor. Sep Sci. Technol. 41, 1345–1370 (2006).
Kuo, D. H.-W. et al. Assessment of human adenovirus removal in a full-scale membrane bioreactor treating municipal wastewater. Water Res. 44, 1520–1530 (2010).
Al-Karaghouli, A. & Kazmerski, L. L. Energy consumption and water production cost of conventional and renewable-energy-powered desalination processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 24, 343–356 (2013).
Rodriguez, C. et al. Indirect potable reuse: a sustainable water supply alternative. Int J. Environ. Res. Public Health 6, 1174–1209 (2009).
Tam, L. S., Tang, T. W., Lau, G. N., Sharma, K. R. & Chen, G. H. A pilot study for wastewater reclamation and reuse with MBR/RO and MF/RO systems. Desalination 202, 106–113 (2007).
Tang, C. Y., Fu, Q. S., Robertson, A. P., Criddle, C. S. & Leckie, J. O. Use of reverse osmosis membranes to remove perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) from semiconductor wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 7343–7349 (2006).
Plumlee, M. H., Lopez-Mesas, M., Heidlberger, A., Ishida, K. P. & Reinhard, M. N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) removal by reverse osmosis and UV treatment and analysis via LC-MS/MS. Water Res. 42, 347–355 (2008).
Stefan, M. I. UV direct photolysis of N‐nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA): kinetic and product study. Helvetica Chim. Acta 85, 1416–1426 (2002).
Master, H. 1,4-Dioxane: The hidden danger in your daily routine http://www.homemasterfiltersblog.com/jon-sigona/2017/5/23/14-dioxane-the-hidden-danger-in-your-daily-routine (2017).
Song, K., Mohseni, M. & Taghipour, F. Application of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) for water disinfection: a review. Water Res. 94, 341–349 (2016).
Collivignarelli, M., Abbà, A., Benigna, I., Sorlini, S. & Torretta, V. Overview of the main disinfection processes for wastewater and drinking water treatment plants. Sustainability 10, 86 (2017).
Li, H. Y., Osman, H., Kang, C. W., Ba, T. & Lou, J. Numerical and experimental studies of water disinfection in UV reactors. Water Sci. Technol. 80, 1456–1465 (2019).
Kalisvaart, B. F. Re-use of wastewater: preventing the recovery of pathogens by using medium-pressure UV lamp technology. Water Sci. Technol. 50, 337–344 (2004).
Jarvis, P., Autin, O., Goslan, E. H. & Hassard, F. Application of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LED) to full-scale drinking-water disinfection. Water 11, 1894 (2019).
Chatterley, C. & Linden, K. Demonstration and evaluation of germicidal UV-LEDs for point-of-use water disinfection. J. Water Health 8, 479–486 (2010).
Beck, S. E. et al. Evaluating UV-C LED disinfection performance and investigating potential dual-wavelength synergy. Water Res. 109, 207–216 (2017).
Zoschke, K., Bornick, H. & Worch, E. Vacuum-UV radiation at 185 nm in water treatment–a review. Water Res. 52, 131–145 (2014).
Li, J. et al. Enhanced germicidal effects of pulsed UV-LED irradiation on biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 109, 2183–2190 (2010).
Wengraitis, S. et al. Pulsed UV-C disinfection of Escherichia coli with light-emitting diodes, emitted at various repetition rates and duty cycles. Photochem. Photobiol. 89, 127–131 (2013).
Hasson, D., Fine, L., Sagiv, A., Semiat, R. & Shemer, H. Modeling remineralization of desalinated water by micronized calcite dissolution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 12481–12488 (2017).
Shemer, H. et al. Remineralization of desalinated water by limestone dissolution with carbon dioxide. Desalin. Water Treat. 51, 877–881 (2013).
Lahav, O. & Birnhack, L. Quality criteria for desalinated water following post-treatment. Desalination 207, 286–303 (2007).
Biyoune, M. G. et al. Remineralization of permeate water by calcite bed in the Daoura’s plant (south of Morocco). Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 226, 931–941 (2017).
3-5mm Alkaline Ceramic Balls Make Alkaline water PH 8-9.5 For Water Filters,Water Purifiers https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32804763534.html (2020).
Chaturvedi, S. I. Electrocoagulation: a novel waste water treatment method. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. 3, 93–100 (2013).
Porada, S., Zhao, R., van der Wal, A., Presser, V. & Biesheuvel, P. M. Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Prog. Mater. Sci. 58, 1388–1442 (2013).
Welgemoed, T. J. & Schutte, C. F. Capacitive Deionization Technology™: an alternative desalination solution. Desalination 183, 327–340 (2005).
Blair, J. W. & Murphy, G. W. Saline water conversion. Adv. Chem. Ser. 27, 206 (1960).
Johnson, A. M., Venolia, A. W., Wilbourne, R. G. & Newman, J. The Electrosorb Process for Desalting Water. (NTRL, 1970).
Lee, J.-B., Park, K.-K., Eum, H.-M. & Lee, C.-W. Desalination of a thermal power plant wastewater by membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 196, 125–134 (2006).
Lee, J., Kim, S., Kim, C. & Yoon, J. Hybrid capacitive deionization to enhance the desalination performance of capacitive techniques. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3683–3689 (2014).
Gao, X., Omosebi, A., Landon, J. & Liu, K. Surface charge enhanced carbon electrodes for stable and efficient capacitive deionization using inverted adsorption–desorption behavior. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 897–909 (2015).
Pasta, M., Wessells, C. D., Cui, Y. & La Mantia, F. A desalination battery. Nano Lett. 12, 839–843 (2012).
Jeon, S. I. et al. Desalination via a new membrane capacitive deionization process utilizing flow-electrodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 1471–1475 (2013).
ElectraMet. Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater with No Chemicals or Sludge https://electramet.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/ElectraMet-Battery.R1.pdf (2020).
Reverse Osmosis Systems https://www.freedrinkingwater.com/products/ (2020).
Reverse Osmosis Under Counter Water Filter https://www.aquasana.com/drinking-water-filter-systems/reverse-osmosis-claryum (2020).
Whole Home Water Filter Systems https://www.aquasana.com/whole-house-water-filters (2020).
AC-30 Good Water Machine Under Sink Water Filtration System https://www.culligan.com/product/ac-30-good-water-machine-under-sink-water-filtration-system (2020).
Aqua-Cleer Advanced Under Sink Water Filter System https://www.culligan.com/product/aqua-cleer-advanced-under-sink-water-filter-system (2020).
UltraEase Reverse Osmosis Filtration System https://www.whirlpoolwatersolutions.com/products/ultraease-reverse-osmosis-filtration-system/ (2020).
Pro Series - UltraEase Reverse Osmosis Filtration System https://www.whirlpoolwatersolutions.com/products/new-pro-series-ultraease-reverse-osmosis-filtration-system/ (2020).
Whole House Sediment Filter Systems https://www.pelicanwater.com/water-filters/sediment-filters/ (2020).
6-Stage Reverse Osmosis (RO) System https://www.pelicanwater.com/drinking-filters/pelican-reverse-osmosis/ (2020).
FX12P | Replacement Water Filters - Reverse Osmosis System https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/FX12P (2020).
GXRM10RBL | Reverse Osmosis Filtration System https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/GXRM10RBL (2020).
2-Stage Under Counter Water Filter | NSF Certified https://www.aquasana.com/drinking-water-filter-systems/under-counter-faucet-2-stage (2020).
Under Sink Water Filters https://www.aquasana.com/under-sink-water-filters (2020).
GXK285JBL | Dual Flow Water Filtration System https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/GXK285JBL (2020).
GXK185KBL | Single Stage Filtration System https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/GXK185KBL (2020).
GXULQK | Full Flow Water Filtration System https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/GXULQK (2020).
iSpring CU-A4 4-Stage Compact, High Efficiency Under Sink / Inline Drinking Water Filter System for Sink, Refrigerator and RV https://www.123filter.com/ac/ultra-filtration-under-sink-water-filter-system/ispring--4-stage-ultrafiltration-water-filtration-system (2020).
iSpring US21B Heavy Duty 2-Stage Undersink Water Filtration System https://www.123filter.com/ac/direct-connect-under-sink-water-filter-system/ispring--2-stage-under-sink-water-filter-45x10-big-blue-1-ports_803 (2020).
Under Counter Drinking Filter System https://www.pelicanwater.com/drinking-filters/undercounter-drinking-filter/ (2020).
Pelican 3-Stage Under-Counter Drinking Water Filter https://www.pelicanwater.com/drinking-filters/pelican-3-stage-drinking-filter/ (2020).
UltraEase Dual Stage Water Filtration System https://www.whirlpoolwatersolutions.com/products/new-ultraease-dual-stage-water-filtration-system/ (2020).
UltraEase Kitchen & Bath Water Filtration System https://www.whirlpoolwatersolutions.com/products/ultraease-kitchen-bath-water-filtration-system/ (2020).
XFWE | Refrigeration Water Filter https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/XWF (2020).
UltraEase In-Line Refrigerator Filtration System https://www.whirlpoolwatersolutions.com/products/ultraease-in-line-refrigerator-water-filtration-system/ (2020).
iSpring CKC1C Countertop water filter, Clear Housing with Carbon https://www.123filter.com/ac/ispring-ckc1c-countertop-water-filter-clear-housing-with-carbon (2020).
iSpring Filter Water Pitcher 10 Cup BPA Free,Blue https://www.amazon.ca/iSpring-Filter-Water-Pitcher-Free/dp/B077SLX54C (2020).
iSpring Water Systems https://www.123filter.com/ac/the-battle-of-the-best-water-conditioner-ispring-ed2000-vs-ispring-wds150k (2020).
DF1/DF2 Series https://www.123filter.com/ac/faucet-mounted-water-filter-df-series/ispring-df1-faucet-mount-water-filters-removal-500gal-filter-life-15gpm-filtration-rate_624 (2020).
iSpring SF3S 15-Stage Never Clog High Output Universal Shower Filter https://www.123filter.com/ac/shower-filter/ispring-sf3s-stylish-multi-stage-high-output-shower-head-filter-with-replaceable-cartridge-to-remove-chlorine-sediment-and-heavy-minerals-chrome_782_783 (2020).
iSpring FT15INRF Universal Refrigerator Water Filter, Fridge Top Water Filter, 1-Stage https://www.123filter.com/ac/ispring-universal-refrigerator-water-filter-fridge-top-water-filter-1-stage (2020).
Faucet Filtration Systems - Products https://www.pur.com/water-filtration/faucet-filtration-systems (2020).
GXSM01HWW | GE GXSM01HWW Universal Shower Filtration System https://www.geapplianceparts.com/store/parts/spec/GXSM01HWW (2020).
Pelican Premium Shower Filter https://www.pelicanwater.com/shower-filters/shower-filter/ (2020).
Wikipedia, Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/S.M.A.R.T (2020).
Silverio-Fernández, M., Renukappa, S. & Suresh, S. What is a smart device? - a conceptualisation within the paradigm of the Internet of Things. Vis. in Eng. 6, 3 (2018).
Filtrete™. Smart Filter Technology https://www.filtrete.com/3M/en_US/filtrete/products/smart-filter-technology/ (2020).
Kinetico Water System https://www.kinetico.com/smart-home/ (2020).
HYDAC. Flow Rate Sensors https://www.hydac.com/de-en/products/sensors/flow-rate-sensors.html (2020).
PUR. Facet Filtration https://www.pur.com/ (2019).
AMI. In-line tds water quality monitors for home ro systems by hm digital https://appliedmembranes.com/tds-water-quality-monitors-for-home-ro-systems.html (2020).
Dual Inline TDS Meter DM https://media.cdn.bulkreefsupply.com/media/catalog/product/cache/1/image/2fcdbae242296b85abb30af0b2420513/2/0/200031-TDS-Meter-Dual-Inline-DM-1-a_1.jpg (2020).
Mousavi Mashhadi, S. K., Yadollahi, H. & Marvian Mashhad, A. Design and manufacture of TDS measurement and control system for water purification in reverse osmosis by PID fuzzy logic controller with the ability to compensate effects of temperature on measurement. Turk. J. Elec. Eng. Comp. Sci. 24, 2589–2608 (2016).
IC Controls. Total Dissolved Solids Measurement https://iccontrols.com/wp-content/uploads/art-v1400001_total_dissolved_solids_measurement.pdf (2020).
Conductivity convertor https://www.lenntech.com/calculators/conductivity/tds_engels.htm (2020).
Gravity: Analog TDS Sensor/Meter for Arduino https://www.dfrobot.com/product-1662.html (2020).
McMaster-Carr. tds (total dissolved solids) probes https://www.mcmaster.com/tds-(total-dissolved-solids)-probes/ (2020).
Single TDS Sensor Probe http://hmdigital.com/product/sp-5 (2020).
Roy, E. Please Stop Using TDS (or ppm) Testers To Evaluate Water Quality https://www.hydroviv.com/blogs/water-smarts/tds-meters-and-testers (2020).
Sensorex. Conductivity Monitoring for Reverse Osmosis https://sensorex.com/blog/2017/07/12/conductivity-monitoring-reverse-osmosis/ (2020).
Gravity: Analog pH Sensor / Meter Kit For Arduino https://www.dfrobot.com/product-1025.html (2020).
Gravity: Analog ORP Sensor Meter For Arduino https://www.dfrobot.com/product-1071.html (2020).
The Combination pH Electrode http://ion.chem.usu.edu/~sbialkow/Classes/3600/Overheads/pH/ionselctive.html (2020).
pH/ORP Measurement for Reverse Osmosis https://www.yokogawa.com/us/library/resources/application-notes/ph-orp-measurement-for-reverse-osmosis/ (2016).
FUNDAMENTALS OF ORP MEASUREMENT https://www.emerson.com/documents/automation/application-data-sheet-fundamentals-of-orp-measurement-rosemount-en-68438.pdf (2020).
Vikesland, P. J. Nanosensors for water quality monitoring. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 651–660 (2018).
Qu, X., Brame, J., Li, Q. & Alvarez, P. J. J. Nanotechnology for a safe and sustainable water supply: enabling integrated water treatment and reuse. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 834–843 (2013).
Bhattacharyya, S. et al. Nanotechnology in the water industry, part 1: occurrence and risks. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 109, 30–37 (2017).
Vikesland, P. J. & Wigginton, K. R. Nanomaterial enabled biosensors for pathogen monitoring-a review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 3656–3669 (2010).
Kudr, J. et al. Magnetic nanoparticles: from design and synthesis to real world applications. Nanomaterials 7, 243 (2017).
Das, R. et al. Recent advances in nanomaterials for water protection and monitoring. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 6946–7020 (2017).
Majdi, H. S., Jaafar, M. S. & Abed, A. M. Using KDF material to improve the performance of multi-layers filters in the reduction of chemical and biological pollutants in surface water treatment. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 28, 39–45 (2019).
Water, E. What is the Alkaline + Ultraviolet RO System https://www.expresswater.com/pages/ro-alkaline-uv (2020).
Yang, Y., Asiri, A. M., Du, D. & Lin, Y. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on a gold nanoparticle–polypyrrole–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite modified electrode for the amperometric detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Analyst 139, 3055–3060 (2014).
Banerjee, T. et al. Multiparametric magneto-fluorescent nanosensors for the ultrasensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. ACS Infect. Dis. 2, 667–673 (2016).
DeSimone, L. A., Hamilton, P. A. & Gilliom, R. J. Quality of Water from Domestic Wells in Principal Aquifers of the United States, 1991–2004, Overview of Major Findings (USGS, 2009).
EPA. Basic Information about Lead in Drinking Water https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/basic-information-about-lead-drinking-water (2020).
Pirbazari, M. & Weber, W. J. Removal of dieldrin from water by activated carbon. J. Environ. Eng. 110, 656–669 (1984).
Moussavi, G., Hosseini, H. & Alahabadi, A. The investigation of diazinon pesticide removal from contaminated water by adsorption onto NH4Cl-induced activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 214, 172–179 (2013).
Oregon Health Authority, Atrazine and Drinking Water https://www.oregon.gov/oha/ph/healthyenvironments/drinkingwater/monitoring/documents/health/atrazine.pdf (2015).
Oregon Health Authority. Alachlor and drinking water https://www.oregon.gov/oha/PH/HealthyEnvironments/DrinkingWater/Monitoring/Documents/health/alachlor.pdf Alachlor and drinking water (2015).
SAMCO. What Are the Different Types of Ion Exchange Resins and What Applications Do They Serve? https://www.samcotech.com/different-types-ion-exchange-resins-applications-serve/ (2017).
Warsinger, D. M. et al. A review of polymeric membranes and processes for potable water reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 81, 209–237 (2016).
Bellona, C., Drewes, J. E., Xu, P. & Amy, G. Factors affecting the rejection of organic solutes during NF/RO treatment - a literature review. Water Res. 38, 2795–2809 (2004).
Sorlini, S. & Collivignarelli, C. Chlorite removal with granular activated carbon. Desalination 176, 255–265 (2005).
Wang, L., Sun, Y. N. & Chen, B. Y. Rejection of haloacetic acids in water by multi-stage reverse osmosis: efficiency, mechanisms, and influencing factors. Water Res. 144, 383–392 (2018).
Woodard, J. How to Remove Chloramines from Water https://www.freshwatersystems.com/blogs/blog/how-to-remove-chloramines-from-water (2020).
Chen, A. S. C., Wang, L. L., Sorg, T. J. & Lytle, D. A. Removing arsenic and co-occurring contaminants from drinking water by full-scale ion exchange and point-of-use/point-of-entry reverse osmosis systems. Water Res. 172, 115455 (2020).
Pehlivan, E. & Altun, T. Ion-exchange of Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, and Ni2+ ions from aqueous solution by Lewatit CNP 80. J. Hazard. Mater. 140, 299–307 (2007).
Mohsen-Nia, M., Montazeri, P. & Modarress, H. Removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from wastewater with a chelating agent and reverse osmosis processes. Desalination 217, 276–281 (2007).
Korngold, E. Iron removal from tap water by a cation exchanger. Desalination 94, 243–249 (1994).
Gamal Khedr, M. Radioactive contamination of groundwater, special aspects and advantages of removal by reverse osmosis and nanofiltration. Desalination 321, 47–54 (2013).
Majlesi, M., Mohseny, S. M., Sardar, M., Golmohammadi, S. & Sheikhmohammadi, A. Improvement of aqueous nitrate removal by using continuous electrocoagulation/electroflotation unit with vertical monopolar electrodes. Sustain. Environ. Res. 26, 287–290 (2016).
Sgroi, M., Vagliasindi, F. G. A., Snyder, S. A. & Roccaro, P. N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) and its precursors in water and wastewater: a review on formation and removal. Chemosphere 191, 685–703 (2018).
Yao, Y., Volchek, K., Brown, C. E., Robinson, A. & Obal, T. Comparative study on adsorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) by different adsorbents in water. Water Sci. Technol. 70, 1983–1991 (2014).
Levchuk, I., Bhatnagar, A. & Sillanpää, M. Overview of technologies for removal of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) from water. Sci. Total Environ. 476-477, 415–433 (2014).
Yue, X., Feng, S., Li, S., Jing, Y. & Shao, C. Bromopropyl functionalized silica nanofibers for effective removal of trace level dieldrin from water. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 406, 44–51 (2012).
Hassan, A. F., Elhadidy, H. & Abdel-Mohsen, A. M. Adsorption and photocatalytic detoxification of diazinon using iron and nanotitania modified activated carbons. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 75, 299–306 (2017).
Castro, C. S., Guerreiro, M. C., Gonçalves, M., Oliveira, L. C. A. & Anastácio, A. S. Activated carbon/iron oxide composites for the removal of atrazine from aqueous medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 609–614 (2009).
Calvo, L., Gilarranz, M. A., Casas, J. A., Mohedano, A. F. & Rodríguez, J. J. Hydrodechlorination of alachlor in water using Pd, Ni and Cu catalysts supported on activated carbon. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 78, 259–266 (2008).
Wang, H., Keller, A. & Li, F. Natural organic matter removal by adsorption onto carbonaceous nanoparticles and coagulation. J. Environ. Eng. 136, 1075 (2010).
Bellona, C., Drewes, J. E., Xu, P. & Amy, G. Factors affecting the rejection of organic solutes during NF/RO treatment—a literature review. Water Res. 38, 2795–2809 (2004).
Dolar, D., Košutić, K. & Vučić, B. RO/NF treatment of wastewater from fertilizer factory — removal of fluoride and phosphate. Desalination 265, 237–241 (2011).
Countertop Filter Replacement | AQ-4035 https://www.aquasana.com/replacement-drinking-water-filters/countertop-replacement-filter (2020).
Countertop Water Filters https://www.aquasana.com/countertop-water-filters (2020).
Lesimple, A., Ahmed, F. E. & Hilal, N. Remineralization of desalinated water: Methods and environmental impact. Desalination 496, 114692 (2020).
Longlast Filter https://www.brita.com/replacement-filters/longlast/ (2020).
Premium Water Bottle FAQs https://www.brita.com/water-bottle-support (2020).
iSpring CKC1 countertop water filter https://www.123filter.com/ac/countertop-portable-water-filter/ispring-ckc1-countertop-water-filter-white-housing-with-carbon (2020).
iSpring CKC2 High Output 2 Stage Countertop Water Filtration Dispenser System https://www.123filter.com/ac/countertop-portable-water-filter/ispring-ckc2-high-output-2-stage-countertop-water-filtration-dispenser-system--includes-activated-carbon-and-carbon-block-filters (2020).
Kinetico K5 Drinking Water Station https://www.kinetico.com/drinking-water-filtration-systems/kinetico-k5-drinking-water-station/ (2020).
AquaKinetic A200 Drinking Water System https://www.kinetico.com/drinking-water-filtration-systems/ (2020).
Countertop Drinking Filter System https://www.pelicanwater.com/drinking-filters/countertop-drinking-filter/ (2020).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for financial support for this study provided by Pacifica Water Solutions, the UCLA Samueli Engineering School, the UCLA Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, and the UCLA Sustainable LA Grand Challenge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.M.V.H. devised the project, the main conceptual ideas and proof outline of this review work. M.C., Z.F., and D.T. reviewed and drafted up the early manuscript. J.W. revised and improved the manuscript according to reviewers’ comments. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research, analysis, and manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Cao, M., Tong, D. et al. A critical review of point-of-use drinking water treatment in the United States. npj Clean Water 4, 40 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00128-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00128-z
This article is cited by
-
Safeguarding drinking water: A brief insight on characteristics, treatments and risk assessment of contamination
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2024)
-
Water woes: the institutional challenges in achieving SDG 6
Sustainable Earth Reviews (2023)
-
Boil water alerts and their impact on the unexcused absence rate in public schools in Jackson, Mississippi
Nature Water (2023)
-
Cationic cellulose filter papers modified with ZnO/Ag/GO nanocomposite as point of use gravity-driven filters for bacterial removal from water
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Smart micro- and nanorobots for water purification
Nature Reviews Bioengineering (2023)