Abstract
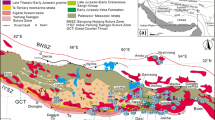
High-Mg andesites (HMAs) and their cognate intrusive rocks constitute volumetrically very small proportions of the total earth, and are mainly distributed along the edges of convergent plates. Petrogenetic studies can provide possible solutions for discrepancies in the geodynamics and subduction zone evolution. This paper presents the first ever reports of the newly discovered high-Mg diorite in Akechukesai area, the western part of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, and provides a reference for the evolutionary history and subduction mechanism of the Proto-Tethys Ocean. Akechukesai high-Mg diorites yielded a weighted mean zircon U-Pb dating age of 427.3 ± 2.3 Ma (Middle Silurian). Results of the geochemical analyses show that the high-Mg diorites were high-K calc-alkaline series with the SiO2 content ranging 50.40 to 55.41 wt%. They are characterized by high values of Mg# (67–77), high MgO (6.92–10.58 wt%), TiO2 (0.53–0.87 wt%), Cr (286–615 ppm), Ni (61–124 ppm), Ba (570–927 ppm) contents, and low FeOtotal/MgO ratios (0.54–0.89). Furthermore, they exhibit nearly flat right-declined rare-earth element (REE) patterns with slight LREE enrichment. The samples are enriched in large ion lithophile elements (e.g., Ba, Rb, and Th) and depleted in high field strength elements (e.g., Ta, Nb, and Ti). These geochemical features are analogous to the sanukitic high-Mg andesites. The mean value of the initial εHf(t) is −1.3, indicating that the source is enriched mantle. The values of Rb/Cs, Ba/La, and La/Sm ratios suggest that subducting sediments formed an important component of the magmatic source. The presence of water-bearing minerals such as amphibole and biotite indicate a water-rich and oxygen-rich primitive magma system. Petrogenetic analysis indicates that the Akechukesai high-Mg diorites probably formed by melts and aqueous fluids produced from partial melting of the subducting sediments interacting with mantle peridotites. We hypothesize that, after the closure of the Proto-Tethys Ocean Basin in the Middle Silurian, the deep subducted slab broke-off and formed a slab window, asthenospheric material upwelled heating the subducting sediments and causing them to melt. Thus, we suggest that the emplacement of the Akechukesai high-Mg diorites mark the commencement of post-collisional magmatism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amelin, Y., Lee, D.C., and Halliday, A.N., 2000, Early-middle Archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64, 4205–4225.
Andersen, T., 2002, Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192, 59–79.
Benoit, M., Aguillon-Robles, A., Calmus, T., Cotten, H., Bourgois, J., and Michaud, F., 2002, Geochemical diversity of late Miocene volcanism in southern Baja California, Mexico: implication of mantle and crustal sources during the opening of an asthenospheric window. The Journal of Geology, 110, 627–648.
Blichert-Toft, J. and Albarède, F., 1997, The Lu-Hf geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148, 243–258.
Chen, N.S., He, L., Sun, M., Wang, G.C., and Zhang, K.X., 2002, Constraint on the metamorphic peak stage and thrust structural deformation age of east Kunlun orogen in the early Paleozoic. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47, 628–631. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Coulon, C., Megartsi, M., Fourcade, S., Maury, R.C., Bellon, H.B., Louni-Hacini, A., Cotten, J., Coutelle, A., and Hermitte, D., 2002, Post-collisional transition from calc-alkaline to alkaline volcanism during the Neogene in Oranie (Algeria): magmatic expression of a slab breakoff. Lithos, 62, 87–110.
Crawford, A.J., Falloon, T.J., and Green, D.H., 1989, Classification, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of boninites. In: Crawford, A.J. (ed.), Boninites and Related Rocks. Unwin Hyman, London, p. 1–49.
Defant, M.J. and Drummond, M.S., 1990, Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347, 662–665.
Defant, M.J. and Kepezhinskas, P., 2001, Evidence suggests slab melting in arc magmas. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 82, 65–69.
Deng, J.F., Liu, C., Feng, Y.F., Xiao, Q.H., Su, S.G., Zhao, G.C., Kong, W.Q., and Cao, W.Y., 2010, High magnesian andesitic/dioritic rocks (HMA) and magnesian andesitic/dioritic rocks (MA): two igneous rock types related to oceanic subduction. Geology in China, 37, 1112–1118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Feng, J.Y., Pei, X.Z., Yu, S.L., Ding, S.P., Li, R.B., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y. F., Li, Z.C., Chen, Y.X., Zhang, X.F., and Chen, G.C., 2010, The discovery of the mafic-ultramafic melange in Kekesha area of Dulan county, east Kunlun region, and its LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age. Geology in China, 37, 28–38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gao, S., Rudnick, R.L., Yuan, H.L., Liu, X.M., Liu, Y.S., Xu, W.L., Ling, W.L., Ayers, J., Wang, X.C., and Wang, Q.H., 2004, Recycling lower continental crust in the north China craton. Nature, 432, 892–897.
Griffin, W.L., Wang, X., Jackson, S.E., Pearson, N.J., O’Reilly, S.Y., Xu, X.S., and Zhou, X.M., 2002, Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: in-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos, 61, 237–269.
Green, T.H., 1994, Experimental studies of trace-element partitioning applicable to igneous petrogenesis: Sedona 16 years later. Chemical Geology, 117, 1–36.
Guo, C.L., Chen, Y.C., Zeng, Z.L., and Lou, F.S., 2012, Petrogenesis of the Xihuashan granites in southeastern China: constraints from geochemistry and in-situ analysis of zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotopes. Lithos, 148, 209–227.
Hanyu, T., Tatsumi, Y., Nakai, S., Chang, Q., Miyazaki, T., Sato., K., Tani, K., Shibata, T., and Yoshida, T., 2006, Contribution of slab melting and slab dehydration to magmatism in the Japanese. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70, A229.
Hao, N., Yuan, W., Zhang, A., Feng, Y., Cao, J., Chen, X., Cheng, X.Q., and Mo, X.X., 2015, Evolution process of the late Silurian-late Devonian tectonic environment in Qimantagh in the western portion of East Kunlun, China: evidence from the geochronology and geochemistry of granitoids. Journal of Earth System Science, 124, 171–196.
Hart, S.R. and Reid, M.R., 1991, Re/Cs fractionation: a link between granulite metamorphism and the S-process. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55, 2379–2383.
He, D.F., Dong, Y.P., Liu, X.M., Yang, Z., Sun, S.S., Cheng, B., and Li, W., 2016, Tectono-thermal events in east Kunlun, northern Tibetan Plateau: evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology. Gondwana Research, 30, 179–190.
Heilimo, E., Halla, J., and Hölttä, P., 2010, Discrimination and origin of the sanukitoid series: geochemical constraints from the Neoarchean western Karelian Province (Finland). Lithos, 115, 27–39.
Hoskin, P.W.O. and Schaltegger, U., 2003, The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53, 27–62.
Kamei, A., Owada, M., Nagao, T., and Shiraki, K., 2004, High-Mg diorites derived from sanukitic HMA magmas, Kyushu Island, southwest Japan arc: evidence from clinopyroxene and whole rock compositions. Lithos, 75, 359–371.
Kay, R.W., 1978, Aleutian magnesian andesites: melts from subducted Pacific Ocean crust. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 4, 117–132.
Kong, H.L., Li, J.C., Li, Y.Z., Jia, Q.Z., Guo, X.Z., and Wang, Y., 2017, Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and its geological significance of the Halongxiuma pyroxene peridotite in east Kunlun, Qinghai province. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 36, 41–47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li, B.L., Zhi, Y.B., Zhang, L., Ding, Q.F., Xu, Q.L., Zhang, Y.J., Qian, Y., Wang, G., Peng, B., and Ao, C., 2015b, U-Pb dating, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd isotopic composition of a granodiorite porphyry from the Jiadanggen Cu-(Mo) deposit in the Eastern Kunlun metallogenic belt, Qinghai Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 67, 1–10.
Li, G.C., Feng, C.Y., Wang, R.J., Ma, S.C., Li, H.M., and Zhou, A.S., 2012, SIMS zircon U-Pb age, petrochemistry and tectonic implications of granitoids in northeastern Baiganhu W-Sn orefield, Xinjiang. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 33, 216–226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li, L., Sun, F.Y., Li, B.L., Li, S.J., Chen, G.J., Wang, W., Yan, J.M., Zhao, T.F., Dong, J., and Zhang, D.X., 2018, Geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of No. 1 complex from the Shitoukengde Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, western China: implications for the magmatic source, geodynamic setting and genesis. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 92, 106–126.
Li, W., Chen, J.L., Dong, Y.P., Xu, X.Y., Li, Z.P., Liu, X.M., and He, D.F., 2016, Early Paleozoic subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: zircon U-Pb geochronological and geochemical evidence from the Kalatag high-Mg andesites, East Tianshan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32, 505–521. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li, X.W., Huang, X.F., Luo, M.F., Dong, G.C., and Mo, X.X., 2015a, Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of the mid-Triassic lavas from east Kunlun, northern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 105, 32–47.
Li, Z.J., Li, C.W., Gao, Y.M., and Zeng, M., 2019, Geochronology and geochemistry characteristics of the late Mid-Jurassic (ca. 163 Ma) OIB-type diabase and high-Mg diorites in Shiquanhe ophiolite: products of early stage oceanic crust subduction? Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35, 816–832.
Liu, B., Ma, C.Q., Guo, P., Zhang, J.Y., Xiong, F.H., Huang, J., and Jiang, H.A., 2013, Discovery of the middle Devonian A-type granite from the eastern Kunlun orogen and its tectonic implications. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 38, 947–962. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu, B., Ma, C.Q., Zhang, J.Y., Xiong, F.H., Huang, J., and Jiang, H.A., 2012, Petrogenesis of early Devonian intrusive rocks in the east part of eastern Kunlun Orogen and implication for early Palaeozoic orogenic processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28, 1785–1807. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu, W.L., Huang, Q.T., Gu, M., Zhong, Y., Zhou, R.J., Gu, X.D., Zheng, H., Liu, J.N., Lu, X.X., and Xia, B., 2018, Origin and tectonic implications of the Shiquanhe high-Mg andesite, western Bangong suture, Tibet. Gondwana Research, 60, 1–14.
Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Gao, S., Günther, D., Xu, J., Gao, C.G., and Chen, H.H., 2008, In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257, 34–43.
Lu, S.N., 2002, Preliminary Study on Precambrian Geology of the Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 125 p. (in Chinese)
Ludwig, K.R., 2003, User’s manual for Isoplot 3.0: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication No. 4, Berkeley, 74 p.
Ma, X.H., Cao, R., Zhou, Z.H., and Zhu, W.P., 2015, Early Cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Yanji area, northeastern China: petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97, 393–405.
Mahéo, G., Guillot, S., Blichert-Toft, J., Rolland, Y., and Pêcher, A., 2002, A slab breakoff model for the Neogene thermal evolution of South Karakorum and South Tibet. Earth and Planetary Sciences Letters, 195, 45–58.
Meng, F.C., Cui, M.H., Wu, X.K., and Ren, Y.F., 2015, Heishan maficultramafic rocks in the Qimantage area of eastern Kunlun, NW China: remnants of an early Paleozoic incipient island arc. Gondwana Research, 27, 745–759.
Meng, F.C., Zhang, J.X., and Cui, M.H., 2013, Discovery of early Paleozoic eclogite from the East Kunlun, western China and its tectonic significance. Gondwana Research, 23, 825–836.
Mo, X.X., Luo, Z.H., Deng, J.F., Yu, X.H., Liu, C.D., Kan, H.W., Yuan, W.M., and Liu, Y.H., 2007, Granitoids and crustal growth in the East Kunlun orogenic belt. Geological Journal of China University, 13, 403–414. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Müntener, O., Kelemen, P.B., and Grove, T.L., 2001, The role of H2O during crystallization of primitive arc magmas under uppermost mantle conditions and genesis of igneous pyroxenites: an experimental study. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 141, 643–658.
Pan, G.T., Wang, L.Q., Li, R.S., Yuan S.H., Ji, W.H., Yin, F.G., Zhang, W.P., and Wang, B.D., 2012, Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 53, 3–14.
Peng, B., Sun, F.Y., Li, B.L., Wang, G., Li, S.J., Zhao, T.F., Li, L., and Zhi, Y.B., 2016, The geochemistry and geochronology of the Xiarihamu II mafic-ultramafic complex, eastern Kunlun, Qinghai province, China: implications for the genesis of magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 73, 13–28.
Rogers, G., Saunders, A.D., Terrell, D.J., Verma, S.P., and Marriner, G.F., 1985, Geochemistry of Holocene volcanic rocks associated with ridge subduction in Baja California, Mexico. Nature, 315, 389–392.
Rudnick, R.L., Gao, S., Ling, W.L., Liu, Y.S., and McDonough, W.F., 2004, Petrology and geochemistry of spinel peridotite xenoliths from Hannuoba and Qixia, North China Craton. Lithos, 77, 609–637.
Shimoda, G., Tatsumi, Y., Nohda, S., Ishizaka, K., and Jahn, B.M., 1998, Setouchi high-Mg andesites revisited: geochemical evidence for melting of subducting sediments. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 160, 479–492.
Smithies, R.H. and Champion, D.C., 2000, The Archaean high-Mg diorite suite: links to tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite magmatism and implications for early Archaean crustal growth. Journal of Petrology, 41, 1653–1671.
Stern, R.A. and Hanson, G.N., 1991, Archean high-Mg granodiorite: a derivative of light rare earth element-enriched monzodiorite of mantle origin. Journal of Petrology, 32, 201–238.
Straub, S.M., Gomez-Tuena, A., Stuart, F.M., Zellmer, G.F., Espinasa-Perena, R., Cai, Y., and Iizuka, Y., 2011, Formation of hybrid arc andesites beneath thick continental crust. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 303, 337–347.
Sun, F.Y., Chen, G.H., and Chi, Q.G., 2003, Report of metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction comprehensive study in Xinjiang-East Kunlun metallogenic belt, China. Geological Survey Institute of Jilin University, Changchun, 247 p. (in Chinese)
Sun, F.Y., Li, B.L., Ding, Q.F., Zhao, J.W., Pan, T., Yu, X.F., Wang, L., Chen, G.J., and Ding, Z.J., 2009, Research on the key problems of ore prospecting in the eastern Kunlun metallogenic belt, China. Geological Survey Institute of Jilin University, Changchun, 258 p. (in Chinese)
Sun, S.S. and McDonough, W.F., 1989, Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders, A.D. and Norry, M.J. (eds.), Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42, p. 313–345.
Tang, G.J. and Wang, Q., 2010, High-Mg andesites and their geodynamic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26, 2495–2512. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tatsumi, Y., 2001, Geochemical modeling of partial melting of subconducting sediments and subsequent melt-mantle. Geology, 29, 323.
Tatsumi, Y., 2006, High-Mg andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, southwestern Japan: analogy to Archean magmatism and continental crust formation? Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 34, 467–499.
Tatsumi, Y. and Hanyu, T., 2003, Geochemical modeling of dehydration and partial melting of subducting lithosphere: toward a comprehensive understanding of high-Mg andesite formation in the Setouchi volcanic belt, SW Japan. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4, 1081.
Taylor, S.R. and Mclennan, S.M., 1995, The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33, 241–265.
Van De Zadde, D.M.A. and Wortle, M.J.R., 2001, Shallow slab detachment as a transient source of heat at midlithospheric depths. Tectonics, 20, 868–882.
Van Hunen, J. and Allen, M.B., 2011, Continental collision and slab break-off: a comparison of 3-D numerical models with observations. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 302, 27–37.
Vervoort, J.D., Pachelt, P.J., Gehrels, G.E., and Nutman, A.P., 1996, Constraints on early earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes. Nature, 379, 624–627.
Von, B.F. and Davis, J.H., 1995, Slab breakoff: a model for syncollisional magmatism and tectonics in the Alps. Tectonics, 14, 120–131.
Wang, G., Sun, F.Y., Li, B.L., Li, S.J., Zhao, J.W., and Yang, Q.A., 2014, Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of diorite in Xiarihamu ore district from East Kunlun, and its geological significance. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44, 876–891. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wood, B.J. and Turne, S.P., 2009, Origin of primitive high-Mg andesite: constraints from natural examples and experiments. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 283, 59–66.
Wu, F.Y., Li, X.H., Zheng, Y.F., and Gao, S., 2007, Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23, 185–220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu, F.Y., Yang, Y.H., Xie, L.W., Yang, J.H., and Xu, P., 2006, Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234, 105–126.
Xiao, X.C. and Li, T.D., 2000, Tectonic Evolution and Uplift of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Guandong Science & Technology Press, Guangzhou, 313 p. (in Chinese)
Xin, W., Sun, F.Y., Li, L., Yan, J.M., Zhang, Y.T., Wang, Y.C., Shen, T.S., and Yang, Y.J., 2018, The Wulonggou metaluminous A2-type granites in the eastern Kunlun orogenic belt, NW China: rejuvenation of subduction-related felsic crust and implications for post-collision extension. Lithos, 312–313, 108–127.
Xiong, F.H., Ma, C.Q., Wu, L., Jiang, H.A., and Liu, B., 2015, Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of an Ordovician appinitic pluton in the east Kunlun orogeny: new evidence for Proto-Tethyan subduction. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111, 681–697.
Xu, Y.G., 2002, Mantle plumes, large igneous provinces and their geologic consequences. Earth Science Frontiers, 9, 341–353. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu, Z.Q., Yang, J.S., Li, H.B., Zhang, J.X., and Wu, C.L., 2007, Terrane Amalgamation, Collision and Uplift in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 458 p. (in Chinese)
Yan, J.M., Sun, F.Y., Li, L., Yang, Y.Q., and Zhang, D.X., 2018, A slab break-off model for mafic-ultramafic igneous complexes in the east Kunlun orogenic belt, northern Tibet: insights from early Palaeozoic accretion related to post-collisional magmatism. International Geology Review, 61, 1171–1188.
Yan, J.M., Sun, F.Y., Qian, Y., Li, L., Zhang, Y.S., and Yang, Z.P., 2019, Geochemistry, geochronology, and Hf-S-Pb isotopes of the Akechukesai IV mafic-ultramafic complex, western China. Minerals, 9, 275–294.
Yang, J.S., Xu, Z.Q., Ma, C.Q., Zhang, J.X., Wang, Z.Q., Wang, G.C., Zhang, H.F., Dong, Y.P., and Lai, S.C., 2010, Compound orogeny and scientific problems concerning the central orogenic belt of China. Geology in China, 37, 1–11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yogodzinski, G.M., Lees, J.M., Churikova, T.G., Dorendorf, F., Werner, G.W., and Volynets, O.N., 2001, Geochemical evidence for the melting of subducting oceanic lithosphere at plate edges. Nature, 409, 500–504.
Yuan, H.L., Gao, S., Liu, X.M., Li, H.M., Günther, D., and Wu, F.Y., 2004, Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28, 353–370.
Yuan, L.Y., Zhang, X.H., Xue, F.H., Liu, Y.H., and Zong, K.Q., 2016, Late Permian high-Mg andesite and basalt association from northern Liaoning, North China: insights into the final closure of the Paleo-Asian ocean and the orogeny-craton boundary. Lithos, 258–259, 58–76.
Zhang, Q., Qian, Q., Zhai, M.G., Jin, W.J., Wang, Y., Jian, P., and Wang, Y.L., 2005, Geochemistry, petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of sanukite. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2, 117–125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Qian, Q., Zhai, M.G., Jin, W.J., Wang, Y.L., and Jian, P., 2004, Sanukite of late Archaean and early Earth evolution. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20, 1355–1362. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng, Z., Chen, Y.J., Deng, X.H., Yue, S.W., Chen, H.J., and Wang, Q.F., 2018, Origin of the Bashierxi monzogranite, Qimantage, east Kunlun orogen, NW China: a magmatic response to the evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean. Lithos, 296–299, 181–194.
Zhuan, S.P., Chen, C., Shen, Z.Y., Pan, Z.L., Zhang, Y.Q., Zhao, H.P., Chen, H.Q., Y.R., and X, D., 2018, Early Paleozoic subduction of the ocean in Beishan region: zircon U-Pb geochronogical and geochemical evidence from the high-Mg diorite in the Shibanjing area. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 37, 533–546. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to Geosciences Journal for his patience and tolerance providing us the revision chance and the reviewers for their careful opinions. This manuscript was funded by Geological Survey Project (20201163) of China Geological Survey, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41402060). We thank the staff of the Yanduzhongshi Geological Analysis Laboratories Ltd., for their advice and assistance during zircon U-Pb dating. Thank Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China for Lu-Hfisotope analyses. We also thank the Key Laboratory of Mineral Resources Evaluation in Northeast Asia, for assistance in analyses of major and trace elements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Sun, F., Liu, D. et al. Discovery of the Early Paleozoic Akechukesai high-Mg diorites in the western segment of East Kunlun Orogenic Belt and its constraints on the mechanism of break-off from Proto-Tethys oceanic subducted slab. Geosci J 26, 1–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-021-0016-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-021-0016-4