Abstract
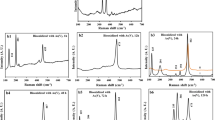
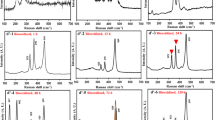
Understanding bacterial adsorption and the evolution of biofilms on arsenopyrite with different surface structures is of great significance to clarifying the mechanism of microbe-mineral interfacial interactions and the production of acidic mine drainage impacting the environment. In this study, the attachment of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans cells and subsequent biofilm formation on arsenopyrite with different surface structures in the presence of dissolved As(III) was studied. Arsenopyrite slices with a specific surface were obtained by electrochemical corrosion at 0.26 V. The scanning electronic microscopy-energy dispersion spectra analyses indicated that the arsenopyrite surface deficient in sulfur and iron obtained by electrochemical treatment was not favorable for the initial adsorption of bacteria, and the addition of As(III) inhibited the adsorption of microbial cells. Epifluorescence microscopy showed that the number of cells attaching to the arsenopyrite surface increased with time; however, biofilm formation was delayed significantly when As(III) was added.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.L. Corkhill and D.J. Vaughan, Arsenopyrite oxidation—A review, Appl. Geochem., 24(2009), No. 12, p. 2342.
D.M. Miller and G.S. Hansford, Batch biooxidation of a gold-bearing pyrite-arsenopyrite concentrate, Miner. Eng., 5(1992), No. 6, p. 613.
F. Espiell, A. Roca, M. Cruells, and C. Núñez, Gold and silver recovery by cyanidation of arsenopyrite ore, Hydrometallurgy, 16(1986), No. 2, p. 141.
H.R. Watling, The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—A review, Hydrometallurgy, 84(2006), No. 1–2, p. 81.
S.F. Wang, B.B. Jiao, M.M. Zhang, G.Q. Zhang, X. Wang, and Y.F. Jia, Arsenic release and speciation during the oxidative dissolution of arsenopyrite by O2 in the absence and presence of EDTA, J. Hazard. Mater., 346(2018), p. 184.
J.S. Liu, Z.H. Wang, M.M. Gen, and G.Z. Qiu, Progress in the study of polyphase interfacial interactions between microorganism and mineral in bio-hydrometallurgy, Min. Metall. Eng., 26(2006), No. 1, p. 40.
W.B. Ling, L. Wang, H.C. Liu, Z.Y. Nie, Y. Yang, Y. Yang, C.Y. Ma, L. Zheng, Y.D. Zhao, and J.L. Xia, The evidence of decisive effect of both surface microstructure and speciation of chalcopyrite on attachment behaviors of extreme thermoacidophile sulfolobus metallicus, Minerals, 8(2018), No. 4, art. No. 159.
G. Vander Voort, Color metallography, Microsc. Microanal., 10(2004), No. S02, p. 70.
R.Y. Zhang, T.R. Neu, S. Bellenberg, U. Kuhlicke, W. Sand, and M. Vera, Use of lectins to in situ visualize glycoconjugates of extracellular polymeric substances in acidophilic archaeal biofilms, Microb. Biotechnol., 8(2015), No. 3, p. 448.
M. Vera, A. Schippers, and W. Sand, Progress in bioleaching: Fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation—part A, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 97(2013), No. 17, p. 7529.
J.L. Xia, H.R. Zhu, L. Wang, H.C. Liu, Z.Y. Nie, Y.D. Zhao, C.Y. Ma, C.H. Hong, and X.J. Zhen, In situ characterization of relevance of surface microstructure and electrochemical properties of chalcopyrite to adsorption of Acidianus manzaensis, Adv. Mater. Res., 1130(2015), p. 183.
D.W. Price and G.W. Warren, The influence of silver ion on the electrochemical response of chalcopyrite and other mineral sulfide electrodes in sulfuric acid, Hydrometallurgy, 15(1986), No. 3, p. 303.
W. Sand, T. Gehrke, P.G. Jozsa, and A. Schippers, (Bio)hemistry of bacterial leaching—direct vs. indirect bioleaching, Hydrometallurgy, 59(2001), No. 2–3, p. 159.
R.H. Lara, J.V. García-Meza, I. González, and R. Cruz, Influence of the surface speciation on biofilm attachment to chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Appl. Microbiol. Bio-technol., 97(2013), No. 6, p. 2711.
R.H. Lara, D. Valdez-Pérez, A.G. Rodríguez, H.R. Navarro-Contreras, R. Cruz, and J.V. García-Meza, Interfacial insights of pyrite colonized by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans cells under acidic conditions, Hydrometallurgy, 103(2010), No. 1–4, p. 35.
H. Ramírez-Aldaba, J. Vázquez-Arenas, F.S. Sosa-Rodríguez, D. Valdez-Pérez, E. Ruiz-Baca, G. Trejo-Córdoba, M.A. Escobedo-Bretado, L. Lartundo-Rojas, P. Ponce-Peña, and R.H. Lara, Changes in biooxidation mechanism and transient biofilm characteristics by As(V) during arsenopyrite colonization with Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 45(2018), No. 8, p. 669.
N. Yee, J.B. Fein, and C.J. Daughney, Experimental study of the pH. ionic strength.and reversibility behavior of bacteria-mineral adsorption, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 64(2000), No. 4, p. 609.
S. Koechler, J. Farasin, J. Cleiss-Arnold, and F. Arsène-Ploetze, Toxic metal resistance in biofilms: Diversity of microbial responses and their evolution, Res. Microbiol., 166(2015), No. 10, p. 764.
J.J. Harrison, H. Ceri, C.A. Stremick, and R.J. Turner, Biofilm susceptibility to metal toxicity, Environ. Microbiol., 6(2004), No. 12, p. 1220.
R.J. Ram, N.C. Verberkmoes, M.P. Thelen, G.W. Tyson, B.J. Baker, R.C. Blake, M. Shah, R.L. Hettich, and J.F. Banfield, Community proteomics of a natural microbial biofilm, Science, 308(2005), No. 5730, p. 1915.
Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, Is arsenic biotransformation a detoxification mechanism for microorganisms?, Aquat. Toxicol., 146(2014), p. 212.
H.C. Liu, Study on the Interfacial Interactions Between Bioleaching Microorganisms and Sulfur-Containing Substrates and Their Molecular Mechanism [Dissertation], Central South University, Changsha, 2016, p. 82.
D.R. Zhang, J.L. Xia, Z.Y. Nie, H.R. Chen, H.C. Liu, Y. Deng, Y.D. Zhao, L.L. Zhang, W. Wen, and H.Y. Yang, Mechanism by which ferric iron promotes the bioleaching of arsenopyrite by the moderate thermophile Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, Process. Biochem., 81(2019), p. 11.
D.R. Zhang, H.R. Chen, J.L. Xia, Z.Y. Nie, X.L. Fan, H.C. Liu, L. Zheng, L.J. Zhang, and H.Y. Yang, Humic acid promotes arsenopyrite bio-oxidation and arsenic immobilization, J. Hazard. Mater., 384(2020), art. No. 121359.
Q. Li, R.Y. Zhang, B.A. Krok, M. Vera, and W. Sand, Biofilm formation of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans on pyrite in the presence of Leptospirillum ferriphilum, Adv. Mater. Res., 1130(2015), p. 141.
T.Y. Gu, S.O. Rastegar, S.M. Mousavi, M. Li, and M.H. Zhou, Advances in bioleaching for recovery of metals and bioremediation of fuel ash and sewage sludge, Bioresour. Technol., 261(2018), p. 428.
K.O. Stetter, A. Segerer, W. Zillig, G. Huber, G. Fiala, R. Huber, and H. König, Extremely thermophilic sulfur-metabolizing archaebacteria, Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 7(1986), No. 2–3, p. 393.
K. Bosecker, Bioleaching: metal solubilization by microorganisms, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 20(1997), No. 3–4, p. 591.
C.L. Liang, J.L. Xia, Y. Yang, Z.Y. Nie, X.J. Zhao, L. Zheng, C.Y. Ma, and Y.D. Zhao, Characterization of the thermo-reduction process of chalcopyrite at 65°C by cyclic voltammetry and XANES spectroscopy, Hydrometallurgy, 107(2011), No. 1–2, p. 13.
C. Castro, R.Y. Zhang, J. Liu, S. Bellenberg, T.R. Neu, E. Donati, W. Sand, and M. Vera, Biofilm formation and interspecies interactions in mixed cultures of thermo-acidophilic archaea Acidianus spand Sulfolobus metallicus, Res. Microbiol., 167(2016), No. 7, p. 604.
A. Koerdt, J. Gödeke, J. Berger, K.M. Thormann, and S.V. Albers, Crenarchaeal biofilm formation under extreme conditions, PLoS One, 5(2010), No. 11, art. No. e14104.
C.J. de Africa, R.P. van Hille, W. Sand, and S.T.L. Harrison, Investigation and in situ visualisation of interfacial interactions of thermophilic microorganisms with metal-sulphides in a simulated heap environment, Miner. Eng., 48(2013), p. 100.
J.L. Xia, Y. Yang, H. He, C.L. Liang, X.J. Zhao, L. Zheng, C.Y. Ma, Y.D. Zhao, Z.Y. Nie, and G.Z. Qiu, Investigation of the sulfur speciation during chalcopyrite leaching by moderate thermophile Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, Int. J. Miner. Process., 94(2010), No. 1–2, p. 52.
A. Ide-Ektessabi, T. Kawakami, and F. Watt, Distribution and chemical state analysis of iron in the Parkinsonian substantia nigra using synchrotron radiation micro beams, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 213(2004), p. 590.
B. Ravel and M. Newville, Athena, Artemis, Hephaestus: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT, J. Synchrotron Radiat., 12(2005), No. 4, p. 537.
N. Noël, B. Florian, and W. Sand, AFM & EFM study on attachment of acidophilic leaching organisms, Hydrometallurgy, 104(2010), No. 3–4, p. 370.
R.Y. Zhang, M. Vera, S. Bellenberg, and W. Sand, Attachment to minerals and biofilm development of extremely acidophilic archaea, Adv. Mater. Res., 825(2013), p. 103.
M.G.M. Fernandez, C. Mustin, P. de Donato, O. Barres, P. Marion, and J. Berthelin, Occurrences at mineral-bacteria interface during oxidation of arsenopyrite by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 46(1995), No. 1, p. 13.
R.M. Donlan, Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces, Emerg. Infect. Dis., 8(2002), No. 9, p. 881.
A. Echeverría-Vega and C. Demergasso, Copper resistance, motility and the mineral dissolution behavior were assessed as novel factors involved in bacterial adhesion in bioleaching, Hydrometallurgy, 157(2015), p. 107.
H. Ramírez-Aldaba, O.P. Valles, J. Vazquez-Arenas, J.A. Rojas-Contreras, D. Valdez-Pérez, E. Ruiz-Baca, M. Meraz-Rodríguez, F.S. Sosa-Rodríguez, Á.G. Rodríguez, and R.H. Lara, Chemical and surface analysis during evolution of arsenopyrite oxidation by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in the presence and absence of supplementary arsenic, Sci. Total Environ., 566–567(2016), p. 1106.
F.F. Leng, K.Y. Li, X.X. Zhang, Y.Q. Li, Y. Zhu, J.F. Lu, and H.Y. Li, Comparative study of inorganic arsenic resistance of several strains of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Hydrometallurgy, 98(2009), No. 3–4, p. 235.
J. Jin, S.Y. Shi, G.L. Liu, Q.H. Zhang, and W. Cong, Arsenopyrite bioleaching by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in a rotating-drum reactor, Miner. Eng., 39(2012), p. 19.
R.Y. Zhang, S. Bellenberg, L. Castro, T.R. Neu, W. Sand, and M. Vera, Colonization and biofilm formation of the extremely acidophilic archaeon Ferroplasma acidiphilum, Hydrometallurgy, 150(2014), p. 245.
S.R. Dave, K.H. Gupta, and D.R. Tipre, Characterization of arsenic resistant and arsenopyrite oxidizing Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans from Hutti gold leachate and effluents, Bioresour. Technol., 99(2008), No. 16, p. 7514.
K.B. Hallberg, H.M. Sehlin, and E.B. Lindström, Toxicity of arsenic during high temperature bioleaching of gold-bearing arsenical pyrite, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 45(1996), No. 1–2, p. 212.
B. Escobar, E. Huenupi, I. Godoy, and J.V. Wiertz, Arsenic precipitation in the bioleaching of enargite by Sulfolobus BC at 70°C, Biotechnol. Lett., 22(2000), No. 3, p. 205.
C.Y. Jia, D.Z. Wei, W.G. Liu, C. Han, S.L. Gao, and Y.J. Wang, Selective adsorption of bacteria on sulfide minerals surface, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 18(2008), No. 5, p. 1247.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51774342, 41802038, U1608254, 51861135305, and 41830318) and Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility Public User Program (2018-BEPC-PT-002240).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Z., Nie, Zy., Liu, Hc. et al. Effect of the surface microstructure of arsenopyrite on the attachment of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans in the presence of dissolved As(III). Int J Miner Metall Mater 28, 1135–1144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2231-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2231-9