Abstract
Background
We evaluated the dynamics of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) and ammonia estimation in acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) patients due to a paucity of evidence.
Methods
ACLF patients recruited from the APASL-ACLF Research Consortium (AARC) were followed up till 30 days, death or transplantation, whichever earlier. Clinical details, including dynamic grades of HE and laboratory data, including ammonia levels, were serially noted.
Results
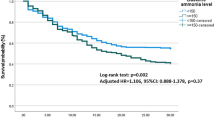
Of the 3009 ACLF patients, 1315 (43.7%) had HE at presentation; grades I–II in 981 (74.6%) and grades III–IV in 334 (25.4%) patients. The independent predictors of HE at baseline were higher age, systemic inflammatory response, elevated ammonia levels, serum protein, sepsis and MELD score (p < 0.05; each). The progressive course of HE was noted in 10.0% of patients without HE and 8.2% of patients with HE at baseline, respectively. Independent predictors of progressive course of HE were AARC score (≥ 9) and ammonia levels (≥ 85 μmol/L) (p < 0.05; each) at baseline. A final grade of HE was achieved within 7 days in 70% of patients and those with final grades III–IV had the worst survival (8.9%). Ammonia levels were a significant predictor of HE occurrence, higher HE grades and 30-day mortality (p < 0.05; each). The dynamic increase in the ammonia levels over 7 days could predict nonsurvivors and progression of HE (p < 0.05; each). Ammonia, HE grade, SIRS, bilirubin, INR, creatinine, lactate and age were the independent predictors of 30-day mortality in ACLF patients.
Conclusions
HE in ACLF is common and is associated with systemic inflammation, poor liver functions and high disease severity. Ammonia levels are associated with the presence, severity, progression of HE and mortality in ACLF patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- ACLF:
-
Acute-on-chronic liver failure
- EASL:
-
European Association for the Study of the Liver
- APASL:
-
Asian Pacific Association for the Study of Liver
- DC:
-
Decompensated cirrhosis
- ALF:
-
Acute liver failure
- ICU:
-
Intensive Care Unit
- AARC:
-
APASL ACLF Research Consortium
- HVPG:
-
Hepatic venous pressure gradient
- CTP:
-
Child-Turcotte-Pugh score
- MELD:
-
Model for endstage liver disease
- MELD-Na:
-
MELD-sodium
- SOFA:
-
Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score
- APACHE-II:
-
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation-II
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- AUROC:
-
Area under receiver operating curve
- SIRS:
-
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- SHR:
-
Sub-distribution hazard ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
References
Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy–definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 2002;35:716–721
Hirode G, Vittinghoff E, Wong RJ. Increasing burden of hepatic encephalopathy among hospitalized adults: an analysis of the 2010–2014 National Inpatient Sample. Dig Dis Sci 2019;64:1448–1457
Tapper EB, Finkelstein D, Mittleman MA, Piatkowski G, Chang M, Lai M. A quality improvement initiative reduces 30-day rate of readmission for patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;14:753–759
Di Pascoli M, Ceranto E, De Nardi P, Donato D, Gatta A, Angeli P, et al. Hospitalizations due to cirrhosis: clinical aspects in a large cohort of italian patients and cost analysis report. Dig Dis 2017;35:433–438
Romero-Gómez M, Montagnese S, Jalan R. Hepatic encephalopathy in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol 2015;62:437–447
Rose CF, Amodio P, Bajaj JS, Dhiman RK, Montagnese S, Taylor-Robinson SD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy: novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J Hepatol 2020;73:1526–1547
Stepanova M, Mishra A, Venkatesan C, Younossi ZM. In-hospital mortality and economic burden associated with hepatic encephalopathy in the United States from 2005 to 2009. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;10:1034.e1031–1041.e1031
Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, Pavesi M, Angeli P, Cordoba J, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013;144(1426–1437):1437.e1421–1429.e1421
Sarin SK, Choudhury A, Sharma MK, Maiwall R, Al Mahtab M, Rahman S, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver (APASL): an update. Hepatol Int 2019;13:353–390
Cordoba J, Ventura-Cots M, Simón-Talero M, Amorós À, Pavesi M, Vilstrup H, et al. Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). J Hepatol 2014;60:275–281
Sawhney R, Holland-Fischer P, Rosselli M, Mookerjee RP, Agarwal B, Jalan R. Role of ammonia, inflammation, and cerebral oxygenation in brain dysfunction of acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Liver Transpl 2016;22:732–742
Lee G-H. Hepatic encephalopathy in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol Int 2015;9:520–526
Choudhury A, Jindal A, Maiwall R, Sharma MK, Sharma BC, Pamecha V, et al. Liver failure determines the outcome in patients of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF): comparison of APASL ACLF research consortium (AARC) and CLIF-SOFA models. Hepatol Int 2017;11:461–471
Nicolao F, Efrati C, Masini A, Merli M, Attili AF, Riggio O. Role of determination of partial pressure of ammonia in cirrhotic patients with and without hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2003;38:441–446
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 2014;60:715–735
Shalimar, Sheikh MF, Mookerjee RP, Agarwal B, Acharya SK, Jalan R. Prognostic role of ammonia in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019;70(3):982–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30534
Cordoba J, Ventura-Cots M, Simon-Talero M, Amoros A, Pavesi M, Vilstrup H, et al. Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). J Hepatol 2014;60:275–281
Goh ET, Stokes CS, Sidhu SS, Vilstrup H, Gluud LL, Morgan MY. l-Ornithine l-aspartate for prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2018;5:Cd012410
Gupta T, Dhiman RK, Ahuja CK, Agrawal S, Chopra M, Kalra N, et al. Characterization of cerebral edema in acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2017;7:190–197
Aldridge DR, Tranah EJ, Shawcross DL. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: role of ammonia and systemic inflammation. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2015;5:S7–S20
Bhatia V, Singh R, Acharya SK. Predictive value of arterial ammonia for complications and outcome in acute liver failure. Gut 2006;55:98–104
Haj M, Rockey DC. Ammonia levels do not guide clinical management of patients with hepatic encephalopathy caused by cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2020;115:723–728
Tan EX, Wang MX, Pang J, Lee GH. Plasma exchange in patients with acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure: a systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:219–245
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (Institutional and National) and with the Declaration of Helsinki 1975, as revised in 2008. The AARC registry for ACLF was approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Board at the nodal center, i.e., ILBS New Delhi (vide letter no F/25/5/64/AC2013/912) and all the participating centres also had necessary approval from the respective ethical board.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants or legally acceptable representatives of the participant included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, N., Dhiman, R.K., Choudhury, A. et al. Dynamic assessments of hepatic encephalopathy and ammonia levels predict mortality in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol Int 15, 970–982 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10221-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-021-10221-7