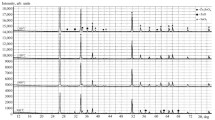
The effect of the anionic composition of zinc salts in interaction with tin (IV) chloride on the preparation of zinc orthostannate by the sol-gel method was investigated. It was determined that the minimum temperature for the synthesis of zinc orthostannate is 1000°C. It was brought to light that on the use of tetraamminezinc chloride is formed, which decomposes on firing.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Hereinafter, unless otherwise stated, the weight content, %.
References
A. Sivapunniyam, N. Wiromrat, M. T. Z. Myint, and J. Dutta, “High-performance liquefied petroleum gas sensing based on nanostructures of zinc oxide and zinc stannate,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 157(1), 232 – 239 (2011).
S. Rama, Y. Avadhesh Kumar, and G. Chandkiram, “Synthesis and humidity sensing investigations of nanostructured ZnSnO3,” J. Sensor Technol., 1, 116 – 124 (2011).
F. Lu and Q. Liu, “Structure and optical band gap of inverse spinel Zn2SnO4 epitaxial films,” J. Low Temp. Phys., 200, 142 – 151 (2020).
S. A. Belousov, A. A. Nosov, S. I. Rembeza, and N. N. Kosheleva, “Synthesis and electrophysical properties of gas-sensitive films of Zn2SnO4,” Izv. YuFU, Tekh. Nauki, No. 10, 19 – 27 (2016).
J. Dou, X. Li, Y. Li, et al., “Fabrication of Zn2SnO4 microspheres with controllable shell numbers for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells,” Solar Energy, 181, 424 – 429 (2019).
Y. C. Chen and Y. R. Shen, “Growth and dielectric characterizations of zinc stannate thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering,” Integrated Ferroelectrics, 192(1), 80 – 87 (2018).
M. Tai, X. Zhao, H. Shen, et al., “Ultrathin Zn2SnO4 (ZTO) passivated ZnO nanocone arrays for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells,” Chem. Eng. J., 361, 60 – 66 (2019).
D.W. Kim, S. S. Shin, I. S. Cho, et al., “Synthesis and photovoltaic property of fine and uniform Zn2SnO4 nanoparticles,” Nanoscale, 4(2), 557 – 562 (2012).
M. V. Nikolić, T. Ivetić, K. M. Paraskevopoulos, et al., “Far infrared reflection spectroscopy of Zn2SnO4 ceramics obtained by sintering mechanically activated ZnO–SnO2 powder mixtures,” J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 27(13 – 15), 3727 – 3730 (2007).
C. K. Govindappa, V. T. Venkatarangaiah, and S. B. Abd Hamid, “Electrochemical generation of cubic shaped nano Zn2SnO4 photocatalysts,” Nano-Micro Lett., 5(2), 101 – 110 (2013).
M. Peiteado, Y. Iglesias, J. De Frutos, et al., “Preparation of ZnO–SnO2 ceramic materials by a coprecipitation method,” Boletin de la Sociedad Espanola de Ceramica y Vidrio, 45(3), 158 – 162 (2006).
A. V. Sidorak, A. A. Shubin, V. V. Ivanov, and N. S. Nikolaeva, “Synthesis of Zn2SnO4 powders by heat treatment of coprecipitated compounds,” Zh. SFU, Khimiya, 4(3), 285 – 293 (2011).
Abdel Gawad Safaa Ramadan Mahmoud, Cordierite Ceramic from Powders Obtained by the Sol-Gel Method, Author’s Abstract of Candidate’s Thesis [in Russian], RKhTU im. D. I. Mendeleeva, Moscow (2006).
P. P. Faikov, Synthesis and Sintering of Powders in the MgO – Al2O3 System Obtained by the Sol-Gel Method, Author’s Abstract of Candidate’s Thesis [in Russian], RKhTU im. D. I. Mendeleeva, Moscow (2007).
A. C. Vlasov and L. I. Krainova, “The use of sol-gel processes in ceramic technology,” Tr. RKhTU im. D. I. Mendeleeva, No. 153, 110 – 115 (1988).
N. T. Andrianov, “Sol-gel method in oxide material technology,” Glass Ceram., 60(10), 320 – 325 (2003) [Steklo Keram., No. 10, 17 – 22 (2003)].
T. Bora, M. H. Al-Hinai, A. T. Al-Hinai, and J. Dutta, “Phase transformation of metastable ZnSnO3 upon thermal decomposition by in-situ temperature-dependent Raman spectroscopy,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 98, 4044 – 4049 (2015).
A. V. Belyakov, “The effect of a difference in the diffusivity of cations on the deviation from stoichiometry in complex oxides,” Glass Ceram., 54(10), 317 – 319 (1997) [Steklo Keram., No. 10, 18 – 20 (1997)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 4, pp. 20 – 25, April, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anisimov, V.V., Saprykin, A.V., Artemkina, I.M. et al. Influence of the Anionic Composition of Initial Salts on Obtaining Zinc Orthostannate by the Sol-Gel Method. Glass Ceram 78, 148–152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00366-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-021-00366-0