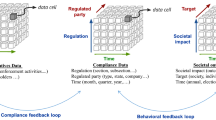
Abstract
Businesses are getting increasingly regulated. Regulatory compliance is a board level concern and one of the top-3 CEO level concerns across business verticals. Failure to comply leads not only to heavy fines but reputational risk too. Current practice of regulatory compliance is document-centric, and therefore, heavily reliant on human experts. Given the large size of modern enterprises, their multi-geography operation, increasing dynamics, and frequent changes in regulations, the current practice of regulatory compliance is found wanting on correctness, responsiveness, and scale. Introduction of appropriate technology seems necessary to overcome these challenges. In this paper, we present an AI-aided model-driven automated approach to regulatory compliance and supporting technology infrastructure. We describe how the approach has fared in real-world industry-scale context and outline future work.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Sergot MJ, Sadri F, Kowalski RA, Kriwaczek F, Hammond P, Cory HT (1986) The British nationality act as a logic program. Commun ACM 29(5):370–386
Antoniou G, Dimaresis N, Governatori G (2007). A system for modal and deontic defeasible reasoning. In AI 2007: Advances in artificial intelligence, 20th Australian joint conference on artificial intelligence, Gold Coast, Australia, December 2–6, 2007, proceedings
Kerrigan S, Law KH (2003). Logic-based regulation compliance-assistance. In Proceedings of the 9th international conference on artificial intelligence and law, ICAIL 2003, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK, June 24–28, 2003. pp. 126–135
Zeni N, Kiyavitskaya N, Mich NL, Cordy JR, Mylopoulos J (2015) GaiusT: supporting the extraction of rights and obligations for regulatory compliance. Requir Eng 20(1):1–22
Sagar S, Kholkar D, Kulkarni V (2016) Informed active learning to aid domain experts in modeling compliance. In: 2016 IEEE 20th international enterprise distributed object computing conference (EDOC). IEEE
Sagar S, Kholkar D, Kulkarni V (2016) Comparison and synergy between fact-orientation and relation extraction for domain model generation in regulatory compliance. In: International conference on conceptual modeling. Springer, Cham
Suman R, et al. (2018) A case study on modeling and validating financial regulations using (semi-) automated compliance framework. In: IFIP Working conference on the practice of enterprise modeling. Springer, Cham
Sunkle S, Kholkar D, Kulkarni V (2015). Model-driven regulatory compliance: a case study of “Know Your Customer” regulations. In 18th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems, MoDELS 2015, Ottawa, ON, Canada, September 30 - October 2, 2015. 436–445
Deepali K, Mulpuru D, Kulkarni V (2018) Balancing model usability and verifiability with SBVR and answer set programming. In: MODELS Workshops, pp. 570–573
Nijssen S (2007) SBVR: Semantics for business
Leone N, Pfeifer G, Faber W, Eiter T, Gottlob G, Perri S, Scarcello F (2006) The DLV system for knowledge representation and reasoning. ACM Trans Comput Log 7(3):499–562
Lifschitz V (2008) What is answer set programming? In: Proceedings of the twentythird AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI 2008, Chicago, Illinois, USA, July pp. 13–17
Dimaresis N (2007) A system for modal and deontic defeasible reasoning. Int J Cooperative Inf Syst 14(2–3):181–216
Yeddula RR, Das P, Reddy S (2015) A model-driven approach to enterprise data migration. In: Zdravkovic J, Kirikova M, Johannesson P (eds). Conference on advanced information systems engineering (CAISE), Stockholm, Sweden, volume 9097 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 230–243. Springer.
Ronen F, Sanger J (2007) The text mining handbook: advanced approaches in analyzing unstructured data. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Vinay K, Barat S, Clark T (2019) Towards adaptive enterprises using digital twins. In: 2019 Winter simulation conference (WSC), pp. 60–74. IEEE
Jordan MI, Mitchell TM (2015) Machine learning: trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 349(6245):255–260
Sutton RS, Barto AG (2018) Reinforcement learning: an introduction. MIT press, Cambridge
Schmidt DC (2006) Model-driven engineering. Computer-IEEE Comput Soc 39(2):25
Kulkarni V, Reddy S, Rajbhoj A (2010) Scaling up model driven engineering–experience and lessons learnt. In: International conference on model driven engineering languages and systems, pp. 331–345. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulkarni, V., Sunkle, S., Kholkar, D. et al. Toward automated regulatory compliance. CSIT 9, 95–104 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-021-00329-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-021-00329-4