Abstract
Background
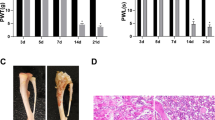
Bone cancer pain (BCP) seriously affects patient’s quality of life, which remains a difficult clinical problem, lacking effective drugs for treating it. The inflammation in the spinal cord involves the pathogenesis of BCP. The inhibition of spinal phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway or spinal P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) has previously been shown to alleviate BCP. Naringenin (NAR) has analgesic role and anti-inflammatory property.
Objective
The present study investigated the protection of NAR against BCP and explored whether the inhibition of spinal inflammation and the blockade of spinal P2X7R/PI3K/AKT signaling involved in this protection.
Result
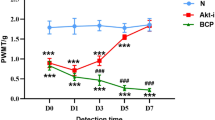
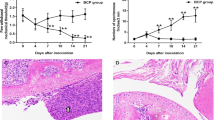
NAR significantly alleviated mechanical allodynia (the increase of paw withdrawal threshold in Von Frey test) and thermal hyperalgesia (the increase of paw withdrawal latency in Hargreaves test) in BCP rats. Additionally, NAR inhibited inflammatory cytokines (the reduced levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were measured using Elisa assay) and down-regulated P2X7R/PI3K/AKT signaling (the decreased P2X7R expression, the reduced ratios of phosphorylated (p)-PI3K/PI3K and p-AKT/AKT, which were detected Western blot) in the spinal cord of BCP rats.
Conclusion
NAR alleviated BCP through inhibiting inflammatory cytokines and down-regulating P2X7R/PI3K/AKT signaling in the spinal cord of rats. These findings revealed that NAR, as an effective agent against BCP, may provide an effective approach in the management of bone cancer patients.
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinolfi E, Giuliani AL, De Marchi E et al (2018) The P2X7 receptor: a main player in inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 151:234–244
Akoury E, Ahangar P, Nour A et al (2019) Low-dose zoledronate for the treatment of bone metastasis secondary to prostate cancer. Cancer Cell Int 19:28
Amoroso F, Capece M, Rotondo A et al (2015) The P2X7 receptor is a key modulator of the PI3K/GSK3beta/VEGF signaling network: evidence in experimental neuroblastoma. Oncogene 34:5240–5251
Burnstock G (2016) Purinergic mechanisms and pain. Adv Pharmacol 75:91–137
Calzaferri F, Ruiz-Ruiz C, de Diego AMG et al (2020) The purinergic P2X7 receptor as a potential drug target to combat neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Med Res Rev 40:2427–2465
Campana G, Rimondini R (2021) Mechanical nociception in mice and rats: measurement with automated von Frey equipment. Methods Mol Biol 2201:195–198
Chen SP, Zhou YQ, Liu DQ et al (2017) PI3K/Akt pathway: a potential therapeutic target for chronic pain. Curr Pharm Des 23:1860–1868
Chen J, Cong X, Zhan X et al (2019) Effects of parecoxib on pain threshold and inflammatory factors IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-in spinal cord of rats with bone cancer pain. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 29:528–531
Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Porro C et al (2016) PI3k/Akt signalling pathway plays a crucial role in the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in LPS-activated microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 36:282–290
Crackower MA, Oudit GY, Kozieradzki I et al (2002) Regulation of myocardial contractility and cell size by distinct PI3K-PTEN signaling pathways. Cell 110:737–749
Di Virgilio F (2007) Liaisons dangereuses: P2X(7) and the inflammasome. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:465–472
Di Virgilio F (2015) P2X receptors and inflammation. Curr Med Chem 22:866–877
Englezou PC, Rothwell SW, Ainscough JS et al (2015) P2X7R activation drives distinct IL-1 responses in dendritic cells compared to macrophages. Cytokine 74:293–304
Frost CO, Hansen RR, Heegaard AM (2016) Bone pain: current and future treatments. Curr Opin Pharmacol 28:31–37
Genetos DC, Karin NJ, Geist DJ et al (2011) Purinergic signaling is required for fluid shear stress-induced NF-kappaB translocation in osteoblasts. Exp Cell Res 317:737–744
Gicquel T, Robert S, Loyer P et al (2015) IL-1beta production is dependent on the activation of purinergic receptors and NLRP3 pathway in human macrophages. FASEB J 29:4162–4173
Griffin R, Nally R, Nolan Y et al (2006) The age-related attenuation in long-term potentiation is associated with microglial activation. J Neurochem 99:1263–1272
Gu W, Sun Y, Gu W et al (2020) The analgesic effects of pioglitazone in the bone cancer pain rats via regulating the PPARgamma/PTEN/mTOR signaling pathway in the spinal dorsal horn. Biomed Pharmacother 131:110692
Guan X, Fu Q, Xiong B et al (2015a) Activation of PI3Kgamma/Akt pathway mediates bone cancer pain in rats. J Neurochem 134:590–600
Guan XH, Fu QC, Shi D et al (2015b) Activation of spinal chemokine receptor CXCR3 mediates bone cancer pain through an Akt-ERK crosstalk pathway in rats. Exp Neurol 263:39–49
Hu CY, Zhao YT (2014) Analgesic effects of naringenin in rats with spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain. Biomed Rep 2:569–573
Huang HJ, Zhang M (2014) Downregulation of PI3Kcb utilizing adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA attenuates bone cancer pain. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:8127–8135
Kaulaskar S, Bhutada P, Rahigude A et al (2012) Effects of naringenin on allodynia and hyperalgesia in rats with chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 10:1482–1489
Liu S, Liu YP, Lv Y et al (2018) IL-18 contributes to bone cancer pain by regulating glia cells and neuron interaction. J Pain 19:186–195
Mantyh P (2013) Bone cancer pain: causes, consequences, and therapeutic opportunities. Pain 154(Suppl 1):S54–S62
Mao-Ying QL, Zhao J, Dong ZQ et al (2006) A rat model of bone cancer pain induced by intra-tibia inoculation of Walker 256 mammary gland carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:1292–1298
Matsuda M, Huh Y, Ji RR (2019) Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J Anesth 33:131–139
Ni H, Wang Y, An K et al (2019) Crosstalk between NFkappaB-dependent astrocytic CXCL1 and neuron CXCR2 plays a role in descending pain facilitation. J Neuroinflamm 16:1
Ni H, Xu M, Xie K et al (2020) Liquiritin alleviates pain through inhibiting CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling pathway in bone cancer pain rat. Front Pharmacol 11:436
Peng S, Lu Y, Li P et al (2019) The short interference RNA (siRNA) targeting NMUR2 relieves nociception in a bone cancer pain model of rat through PKC-ERK and PI3K-AKT pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 512:616–622
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC, Fattori V et al (2016) Naringenin reduces inflammatory pain in mice. Neuropharmacology 105:508–519
Rodriguez C, Ji M, Wang HL et al (2019) Cancer pain and quality of life. J Hosp Palliat Nurs 21:116–123
Shen W, Hu XM, Liu YN et al (2014) CXCL12 in astrocytes contributes to bone cancer pain through CXCR4-mediated neuronal sensitization and glial activation in rat spinal cord. J Neuroinflamm 11:75
Shen HH, Yang YX, Meng X et al (2018) NLRP3: a promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 17:694–702
Shi ZM, Han YW, Han XH et al (2016) Upstream regulators and downstream effectors of NF-kappaB in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 366:127–134
Singh P, Bansal S, Kuhad A et al (2020) Naringenin ameliorates diabetic neuropathic pain by modulation of oxidative-nitrosative stress, cytokines and MMP-9 levels. Food Funct 11:4548–4560
Urch C (2004) The pathophysiology of cancer-induced bone pain: current understanding. Palliat Med 18:267–274
Xu M, Ni H, Xu L et al (2019) B14 ameliorates bone cancer pain through downregulating spinal interleukin-1beta via suppressing neuron JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Mol Pain 15:1744806919886498
Yan J, Sun J, Zeng Z (2018) Teniposide ameliorates bone cancer nociception in rats via the P2X7 receptor. Inflammopharmacology 26:395–402
Yang Y, Li H, Li TT et al (2015) Delayed activation of spinal microglia contributes to the maintenance of bone cancer pain in female Wistar rats via P2X7 receptor and IL-18. J Neurosci 35:7950–7963
Yang L, Liu X, Zhang N et al (2020) Flavonoids in resina draconis protect against pulmonary fibrosis via the TGF-β1/NOTCH1 pathway. Mol Cell Toxicol 16:193–201
Yeung YT, Aziz F, Guerrero-Castilla A, Arguelles S (2018) Signaling pathways in inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapies. Curr Pharm Des 24:1449–1484
Zeng W, Jin L, Zhang F et al (2018) Naringenin as a potential immunomodulator in therapeutics. Pharmacol Res 135:122–126
Zhang Y, Cheng H, Li W et al (2019) Highly-expressed P2X7 receptor promotes growth and metastasis of human HOS/MNNG osteosarcoma cells via PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta/beta-catenin and mTOR/HIF1alpha/VEGF signaling. Int J Cancer 145:1068–1082
Zhao M, Li C, Shen F et al (2017) Naringenin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury through its anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activity and by inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Ther Med 14:2228–2234
Zhou J, Xia L, Zhang Y (2019) Naringin inhibits thyroid cancer cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis through repressing PI3K/AKT pathway. Pathol Res Pract 215:152707
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (CX2020B633).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JGS performed the experiments, analyzed the data and writing the manuscript. LL responsible for the experimental design and manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author Jian-Gang Song declares that he has no conflict of interest and author Lv Liu also declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the University Animal Care and Use Committee of Hengyang Center Hospital (Hengyang, China).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, JG., Liu, L. Naringenin alleviates bone cancer pain in rats via down-regulating spinal P2X7R /PI3K/AKT signaling: involving suppression in spinal inflammation. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 17, 475–484 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00156-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00156-3