Abstract
Purpose
There are several studies on the use of RNA interference (RNAi) for gene function analysis in fungi. However, most studies on filamentous fungi are based on in vitro-transcribed or -synthesized small interfering RNA (siRNA), and only a few have reported the use of vector-based RNAi. Here we want to develop and evaluate a new vector-based RNAi method using the mouse U6 promoter to drive short hairpin RNA (shRNA) expression in the filamentous fungi.
Methods
Molecular techniques were employed to develop and evaluate a new vector-based RNAi method using the mouse U6 promoter to drive short hairpin RNA (shRNA) expression in the filamentous fungus Blakeslea trispora.
Results
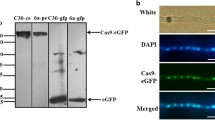
We characterized the mouse U6 promoter and utilized it for the expression of shRNA in B. trispora. Using real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting analyses, we confirmed the decrease in the mRNA and protein expression of carRA, respectively, in cells transformed with the mouse U6 promoter-driven shRNA expression vector. This indicated that the shRNA was transcribed from the mouse U6 promoter and correctly processed into siRNA and that the mouse U6 promoter exhibited transcription ability in the filamentous fungi.
Conclusions
The results suggest that the mouse U6 promoter that drives the expression of shRNA vectors may serve as a novel tool for RNAi induction in filamentous fungi.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boettcher M, McManus MT (2015) Choosing the right tool for the job: RNAi, TALEN, or CRISPR. Mol Cell 58:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.04.028
Boonanuntanasarn S, Panyim S, Yoshizaki G (2008) Characterization and organization of the U6 snRNA gene in zebrafish and usage of their promoters to express short hairpin RNA. Mar Genomics 1:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2008.10.001
Calo S, Nicolas FE, Vila A, Torres-Martinez S, Ruiz-Vazquez RM (2012) Two distinct RNA-dependent RNA polymerases are required for initiation and amplification of RNA silencing in the basal fungus Mucor circinelloides. Mol Microbiol 83:379–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07939.x
Catalanotto C, Pallotta M, ReFalo P, Sachs MS, Vayssie L, Macino G, Cogoni C (2004) Redundancy of the two dicer genes in transgene-induced posttranscriptional gene silencing in Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol 24:2536–2545
Cogoni C, Macino G (1999) Gene silencing in Neurospora crassa requires a protein homologous to RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature 399:166–169
Cogoni C, Macino G (2000) Post-transcriptional gene silencing across kingdoms. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:638–643
Cummins DM, Tyack SG, Doran TJ (2011) Characterisation and comparison of the chicken H1 RNA polymerase III promoter for short hairpin RNA expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 416:194–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.024
de Haro JP, Calo S, Cervantes M, Nicolas FE, Torres-Martinez S, Ruiz-Vazquez RM (2009) A single dicer gene is required for efficient gene silencing associated with two classes of small antisense RNAs in Mucor circinelloides. Eukaryot Cell 8:1486–1497. https://doi.org/10.1128/ec.00191-09
Duvoisin R, Ayuk MA, Rinaldi G, Suttiprapa S, Mann VH, Lee CM, Harris N, Brindley PJ (2012) Human U6 promoter drives stronger shRNA activity than its schistosome orthologue in Schistosoma mansoni and human fibrosarcoma cells. Transgenic Res 21:511–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-011-9548-0
Fellmann C, Lowe SW (2014) Stable RNA interference rules for silencing. Nat Cell Biol 16:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2895
Gonzalez R, Ferrer S, Buesa J, Ramon D (1989) Transformation of the dermatophyte Trichophyton mentagrophytes to hygromycin B resistance. Infect Immun 57:2923–2925. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.57.9.2923-2925.1989
Hannon GJ (2002) RNA interference. Nature 418:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1038/418244a
Jinek M, Doudna JA (2009) A three-dimensional view of the molecular machinery of RNA interference. Nature 457:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07755
Kim NY, Baek JY, Choi HS, Chung IS, Shin S, Lee JI, Choi JY, Yang JM (2012) Short-hairpin RNA-mediated gene expression interference in Trichoplusia ni cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:190–198. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1108.08045
Lambeth LS, Moore RJ, Muralitharan M, Dalrymple BP, Mc WS, Doran TJ (2005) Characterisation and application of a bovine U6 promoter for expression of short hairpin RNAs. BMC Biotechnol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-5-13
Lambeth LS, Wise TG, Moore RJ, Muralitharan MS, Doran TJ (2006) Comparison of bovine RNA polymerase III promoters for short hairpin RNA expression. Anim Genet 37:369–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2006.01468.x
Lax C, Tahiri G, Patino-Medina JA, Canovas-Marquez JT, Perez-Ruiz JA, Osorio-Concepcion M, Navarro E, Calo S (2020) The evolutionary significance of RNAi in the fungal kingdom. Int J Mol Sci 21:9348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249348
Li W, Yuan Q, Li Y, Cheng B (2007) Construction of eukaryotic expression vector of siRNA specific to squalene synthetase gene. Sheng Wu Ji Shu Tong Bao 3:115–117. https://doi.org/10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2007.03.025
Li Y, Yuan Q, Du X (2008) Protoplast from β-carotene-producing fungus Blakeslea trispora: preparation, regeneration and validation. Korean J Chem Eng 25:1416–1421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-008-0232-x
Li Y, Wei Q, Jin L, Wang X, Xin X, Su D, Yuan Q (2013) Preparation and identification of polyclone antibody against Blakeslea trispora CarRA. Gao Xiao Hua Xue Gong Cheng Xue Bao 27(06):1039–1044. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2013.06.019
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TG (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Miyagishi M, Taira K (2002) U6 promoter driven shRNAs with four uridine 3’ overhangs efficiently suppress targeted gene expression in mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 20:497–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0502-497
Nakayashiki H, Hanada S, Nguyen BQ, Kadotani N, Tosa Y, Mayama S (2005) RNA silencing as a tool for exploring gene function in ascomycete fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 42:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2005.01.002
Nakayashiki H, Kadotani N, Mayama S (2006) Evolution and diversification of RNA silencing proteins in fungi. J Mol Evol 63:127–135
Nicolás FE, Torres-Martínez S, Ruiz-Vázquez RM (2003) Two classes of small antisense RNAs in fungal RNA silencing triggered by non-integrative transgenes. EMBO J 22:3983–3991. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg384
Quiles-Rosillo MD, Ruiz-Vázquez RM, Torres-Martínez S, Garre V (2005) Light induction of the carotenoid biosynthesis pathway in Blakeslea trispora. Fungal Genet Biol 42:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2004.10.008
Rao DD, Vorhies JS, Senzer N, Nemunaitis J (2009) siRNA vs. shRNA: similarities and differences. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:746–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2009.04.004
Romano N, Macino G (1992) Quelling: transient inactivation of gene expression in Neurospora crassa by transformation with homologous sequences. Mol Microbiol 6:3343–3353
Rosa C, Kuo YW, Wuriyanghan H, Falk BW (2018) RNA interference mechanisms and applications in plant pathology. Annu Rev Phytopathol 56:581–610. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080417-050044
Schmidt AD, Heinekamp T, Matuschek M, Liebmann B, Bollschweiler C, Brakhage AA (2005) Analysis of mating-dependent transcription of B. trispora carotenoid biosynthesis genes carB and carRA by quantitative real-time PCR. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-1941-2
Semaan M, Kaulitz D, Petersen B, Niemann H, Denner J (2012) Long-term effects of PERV-specific RNA interference in transgenic pigs. Xenotransplantation 19:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3089.2012.00683.x
Setten RL, Rossi JJ, Han SP (2019) The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:421–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0017-4
Tomari Y, Zamore PD (2005) Perspective: machines for RNAi. Genes Dev 19:517–529
Torres-Martínez S, Ruiz-Vázquez RM (2017) The RNAi universe in fungi: a varied landscape of small RNAs and biological functions. Annu Rev Microbiol 71:371–391. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-090816-093352
Trieu TA, Navarro-Mendoza MI, Perez-Arques C, Sanchis M, Capilla J, Navarro-Rodriguez P, Lopez-Fernandez L, Torres-Martinez S, Garre V, Ruiz-Vazquez RM, Nicolás FE (2017) RNAi-based functional genomics identifies new virulence determinants in mucormycosis. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006150. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006150
Turowski TW, Tollervey D (2016) Transcription by RNA polymerase III: insights into mechanism and regulation. Biochem Soc Trans 44:1367–1375. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160062
Vannini A, Cramer P (2012) Conservation between the RNA polymerase I, II, and III transcription initiation machineries. Mol Cell 45:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.023
Yu JY, DeRuiter SL, Turner DL (2002) RNA interference by expression of short interfering RNAs and hairpin RNAs in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:6047–6052. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.092143499
Zhang P, Wang JG, Wan JG, Liu WQ (2010) Screening efficient siRNAs in vitro as the candidate genes for chicken anti-avian influenza virus H5N1 breeding. Mol Biol (Mosk) 44:42–50
Zheng X, Vladau C, Shunner A, Min WP (2010) siRNA specific delivery system for targeting dendritic cells. Methods Mol Biol 623:173–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-588-0_11
Zhu KY, Palli SR (2020) Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA interference. Annu Rev Entomol 65:293–311. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-011019-025224
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge financial support from the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (2182019), Excellent Talents of Organization Department of Beijing Municipal Committee (2020Z002-002-KWT), and General Projects of the Scientific Research Plan of the Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (KM201910858002). We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for their assistance with English language editing.
Supplementary Information
Online Resource 1—Color phenotype of B. trispora left untreated or transformed with shRNA-control or shRNA-carRA. Mycelia were harvested at 120 h post-transfection. A. Untreated B. trispora. B. B. trispora transformed with shRNA-control. C. B. trispora transformed with shRNA-carRA.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (2182019), Excellent Talents of Organization Department of Beijing Municipal Committee (2020Z002-002-KWT), and General Projects of the Scientific Research Plan of the Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (KM201910858002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Feng, H., Jin, L. et al. A novel vector-based RNAi method using mouse U6 promoter-driven shRNA expression in the filamentous fungus Blakeslea trispora. Biotechnol Lett 43, 1821–1830 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03155-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03155-5