Abstract
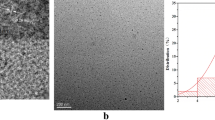
Although carbon dots (CDs) as fluorescent sensors have been widely exploited, multi-component detection using CDs without tedious surface modification is always a challenging task. Here, two kinds of nitrogen-doped CDs (NCD-m and NCD-o) based on soluble starch (SS) as carbon source were prepared through one-pot hydrothermal process using m-phenylenediamine and o-phenylenediamine as nitrogenous dopant respectively. Through fluorescence “on–off” mechanism of CDs, NCD-m and NCD-o could be used as a fluorescence sensor for detection of Fe 3+ and Ag + with LOD of 0.25 and 0.51 μM, respectively. Additionally, NCD-m could be used for indirect detection of ascorbic acid (AA) with LOD of 5.02 μM. Moreover, fluorescence intensity of NCD-m also exhibited the sensitivity to pH change from 2 to 13. More importantly, Both NCD-m and NCD-o had potential application for analysis of complicated real samples such as tap water, Vitamin C tablets and orange juice. Ultimately, the small size of NCD-m could contribute to reinforcing intracellular endocytosis, which allowed them to be used for bacteria imaging. Obviously, these easily obtainable nitrogen-doped CDs were able to be used for multi-components detection.
Graphical abstract
Strategy for synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots (NCDs) and a schematic for fabrication of as-prepared NCDs for detection of Fe 3+, Ag + and ascorbic acid (AA).











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary materials.
References
Brugnara C (2003) Iron Deficiency and Erythropoiesis: New Diagnostic Approaches. Clin Chem 49:1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1373/49.10.1573
Marchetti F, Palmucci J, Pettinari C, Pettinari R, Marangoni M, Ferraro S, Giovannetti R, Scuri S, Grappasonni I, Cocchioni M, Maldonado Hodar FJ, Gunnella R (2016) Preparation of Polyethylene Composites Containing Silver(I) Acylpyrazolonato Additives and SAR Investigation of their Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 43:29676–29687. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b09742
Sahai RSN, Gaval VR, Bhat B (2019) Preparation of low-density polyethylene–silver ion antimicrobial film with and without ethylene-vinyl acetate. Polym Polym Compos 28:554–561. https://doi.org/10.1177/0967391119892473
Marambio-Jones C, Hoek EMV (2010) A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J Nanopart Res 12:1531–1551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9900-y
Hadrup N, Sharma AK, Loeschner K, Jacobsen NR (2020) Pulmonary toxicity of silver vapours, nanoparticles and fine dusts: A review. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 115:104690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104690
De Acha N, Elosua C, Corres JM, Arregui FJ (2019) Fluorescent Sensors for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media. Sensors 19:599. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030599
Chowdhury S, Rooj B, Dutta A, Mandal U (2018) Review on Recent Advances in Metal Ions Sensing Using Different Fluorescent Probes. J Fluoresc 28:999–1021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-018-2263-y
Park SH, Kwon N, Lee JH, Yoon J, Shin I (2020) Synthetic ratiometric fluorescent probes for detection of ions. Chem Soc Rev 49:143–179. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CS00243J
Wu P, Zhao T, Wang S, Hou X (2014) Semicondutor quantum dots-based metal ion probes. Nanoscale 6:43–64. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR04628A
Li J, Zhu JJ, Xu K (2014) Fluorescent metal nanoclusters: From synthesis to applications. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 58:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.02.011
Karmakar A, Samanta P, Dutta S, Ghosh SK (2019) Fluorescent “Turn-on” Sensing Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Chemistry-an Asian Journal 14:4506–4519. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201901168
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00269e
Li X, Zhao Z, Pan C (2016) Ionic liquid-assisted electrochemical exfoliation of carbon dots of different size for fluorescent imaging of bacteria by tuning the water fraction in electrolyte. Mikrochim Acta 183:2525–2532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1877-5
Zhang X, Jiang M, Niu N, Chen Z, Li S (2018) Natural-Product-Derived Carbon Dots: From Natural Products to Functional Materials. Chemsuschem 11:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201701847
Luo PG, Sahu S, Yang S-T, Sonkar SK, Wang J, Wang H, LeCroy GE, Cao L, Sun Y-P (2013) Carbon “quantum” dots for optical bioimaging. J Mater Chem B 1:2116–2127. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb00018d
Zhu S, Zhao X, Song Y, Lu S, Yang B (2016) Beyond bottom-up carbon nanodots: Citric-acid derived organic molecules. Nano Today 11:128–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2015.09.002
Miao S, Liang K, Zhu J, Yang B, Zhao D, Kong B (2020) Hetero-atom-doped carbon dots: Doping strategies, properties and applications. Nano Today 33:100879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100879
Wang W, Wang B, Embrechts H, Damm C, Cadranel A, Strauss V, Distaso M, Hinterberger V, Guldi DM, Peukert W (2017) Shedding light on the effective fluorophore structure of high fluorescence quantum yield carbon nanodots. RSC Adv 7:24771–24780. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA04421F
Wang N, Chai H, Dong X, Zhou Q, Zhu L (2018) Detection of Fe(III)EDTA by using photoluminescent carbon dot with the aid of F(-) ion. Food Chem 258:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.050
Rooj B, Dutta A, Islam S, Mandal U (2018) Green Synthesized Carbon Quantum Dots from Polianthes tuberose L. Petals for Copper (II) and Iron (II) Detection. J Fluoresc 28:1261–1267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-018-2292-6
Omer KM, Tofiq DI, Hassan AQ (2018) Solvothermal synthesis of phosphorus and nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for iron(III). Mikrochim Acta 185:466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3002-4
Liu Y, Xue H, Liu J, Wang Q, Wang L (2018) Carbon quantum dot-based fluorometric nitrite assay by exploiting the oxidation of iron(II) to iron(III). Mikrochim Acta 185:129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2668-y
Lv P, Yao Y, Zhou H, Zhang J, Pang Z, Ao K, Cai Y, Wei Q (2017) Synthesis of novel nitrogen-doped carbon dots for highly selective detection of iron ion. Nanotechnology 28:165502. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa6320
Wang C, Huang Y, Jiang K, Humphrey MG, Zhang C (2016) Dual-emitting quantum dot/carbon nanodot-based nanoprobe for selective and sensitive detection of Fe(3+) in cells. Analyst 141:4488–4494. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6an00605a
Hamishehkar H, Ghasemzadeh B, Naseri A, Salehi R, Rasoulzadeh F (2015) Carbon dots preparation as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of Fe(III) ions in biological systems. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 150:934–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.06.061
Zhang J, Yang H, Pan S, Liu H, Hu X (2021) A novel “off-on-off” fluorescent-nanoprobe based on B, N co-doped carbon dots and MnO2 nanosheets for sensitive detection of GSH and Ag+. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 244:118831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118831
Dang DK, Sundaram C, Ngo Y-LT, Chung JS, Kim EJ, Hur SH (2018) One pot solid-state synthesis of highly fluorescent N and S co-doped carbon dots and its use as fluorescent probe for Ag+ detection in aqueous solution. Sens Actuators, B Chem 255:3284–3291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.155
Huang S, Yang E, Yao J, Liu Y, Xiao Q (2018) Red emission nitrogen, boron, sulfur co-doped carbon dots for “on-off-on” fluorescent mode detection of Ag+ ions and l-cysteine in complex biological fluids and living cells. Anal Chim Acta 1035:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.06.051
Ren G, Zhang Q, Li S, Fu S, Chai F, Wang C, Qu F (2017) One pot synthesis of highly fluorescent N doped C-dots and used as fluorescent probe detection for Hg2+ and Ag+ in aqueous solution. Sens Actuators, B Chem 243:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.149
Ma X, Lin S, Dang Y, Dai Y, Zhang X, Xia F (2019) Carbon dots as an “on-off-on” fluorescent probe for detection of Cu(II) ion, ascorbic acid, and acid phosphatase. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:6645–6653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02038-z
Gong X, Liu Y, Yang Z, Shuang S, Zhang Z, Dong C (2017) An “on-off-on” fluorescent nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on phosphorus/nitrogen dual-doped carbon quantum dot. Anal Chim Acta 968:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.02.038
Valko M, Jomova K, Rhodes CJ, Kuča K, Musílek K (2016) Redox- and non-redox-metal-induced formation of free radicals and their role in human disease. Arch Toxicol 90:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1579-5
Cathcart RF (1985) Vitamin C: The nontoxic, nonrate-limited, antioxidant free radical scavenger. Med Hypotheses 18:61–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-9877(85)90121-5
Schoenfeld JD, Sibenaller ZA, Mapuskar KA, Bradley MD, Wagner BA, Buettner GR, Monga V, Milhem M, Spitz DR, Allen BG (2018) Redox active metals and H2O2 mediate the increased efficacy of pharmacological ascorbate in combination with gemcitabine or radiation in pre-clinical sarcoma models. Redox Biol 14:417–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.012
Carr AC, Maggini S (2017) Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients 9:1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111211
Minor EA, Court BL, Young JI, Wang G (2013) Ascorbate Induces Ten-Eleven Translocation (Tet) Methylcytosine Dioxygenase-mediated Generation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine*♦. J Biol Chem 288:13669–13674. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C113.464800
Moser MA, Chun OK (2016) Vitamin C and Heart Health: A Review Based on Findings from Epidemiologic Studies. Int J Mol Sci 17:1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081328
Vallès-Pàmies B, Barclay F, Hill SE, Mitchell JR, Paterson LA, Blanshard JMV (1997) The effects of low molecular weight additives on the viscosities of cassava starch. Carbohyd Polym 34:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(97)00094-5
Buettner GR, Jurkiewicz BA (1996) Catalytic Metals, Ascorbate and Free Radicals: Combinations to Avoid. Radiat Res 145:532–541. https://doi.org/10.2307/3579271
Lu W, Qin X, Liu S, Chang G, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun X (2012) Economical, Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles and Their Use as Probes for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Mercury(II) Ions. Anal Chem 84:5351–5357. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3007939
Lu J, Yang JX, Wang J, Lim A, Wang S, Loh KP (2009) One-Pot Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoribbons, Nanoparticles, and Graphene by the Exfoliation of Graphite in Ionic Liquids. ACS Nano 3:2367–2375. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900546b
Martindale BCM, Hutton GAM, Caputo CA, Reisner E (2015) Solar Hydrogen Production Using Carbon Quantum Dots and a Molecular Nickel Catalyst. J Am Chem Soc 137:6018–6025. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b01650
Vikneswaran R, Ramesh S, Yahya R (2014) Green synthesized carbon nanodots as a fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of iron(III) ions. Mater Lett 136:179–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.08.063
Liu Y, Li W, Wu P, Ma C, Wu X, Xu M, Luo S, Xu Z, Liu S (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon quantum dots for application in acetone and dopamine sensors and multicolor cellular imaging. Sens Actuators, B Chem 281:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.075
Wang J, Peng F, Lu Y, Zhong Y, Wang S, Xu M, Ji X, Su Y, Liao L, He Y (2015) Large-Scale Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanodots and Their Use in Optics Applications. Advanced Optical Materials 3:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201400307
Ding H, Yu S-B, Wei J-S, Xiong H-M (2016) Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 10:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05406
Lu S, Xiao G, Sui L, Feng T, Yong X, Zhu S, Li B, Liu Z, Zou B, Jin M, Tse JS, Yan H, Yang B (2017) Piezochromic Carbon Dots with Two-photon Fluorescence. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 56:6187–6191. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201700757
Hu M, Yang Y, Gu X, Hu Y, Huang J, Wang C (2014) One-pot synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots by carbonization of cyclodextrin and their application in Ag+ detection. RSC Adv 4:62446–62452. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA11491D
Yuan YH, Liu ZX, Li RS, Zou HY, Lin M, Liu H, Huang CZ (2016) Synthesis of nitrogen-doping carbon dots with different photoluminescence properties by controlling the surface states. Nanoscale 8:6770–6776. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR00402D
Liu W, Li C, Sun X, Pan W, Yu G, Wang J (2017) Highly crystalline carbon dots from fresh tomato: UV emission and quantum confinement. Nanotechnology 28:485705. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa900b
Deng Z, Liu C, Jin Y, Pu J, Wang B, Chen J (2019) High quantum yield blue- and orange-emitting carbon dots: one-step microwave synthesis and applications as fluorescent films and in fingerprint and cellular imaging. Analyst 144:4569–4574. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN00672A
Li C, Liu W, Ren Y, Sun X, Pan W, Wang J (2017) The selectivity of the carboxylate groups terminated carbon dots switched by buffer solutions for the detection of multi-metal ions. Sens Actuators, B Chem 240:941–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.068
Guo Y, Wang Z, Shao H, Jiang X (2013) Hydrothermal synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon nanoparticles from sodium citrate and their use for the detection of mercury ions. Carbon 52:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.10.028
Ju J, Chen W (2014) Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens Bioelectron 58:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.02.061
Meng A, Xu Q, Zhao K, Li Z, Liang J, Li Q (2018) A highly selective and sensitive “on-off-on” fluorescent probe for detecting Hg(II) based on Au/N-doped carbon quantum dots. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical 255:657–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.028
Wang M, Wan Y, Zhang K, Fu Q, Wang L, Zeng J, Xia Z, Gao D (2019) Green synthesis of carbon dots using the flowers of Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Lour. as precursors: application in Fe(3+) and ascorbic acid determination and cell imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:2715–2727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01712-6
Li J, Tang K, Yu J, Wang H, Tu M, Wang X (2019) Nitrogen and chlorine co-doped carbon dots as probe for sensing and imaging in biological samples. Royal Society Open Science 6:181557. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181557
Chen K, Qing W, Hu W, Lu M, Wang Y, Liu X (2019) On-off-on fluorescent carbon dots from waste tea: Their properties, antioxidant and selective detection of CrO4(2-), Fe(3+), ascorbic acid and L-cysteine in real samples. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 213:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.01.066
Shamsipur M, Molaei K, Molaabasi F, Alipour M, Alizadeh N, Hosseinkhani S, Hosseini M (2018) Facile preparation and characterization of new green emitting carbon dots for sensitive and selective off/on detection of Fe(3+) ion and ascorbic acid in water and urine samples and intracellular imaging in living cells. Talanta 183:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.042
Ma X, Lin S, Dang Y, Dai Y, Zhang X, Xia F (2019) Carbon dots as an “on-off-on” fluorescent probe for detection of Cu(II) ion, ascorbic acid, and acid phosphatase. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:6645–6653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02038-z
Huang Y, Zhou J, Feng H, Zheng J, Ma HM, Liu W, Tang C, Ao H, Zhao M, Qian Z (2016) A dual-channel fluorescent chemosensor for discriminative detection of glutathione based on functionalized carbon quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 86:748–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.081
Guo Y, Yang L, Li W, Wang X, Shang Y, Li B (2016) Carbon dots doped with nitrogen and sulfur and loaded with copper(II) as a “turn-on” fluorescent probe for cystein, glutathione and homocysteine. Microchim Acta 183:1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1779-6
Liao S, Huang X, Yang H, Chen X (2018) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe to detect copper ions, glutathione, and intracellular pH. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:7701–7710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1387-x
Chen BB, Liu ML, Huang CZ (2021) Recent advances of carbon dots in imaging-guided theranostics. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 134:116116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116116
Qiao G, Chen G, Wen Q, Liu W, Gao J, Yu Z, Wang Q (2020) Rapid conversion from common precursors to carbon dots in large scale: Spectral controls, optical sensing, cellular imaging and LEDs application. J Colloid Interface Sci 580:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.034
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81902168).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuanyuan Hu conceived and designed the study. Jun Luo conducted the literature search. Yuanyuan Hu and Wenxuan Ji performed the related experiments. Yuanyuan Hu, Wenxuan Ji, Jinjuan Qiao, Heng Li, Yun Zhang, and Jun Luo were involved in the analysis and interpretation of data. Yuanyuan Hu and Jun Luo drafted the manuscript. The study was supervised by Jinjuan Qiao, Heng Li and Yun Zhang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
This research did not involve clinical trials and animal experiments which were related to humans and animals as the experimental subjects. Currently, our institutions only require employees to get approval from the ethics committee before carrying out the above two kinds of experiments.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Ji, W., Qiao, J. et al. Simple and Sensitive Multi-components Detection Using Synthetic Nitrogen-doped Carbon Dots Based on Soluble Starch. J Fluoresc 31, 1379–1392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-021-02764-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-021-02764-7