Abstract
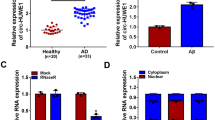
Our study aimed to explore the function and mechanism of action of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) SRY-Box 21 antisense RNA 1 (SOX21-AS1) in amyloid beta25–35 (Aβ25–35)-induced neuronal damage. To induce neuronal damage, neuronal cells and differentiated IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells were challenged by Aβ25–35. SOX21-AS1 and miR-132 quantities were detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Cell damage was evaluated by detecting the changes of cell viability, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Cell viability was measured using cell counting kit-8. Cell apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry and caspase-3 activity. The oxidative stress was analyzed by reactive oxygen species level. The expression of proteins associated with the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway was examined by western blot. SOX21-AS1 abundance was up-regulated in Aβ25–35-challenged neuronal cells. Silencing of SOX21-AS1 attenuated Aβ25–35-induced viability reduction and promotion of apoptosis and oxidative stress, suggesting that silencing of SOX21-AS1 repressed Aβ25–35-induced neuronal damage. miR-132 quantity was reduced in Aβ25–35-challenged neuronal cells, and negatively controlled by SOX21-AS1. miR-132 knockdown abolished the effect of SOX21-AS1 silencing on Aβ25–35-induced neuronal damage, indicating that SOX21-AS1 controls Aβ25–35-induced neuronal damage via regulating miR-132. The PI3K/AKT signaling was repressed in Aβ25–35-challenged cells, but this effect was counteracted upon overexpression of miR-132. In conclusion, SOX21-AS1 knockdown mitigated Aβ25–35-dependent neuronal cell damage by promoting miR-132/PI3K/AKT pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Long JM, Holtzman DM (2019) Alzheimer disease: an update on pathobiology and treatment strategies. Cell 179:312–339
Wang J, Gu BJ, Masters CL, Wang YJ (2017) A systemic view of Alzheimer disease—insights from amyloid-β metabolism beyond the brain. Nat Rev Neurol 13:612–623
Forest KH, Nichols RA (2019) Assessing neuroprotective agents for Aβ-induced neurotoxicity. Trends Mol Med 25:685–695
Fricker M, Tolkovsky AM, Borutaite V, Coleman M, Brown GC (2018) Neuronal cell death. Physiol Rev 98:813–880
Butterfield DA, Halliwell B (2019) Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 20:148–160
Oe S, Kimura T, Yamada H (2019) Regulatory non-coding RNAs in nervous system development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 24:1203–1240
Maoz R, Garfinkel BP, Soreq H (2017) Alzheimer’s disease and ncRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol 978:337–361
Maniati MS, Maniati M, Yousefi T, Ahmadi-Ahangar A, Tehrani SS (2019) New insights into the role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in most common neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Biochem 120:8908–8918
Cortini F, Roma F, Villa C (2019) Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 50:19–26
Zhou M, Zhao H, Wang X, Sun J, Su J (2019) Analysis of long noncoding RNAs highlights region-specific altered expression patterns and diagnostic roles in Alzheimer’s disease. Brief Bioinform 20:598–608
Li X, Wang SW, Li XL, Yu FY, Cong HM (2020) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA TUG1 depresses apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in Alzheimer’s disease by elevating microRNA-15a and repressing ROCK1 expression. Inflamm Res 69:897–910
Gao Y, Zhang N, Lv C, Li N, Li X, Li W (2020) lncRNA SNHG1 knockdown alleviates amyloid-β-induced neuronal injury by regulating ZNF217 via sponging miR-361-3p in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 77:85–98
Xu W, Li K, Fan Q, Zong B, Han L (2020) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA SOX21-AS1 attenuates amyloid-β-induced neuronal damage by sponging miR-107. Biosci Rep 40:BSR20194295
Segaran RC, Chan LY, Wang H, Sethi G, Tang FR (2021) Neuronal development-related miRNAs as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease, depression, schizophrenia and ionizing radiation exposure. Curr Med Chem 28:19–52
El Fatimy R, Li S, Chen Z, Mushannen T, Gongala S, Wei Z, Balu DT, Rabinovsky R, Cantlon A, Elkhal A, Selkoe DJ, Sonntag KC, Walsh DM, Krichevsky AM (2018) MicroRNA-132 provides neuroprotection for tauopathies via multiple signaling pathways. Acta Neuropathol 136:537–555
Salta E, De Strooper B (2017) microRNA-132: a key noncoding RNA operating in the cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 31:424–433
Wang X, Wang C, Geng C, Zhao K (2018) LncRNA XIST knockdown attenuates Aβ25-35-induced toxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons by targeting miR-132. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 11:3915–3924
Rai SN, Dilnashin H, Birla H, Singh SS, Zahra W, Rathore AS, Singh BK, Singh SP (2019) The role of PI3K/Akt and ERK in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotox Res 35:775–795
Wang Y, Chang Q (2020) MicroRNA miR-212 regulates PDCD4 to attenuate Aβ25-35-induced neurotoxicity via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Biotechnol Lett 42:1789–1797
Wang T, Cheng Y, Han H, Liu J, Tian B, Liu X (2019) miR-194 accelerates apoptosis of aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons by inhibiting Nrn1 and decreasing PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activity. Genes (Basel) 10:313
Lian R, Lu B, Jiao L, Li S, Wang H, Miao W, Yu W (2016) MiR-132 plays an oncogenic role in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 792:1–6
Slanzi A, Iannoto G, Rossi B, Zenaro E, Constantin G (2020) In vitro models of neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:328
Ge Y, Song X, Liu J, Liu C, Xu C (2020) The combined therapy of berberine treatment with lncRNA BACE1-AS depletion attenuates Aβ25-35 induced neuronal injury through regulating the expression of miR-132-3p in neuronal cells. Neurochem Res 45:741–751
Sarkar B, Dhiman M, Mittal S, Mantha AK (2017) Curcumin revitalizes amyloid beta (25–35)-induced and organophosphate pesticides pestered neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y and IMR-32 cells via activation of APE1 and Nrf2. Metab Brain Dis 32:2045–2061
Wang Y, Zheng ZJ, Jia YJ, Yang YL, Xue YM (2018) Role of p53/miR-155-5p/sirt1 loop in renal tubular injury of diabetic kidney disease. J Transl Med 16:146
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopes TZ, de Moraes FR, Tedesco AC, Arni RK, Rahal P, Calmon MF (2020) Berberine associated photodynamic therapy promotes autophagy and apoptosis via ROS generation in renal carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 123:109794
Paraskevopoulou MD, Vlachos IS, Karagkouni D, Georgakilas G, Kanellos I, Vergoulis T, Zagganas K, Tsanakas P, Floros E, Dalamagas T, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2016) DIANA-LncBase v2: indexing microRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D231-238
Zhou P, Xu W, Peng X, Luo Z, Xing Q, Chen X, Hou C, Liang W, Zhou J, Wu X, Songyang Z, Jiang S (2013) Large-scale screens of miRNA-mRNA interactions unveiled that the 3’UTR of a gene is targeted by multiple miRNAs. PLoS ONE 8:68204
Han L, Yue X, Zhou X, Lan FM, You G, Zhang W, Zhang KL, Zhang CZ, Cheng JQ, Yu SZ, Pu PY, Jiang T, Kang CS (2012) MicroRNA-21 expression is regulated by β-catenin/STAT3 pathway and promotes glioma cell invasion by direct targeting RECK. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:573–583
Wang SH, Zhang WJ, Wu XC, Weng MZ, Zhang MD, Cai Q, Zhou D, Wang JD, Quan ZW (2016) The lncRNA MALAT1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate MCL-1 expression by sponging miR-363-3p in gallbladder cancer. J Cell Mol Med 20:2299–2308
Jin Y, Chen Z, Liu X, Zhou X (2013) Evaluating the microRNA targeting sites by luciferase reporter gene assay. Methods Mol Biol 936:117–127
Torres M, Becquet D, Guillen S, Boyer B, Moreno M, Blanchard MP, Franc JL, François-Bellan AM (2018) RNA pull-down procedure to identify RNA targets of a long non-coding RNA. J Vis Exp 134:57379
Millan MJ (2017) Linking deregulation of non-coding RNA to the core pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease: an integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 156:1–68
Wang X, Shen C, Zhu J, Shen G, Li Z, Dong J (2019) Long noncoding RNAs in the regulation of oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1318795
Wei AW, Li LF (2017) Long non-coding RNA SOX21-AS1 sponges miR-145 to promote the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer by targeting MYO6. Biomed Pharmacother 96:953–959
Gai SY, Yuan ZH (2020) Long non-coding RNA SOX21-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through upregulating PAK7 expression by sponging miR-144-3p in glioma cells. Neoplasma 67:333–343
Liu X, Song J, Kang Y, Wang Y, Chen A (2020) Long noncoding RNA SOX21-AS1 regulates the progression of triple-negative breast cancer through regulation of miR-520a-5p/ORMDL3 axis. J Cell Biochem 121:4601–4611
Yang CM, Wang TH, Chen HC, Li SC, Lee MC, Liou HH, Liu PF, Tseng YK, Shiue YL, Ger LP, Tsai KW (2016) Aberrant DNA hypermethylation-silenced SOX21-AS1 gene expression and its clinical importance in oral cancer. Clin Epigenetics 8:129
Zhang L, Fang Y, Cheng X, Lian YJ, Xu HL (2019) Silencing of long noncoding RNA SOX21-AS1 relieves neuronal oxidative stress injury in mice with alzheimer’s disease by upregulating FZD3/5 via the Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Neurobiol 56:3522–3537
Frozza RL, Horn AP, Hoppe JB, Simão F, Gerhardt D, Comiran RA, Salbego CG (2009) A comparative study of β-amyloid peptides Aβ1-42 and Aβ25-35 toxicity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Neurochem Res 34:295–303
Wu YY, Kuo HC (2020) Functional roles and networks of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. J Biomed Sci 27:49
Zhao Y, Zhao R, Wu J, Wang Q, Pang K, Shi Q, Gao Q, Hu Y, Dong X, Zhang J, Sun J (2018) Melatonin protects against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in primary neurons via miR-132/PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a pathway. BioFactors 44:609–618
Xu N, Li AD, Ji LL, Ye Y, Wang ZY, Tong L (2019) miR-132 regulates the expression of synaptic proteins in APP/PS1 transgenic mice through C1q. Eur J Histochem 63:3008
Hernandez-Rapp J, Rainone S, Goupil C, Dorval V, Smith PY, Saint-Pierre M, Vallee M, Planel E, Droit A, Calon F, Cicchetti F, Hebert SS (2016) microRNA-132/212 deficiency enhances Aβ production and senile plaque deposition in Alzheimer’s disease triple transgenic mice. Sci Rep 6:30953
Barker RM, Holly JMP, Biernacka KM, Allen-Birt SJ, Perks CM (2020) Mini review: opposing pathologies in cancer and Alzheimer’s disease: does the PI3K/Akt pathway provide clues? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:403
Matsuda S, Nakagawa Y, Tsuji A, Kitagishi Y, Nakanishi A, Murai T (2018) Implications of PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling on superoxide dismutases expression and in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Diseases 6:28
Gu Y, Cai R, Zhang C, Xue Y, Pan Y, Wang J, Zhang Z (2019) miR-132-3p boosts caveolae-mediated transcellular transport in glioma endothelial cells by targeting PTEN/PI3K/PKB/Src/Cav-1 signaling pathway. FASEB J 33:441–454
Zhang CJ, Huang Y, Lu JD, Lin J, Ge ZR, Huang H (2019) Upregulated microRNA-132 rescues cardiac fibrosis and restores cardiocyte proliferation in dilated cardiomyopathy through the phosphatase and tensin homolog-mediated PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway. J Cell Biochem 120:1232–1244
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, F., Ji, D., Ni, H. et al. SRY-Box 21 Antisense RNA 1 Knockdown Diminishes Amyloid Beta25–35-Induced Neuronal Damage by miR-132/PI3K/AKT Pathway. Neurochem Res 46, 2376–2386 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03373-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03373-3