Abstract
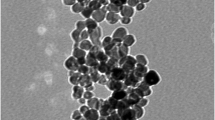
For the first time, a highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor was fabricated based on a MoWS2 nanoparticles modified screen printed electrode (MoWS2/SPE) for the simultaneous determination of Sudan I and bisphenol A. The MoWS2 nanoparticles synthesized by a hydrothermal method were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The MoWS2/SPE exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activity towards the oxidations of Sudan I and bisphenol A in a phosphate buffer solution at pH 7.0, and the corresponding electrochemical signals have appeared as two well resolved oxidation peaks with significant peak potential differences of 120 mV. For selective determination, the linear response of Sudan I was in a concentration range of 0.05 to 700.0 μM with a detection limit of 0.01 μM. The proposed sensor has proved to be applicable for the determination of the target analytes in tap water and food samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Li, B.L., Luo, J.H., Luo, H.Q., and Li, N.B., A novel conducting poly(p-aminobenzene sulphonic acid)-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of Sudan I and its application for detection in food stuffs, Food Chem., 2015, vol. 173, p. 594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.060
Xiao, F., Zhang, N., Gu, H., Qian, M., et al., A monoclonal antibody-based immunosensor for detection of Sudan I using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, Talanta, 2011, vol. 84, p. 204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.01.001
Li, J., Feng, H., Li, J., Feng, Y., et al., Fabrication of gold nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide as a high performance electrochemical sensing platform for the detection of toxicant Sudan I, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 167, p. 226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.03.201
Mo, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhao, F., Xiao, F., et al., Sensitive voltammetric determination of Sudan I in food samples by using gemini surfactant-ionic liquid-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite film modified glassy carbon electrodes, Food Chem., 2010, vol. 121, p. 233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.077
Chen, S., Du, D., Huang, J., Zhang, A., et al., Rational design and application of molecularly imprinted sol-gel polymer for the electrochemically selective and sensitive determination of Sudan I, Talanta, 2011, vol. 84, p. 451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.01.047
Yang, D., Zhu, L., and Jiang, X., Electrochemical reaction mechanism and determination of Sudan I at a multi wall carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2010, vol. 640, p. 17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2009.12.022
Yang, D., Zhu, L., Jiang, X., and Guo, L., Sensitive determination of Sudan I at an ordered mesoporous carbon modified glassy carbon electrode, Sens. Actuators, B, 2009, vol. 141, p. 124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.05.030
Rebane, R., Leito, I., Yurchenko, S., and Herodes, K., A review of analytical techniques for determination of Sudan I–IV dyes in food matrixes, J. Chromatogr. A, 2010, vol. 1217, p. 2747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.02.038
Wu, M., Tang, W., Guimaraes, J., Wang, Q., et al., Electrochemical detection of Sudan I using a multi-walled carbon nanotube/chitosan composite modified glassy carbon electrode, Am. J. Anal. Chem., 2013, vol. 4, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2013.46A001
Chailapakul, O., Wonsawat, W., Siangproh, W., Grudpan, K., et al., Analysis of Sudan I, Sudan II, Sudan III, and Sudan IV in food by HPLC with electrochemical detection: comparison of glassy carbon electrode with carbon nanotube-ionic liquid gel modified electrode, Food Chem., 2008, vol. 109, p. 876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.018
Koyun, O., Gorduk, S., Gencten, M., and Sahin, Y., A novel copper(II) phthalocyanine-modified multiwalled carbon nanotube-based electrode for sensitive electrochemical detection of bisphenol A, New J. Chem., 2019, vol. 43, p. 85. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ03721C
Yu, Z., Luan, Y., Li, H., Wang, W., et al., A disposable electrochemical aptasensor using single-stranded DNA–methylene blue complex as signal-amplification platform for sensitive sensing of bisphenol A, Sens. Actuators, B, 2019, vol. 284, p. 73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.126
Mo, F., Xie, J., Wu, T., Liu, M., et al., A sensitive electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A on the basis of the AuPd incorporated carboxylic multi-walled carbon nanotubes, Food Chem., 2019, vol. 292, p. 253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.034
Ali, H., Mukhopadhyay, S., and Jana, N.R., Selective electrochemical detection of bisphenol A using a molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite, New J. Chem., 2019, vol. 43, p. 1536. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ05883K
Wu, L., Yan, H., Wang, J., Liu, G., et al., Tyrosinase incorporated with Au–Pt·SiO2 nanospheres for electrochemical detection of bisphenol A, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, vol. 166, p. B562.
Sidwaba, U., Ntshongontshi, N., Feleni, U., Wilson, L., et al., Manganese peroxidase-based electro-oxidation of bisphenol A at hydrogellic polyaniline-titania nanocomposite-modified glassy carbon electrode, Electrocatalysis, 2019, vol. 10, p. 323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-019-0510-x
Gupta, V.K., Singh, A.K., and Kumawat, L.K., Thiazole Schiff base turn-on fluorescent chemosensor for Al3+ ion, Sens. Actuators, B, 2014, vol. 195, p. 98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.12.092
Stradiotto, N.R., Yamanaka, H., and Zanoni, M.V.B., Electrochemical sensors: a powerful tool in analytical chemistry, J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2003, vol. 14, p. 159. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532003000200003
Gupta, V.K., Mergu, N., Kumawat, L.K., and Singh, A.K., Selective naked-eye detection of magnesium (II) ions using a coumarin-derived fluorescent probe, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, vol. 207, p. 216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.10.044
Gupta, V.K., Mergu, N., Kumawat, L.K., and Singh, A.K., A reversible fluorescence “off-on-off” sensor for sequential detection of aluminum and acetate/fluoride ions, Talanta, 2015, vol. 144, p. 80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.053
Khalilzadeh, M.A., Tajik, S., Beitollahi, H., and Venditti, R.A., Green synthesis of magnetic nanocomposite with iron oxide deposited on cellulose nanocrystals with copper (Fe3O4·CNC/Cu): Investigation of catalytic activity for the development of a venlafaxine electrochemical sensor, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2020, vol. 59, p. 4219. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b06214
Goyal, R.N., Gupta, V.K., and Chatterjee, S., Fullerene-C60-modified edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode for the determination of dexamethasone in pharmaceutical formulations and human biological fluids, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2009, vol. 24, p. 1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.08.024
Goyal, R.N., Gupta, V.K., and Chatterjee, S., A sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of synthetic corticosteroid triamcinolone, abused for doping, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2009, vol. 24, p. 3562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.05.016
Gupta, V.K., Karimi-Maleh, H., and Sadegh, R., Simultaneous determination of hydroxylamine, phenol and sulfite in water and waste water samples using a voltammetric nanosensor, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2015, vol. 10, p. 303.
Beitollahi, H., Khalilzadeh, M.A., Tajik, S., Safaei, M., et al., Recent advances in applications of voltammetric sensors modified with ferrocene and its derivatives, ACS Omega, 2020, vol. 5, p. 2049. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03788
Gupta, V.K., Kumar, S., Singh, R., Singh, L.P., et al., Cadmium(II) ion sensing through p-tert-butyl calix[6]arene based potentiometric sensor, J. Mol. Liq., 2014, vol. 195, p. 65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.02.001
Beitollahi, H., Karimi-Maleh, H., and Khabazzadeh, H., Nanomolar and selective determination of epinephrine in the presence of norepinephrine using carbon paste electrode modified with carbon nanotubes and novel 2-(4-oxo-3-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-quinazolinyl)-N'-phenyl-hydrazinecarbothioamide, Anal. Chem., 2008, vol. 80, p. 9848. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac801854j
Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, V.K., Dwivedi, M.K., and Jain, S., Caesium PVC–crown (dibenzo-24-crown-8) based membrane sensor, Anal. Proc. Incl. Anal. Commun., 1995, vol. 32, p. 21. https://doi.org/10.1039/AI9953200021
Elobeid, W.H. and Elbashir, A.A., Development of chemically modified pencil graphite electrode based on benzo-18-crown-6 and multi-walled CNTs for determination of lead in water samples, Prog. Chem. Biochem. Res., 2019, vol. 2, p. 24.
Gupta, V.K., Nayak, A., Agarwal, S., and Singhal, B., Recent advances on potentiometric membrane sensors for pharmaceutical analysis, Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screening, 2011, vol. 14, p. 284. https://doi.org/10.2174/138620711795222437
Beitollahi, H., Tajik, S., Asadi, M.H., and Biparva, P., Application of a modified graphene nanosheet paste electrode for voltammetric determination of methyldopa in urine and pharmaceutical formulation, J. Anal. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 5, p. 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-014-0029-y
Gupta, V.K., Sethi, B., Sharma, R.A., Agarwal, S., et al., Mercury selective potentiometric sensor based on low rim functionalized thiacalix [4]-arene as a cationic receptor, J. Mol. Liq., 2013, vol. 177, p. 114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.10.008
Srikanta, S.A., Naik, P.N.P., and Krishanamurthy, G.N., Electrochemical behaviour of 5-methoxy-5,6-bis(3-nitropheyl-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazine-3(2H))-thione in presence of salicylaldehyde on zinc cathode with surface morphology and biological activity, Asian J. Green Chem., 2020, vol. 4, p. 149.
Gupta, V.K., Neutral carrier and organic resin based membranes as sensors for uranyl ions, Anal. Proc. Incl. Anal. Commun., 1995, vol. 32, p. 263. https://doi.org/10.1039/AI9953200263
Motaghi, M.M., Beitollahi, H., Tajik, S., and Hosseinzadeh, R., Nanostructure electrochemical sensor for voltammetric determination of vitamin C in the presence of vitamin B6: Application to real sample analysis, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2016, vol. 11, p. 7849.
Gupta, V.K., Ganjali, M.R., Norouzi, P., Khani, H., et al., Electrochemical analysis of some toxic metals by ion-selective electrodes, Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2011, vol. 41, p. 282. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2011.589773
Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H., Beitollahi, H., Tajik, S., Malakootian, M., et al., Simultaneous determination of hydroxylamine and phenol using a nanostructure-based electrochemical sensor, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2014, vol. 186, p. 7431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3938-8
Gupta, V.K., Singh, L.P., Singh, R., Upadhyay, N., et al., A novel copper (II) selective sensor based on dimethyl 4,4'(o-phenylene) bis(3-thioallophanate) in PVC matrix, J. Mol. Liq., 2012, vol. 174, p. 11.
Tajik, S., Taher, M.A., Beitollahi, H., and Torkzadeh-Mahani, M., Electrochemical determination of the anticancer drug taxol at a ds-DNA modified pencil-graphite electrode and its application as a label-free electrochemical biosensor, Talanta, 2015, vol. 134, p. 60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.063
Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, V.K., and Jain, S., Determination of lead using a poly (vinyl chloride)-based crown ether membrane, Analyst, 1995, vol. 120, p. 495. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9952000495
Esfandiari-Baghbamidi, S., Beitollahi, H., Tajik, S., and Hosseinzadeh, R., Voltammetric sensor based on 1-benzyl-4-ferrocenyl-1H-[1,2,3]-triazole/carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode; detection of hydrochlorothiazide in the presence of propranolol, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2016, vol. 11, p. 10874.
Jain, A.K., Gupta, V.K., Sahoo, B.B., and Singh, L.P., Copper(II)-selective electrodes based on macrocyclic compounds, Anal. Proc. Incl. Anal. Commun., 1995, vol 32, p. 99. https://doi.org/10.1039/AI9953200099
Tajik, S. and Beitollahi, H., Electrochemical determination of sertraline at screen printed electrode modified with feather like La3+/ZnO nano-flowers and its determination in pharmaceutical and biological samples, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2020, vol. 56, p. 222.
Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, V.K., and Jain, S., PVC-based 2,2,2-cryptand sensor for zinc ions, Anal. Chem., 1996, vol. 68, p. 1272. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9507000
Taherkhani, A., Jamali, T., Hadadzadeh, H., Karimi-Maleh, H., et al., ZnO nanoparticle-modified ionic liquid-carbon paste electrode for voltammetric determination of folic acid in food and pharmaceutical samples, Ionics, 2014, vol. 20, p. 421.
Mazloum-Ardakani, M., Beitollahi, H., Amini, M.K., Mirkhalaf, F., et al., Application of 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1, 3-dithialone self-assembled monolayer on gold electrode as a nanosensor for electrocatalytic determination of dopamine and uric acid, Analyst, 2011, vol. 136, p. 1965. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AN00823K
Gupta, V.K., Goyal, R.N., and Sharma, R.A., Comparative studies of neodymium(III)-selective PVC membrane sensors, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2009, vol. 647, p. 66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.05.031
Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, V.K., and Jain, S., A PVC-based benzo-15-crown-5 membrane sensor for cadmium, Electroanalysis, 1996, vol. 8, p. 938. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.1140081017
Gupta, V.K. and Kumar, P., Cadmium(II)-selective sensors based on dibenzo-24-crown-8 in PVC matrix, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1999, vol. 389, p. 205. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00154-3
Ali, T.A., Mohamed, G.G., Aglan, R.F., and Mourad, M.A., A novel screen-printed and carbon paste electrodes for potentiometric determination of uranyl(II) ion in spiked water samples, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2018, vol. 54, p. 201. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193517110027
Thivya, P., Ramya, R., and Wilson, J., Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/taurine biocomposite on screen printed electrode: Non-enzymatic cholesterol biosensor, Microchem. J., 2020, vol. 157, art. ID 105037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105037
Beitollahi, H., Dourandish, Z., Tajik, S., Ganjali, M.R., et al., Application of graphite screen printed electrode modified with dysprosium tungstate nanoparticles in voltammetric determination of epinephrine in the presence of acetylcholine, J. Rare Earth, 2018, vol. 36, p. 750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.01.010
Ganjali, M.R., Dourandish, Z., Beitollahi, H., Tajik, S., et al., Highly sensitive determination of theophylline based on graphene quantum dots modified electrode, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2018, vol. 13, p. 2448.
Gevaerd, A., Banks, C.E., Bergamini, M.F., and Marcolino-Junior, L.H., Nanomodified screen-printed electrode for direct determination of aflatoxin B1 in malted barley samples, Sens. Actuators, B, 2020, vol. 307, p. 127547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127547
Karimi-Maleh, H., Tahernejad-Javazmi, F., Atar, N., Yola, M.L., et al., A novel DNA biosensor based on a pencil graphite electrode modified with polypyrrole/functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes for determination of 6-mercaptopurine anticancer drug, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2015, vol. 54, p. 3634. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie504438z
Yola, M.L., Gupta, V.K., Eren, T., Sen, A.E., et al., A novel electro analytical nanosensor based on graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of quercetin and morin, Electrochim. Acta, 2014, vol. 120, p. 204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.12.086
Goyal, R.N., Gupta, V.K., Sangal, A., and Bachheti, N., Voltammetric determination of uric acid at a fullerene-C(60)-modified glassy carbon electrode, Electroanalysis, 2005, vol. 17, p. 2217. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200503353
Beitollahi, H. and Garkani-Nejad, F., A carbon paste electrode modified by graphene oxide/Fe3O4SiO2/ionic liquid nanocomposite for voltammetric determination of acetaminophen in the presence of tyrosine, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2019, vol. 55, p. 1162. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193519120024
Wei, Z., Yang, Y., Xiao, X., Zhang, W., et al., Fabrication of conducting polymer/noble metal nanocomposite modified electrodes for glucose, ascorbic acid and tyrosine detection and its application to identify the marked ages of rice wines, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, vol. 255, p. 895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.155
Parlak, O., Incel, A., Uzun, L., Turner, A.P., et al., Structuring Au nanoparticles on two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets for electrochemical glucose biosensors, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, vol. 89, p. 545.
Su, S., Sun, H., Xu, F., Yuwen, L., et al., Highly sensitive and selective determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using gold nanoparticles-decorated MoS2 nanosheets modified electrode, Electroanalysis, 2013, vol. 25, p. 2523. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201300332
Ela, S.E., Remskar, M., Karaca, G.Y., Oksuz, L., et al., RF plasma modified W5O14 and MoS2 hybrid nanostructures and photovoltaic properties, Part. Sci. Technol., 2019, vol. 37, pp. 616–622. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2017.1414091
Barua, S., Dutta, H.S., Gogoi, S., Devi, R., et al., Nanostructured MoS2-based advanced biosensors: a review, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2017, vol. 1, pp. 2–25. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.7b00157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Zohreh Ghazanfari, Sarhadi, H. & Tajik, S. Determination of Sudan I and Bisphenol A in Tap Water and Food Samples Using Electrochemical Nanosensor. Surf. Engin. Appl.Electrochem. 57, 397–407 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375521030066
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375521030066



