Abstract
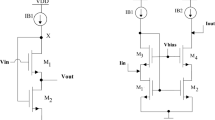
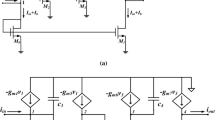
High performance sub-volt current mirror are widely used in building mixed-mode low power VLSI systems. The performance of current mirror is decided by its key parameters which includes large operating range, low input compliance voltage, wide swing, large bandwidth along with very low input and very high output resistances. In this paper, a design of high performance low power current mirror is shown. The proposed current mirror is based on flipped voltage follower which enables the current mirror to work at low voltage. For improvement in input output resistance the proposed current mirror is employed with super transistor and super cascode stage. The current mirroring with minimum error is achieved till 1mA with power dissipation in the range of micro watt. The achieved bandwidth is 2.1 GHz along with low input and high output resistances as 0.407 ohm and 50 giga ohm, respectively. The process corner, temperature analysis and noise analysis of the proposed current mirror is also shown in this paper. The complete analysis is done using HSpice on 0.18 um technology at a dual supply voltage of 0.5 V.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari M, Javid A and Hashemipour O 2014 A high input dynamic range, low voltage cascode current mirror and enhanced phase-margin folded cascode amplifier. In: Proceedings of the Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, pp. 77–81
Chavoshisani R and Hashemipour O 2011 A high-speed current conveyor based current comparator. Microelectron. Journal. 42: 28–32
Khateb F, Bay S, Dabbous A and Vlassis S 2013 A Survey of Non-Conventional Techniques for Low-voltage Low-power Analog Circuit Design. Radioengineering. 22: 415–427
Blalock B J and Allen P E 1995 A low-voltage, bulk-driven MOSFET current mirror for CMOS technology. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1972-1975
Zhang X and El-Masry E 2004 A regulated body-driven CMOS current mirror for low-voltage applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs. 51: 571–577
Aggarwal B, Gupta M and Gupta A K 2013 Analysis of low voltage bulk-driven self-biased high swing cascode current mirror. Microelectronics Journal. 44: 225–235
Sharma S, Rajput S S, Mangotra L K and Jamuar S S 2006 FGMOS current mirror: behavior and bandwidth enhancement. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing. 46: 281–286
Manhas P S, Sharma S, Pal K, Mangotra L K and Jamwal K K S 2008 High performance FGMOS-based low voltage current mirror. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics. 46: 355–358
Gupta M, Srivastava R and Singh U 2014 Low voltage high performance FGMOS based Wilson current mirror, In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks, pp. 565-570
Lopez-Martin A J, Ramirez-Angulo J, Carvajal R G and Algueta J M 2008 Compact class AB CMOS current mirror. Electronics Letters. 44: 1335–1336
Esparza-Alfaro F, Lopez-Martin A J, Ramírez-Anguloa J and Carvajal R G 2012 Low-voltage highly-linear class AB current mirror with dynamic cascode biasing. Electronics Letters. 48: 1336–1338
Raj N, Singh A K and Gupta A K 2014 Low power high output impedance high bandwidth QFGMOS current mirror. Microelectronics Journal. 45: 1132–1142
Esparza-Alfaro F, Lopez-Martin A J, Carvajal R G and Ramirez-Angulo J 2014 Highly linear micropower class AB current mirrors using Quasi-Floating Gate transistors. Microelectronics Journal. 45: 1261–1267
Raj N, Singh A K and Gupta A K 2014 Low-voltage bulk-driven self-biased cascode current mirror with bandwidth enhancement. Electronics Letters. 50: 23–25
Raj N, Singh A K and Gupta A K 2016 Low voltage high output impedance bulk-driven quasi-floating gate self-biased high-swing cascode current mirror. Circuit System and Signal Processing. 35: 2683–2703
Raj N, Singh A K and Gupta A K 2016 Low voltage high performance bulk-driven quasi-floating gate self-biased cascode current mirror. Microelectronics Journal. 52: 124–133
Carvajal R G, Ramirez-Angulo J, Lopez-Martin A J, Torralba A, Galan J A G, Carlosena A and Chavero F M 2005 The flipped voltage follower: a useful cell for low-voltage low-power circuit design. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers. 52: 1276–1291
Peluso V, Steyaert M and Sansen W 1999 Design of Low-Voltage Low-Power Sigma-Delta A/D Converters. Kluwer, MA Boston
Rijns J F 1993 54 MHz switched-capacitor video channel equalizer. Electronics Letters. 29: 2181–2182
Prodanov V I and Green M M 1996 CMOS current mirrors with reduced input and output voltage requirements. Electronics Letters. 32: 104–105
Torralba A, Carvajal R G, Ramirez-Angulo J and Munoz E 2002 Output stage for low supply voltage high-performance CMOS current mirrors. Electronics Letters. 38: 1528–1529
Ramírez-Angulo J, Carvajal R G and Torralba A 2004 Low supply voltage high-performance CMOS current mirror with low input and output voltage requirements. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs. 51: 124–129
Azhari S, Baghtash H F and Monfaredi K 2011 A novel ultra-high compliance, high output impedance low power very accurate high performance current mirror. Microelectronics Journal. 42: 432–439
Bastan Y, Hamzehil E and Amiri P 2016 Output impedance improvement of a Low Voltage Low Power Current mirror based on body driven technique. Microelectronics Journal. 56: 163–170
Aggarwal B, Gupta M, Gupta A K and Sangal A 2016 A new low voltage level-shifted FVF current mirror with enhanced bandwidth and output resistance. International Journal of Electronics. 103: 1759–1775
Safari L and Minaei S 2017 A low-voltage low-power resistor-based current mirror and its applications. Journal of Circuit System and Computers. 26: 175–180
Doreyatim M S, Akbari M and Nazari M 2019 A low-voltage gain boosting-based current mirror with high input/output dynamic range. Microelectronics Journal. 90: 88–95
Bchir M, Aloui I and Hassen N 2020 A bulk-driven quasi-floating gate FVF current mirror for low voltage, low power applications. Integration. 74: 45–54
Martinez-Heredia J M and Torralba A 2011 Enhanced source-degenerated CMOS differential transconductor. Microelectronics Journal. 42: 396–402
Safari L and Azhari S J 2013 A novel wide band super transistor based voltage feedback current amplifier. International Journal of Electronics and Communication. 67: 624–631
Hassen N and Gabbouj H 2011 Low voltage high performance current mirrors: application to linear voltage to current converter. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Application. 39: 47–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domala, N., Sasikala, G. Low power flipped voltage follower current mirror with improved input output impedances. Sādhanā 46, 142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-021-01665-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-021-01665-6