Abstract
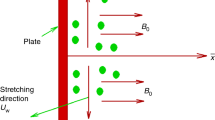
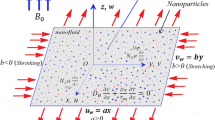
Micropolar fluids are used in lubrication theory, thrust bearing technologies, cervical flows, lubricants, paint rheology, and the polymer industry. This study develops the numerical simulation of the magneto-Darcy flow of a polarized nanoliquid with Joule heating and viscous heating mechanisms on an exponentially elongated surface. The effects of linearized Rosseland radiation and temperature-dependent heat generation are considered. The flow is generated by an exponential form of elongation of a flexible sheet. The porous matrix and nanoparticle effects are characterized by the Darcy expression and the two-component Buongiorno model correspondingly. The resulting partial differential systems are solved numerically using the Runge–Kutta-based shooting technique to interpret the importance of key parameters in physical quantities. A direct comparison is made to validate the results. Our results demonstrated that arbitrary movement of the nanoparticles significantly advances the temperature profile by reducing the concentration of nanoparticles. Both Joule heating and viscous heating mechanisms improve the structure of the thermal boundary layer. The porous matrix reduces the velocity of the nanoliquid and thus the width of the velocity boundary layer is reduced.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(u\) and \(v\) :
-
Velocity along \(x\) and y direction \(\left( {{\rm m\,s}^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(k\) :
-
Vortex viscosity \(\left( {{\rm m}^{2} ~{\rm s}^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(m\) :
-
Surface condition parameter \(\left( {0 \le m \le 1} \right)\)
- \(B\) :
-
Variable magnetic field (T)
- \(Kp^{*}\) :
-
Porous matrix
- \(C_{\rm f}\) :
-
Local skin friction coefficient
- \(Q\) :
-
Heat source/sink coefficients
- \(v_{w} \left( x \right)\) :
-
Suction/injection velocity \(\left( {{\rm m\,s}^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(K\) :
-
Material parameter
- \(j\) :
-
Microinertia per unit mass
- \(R\) :
-
Radiation parameter
- \(k^{*}\) :
-
Absorption coefficient
- \(M_{x}\) :
-
Local couple stress
- \(C_{p}\) :
-
Specific heat \(\left( {{\rm J}~{\rm kg}^{{ - 1}} {\rm K}^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(M\) :
-
Magnetic field factor
- \(C\) :
-
Concentration
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature (K)
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- \(D_{\rm B}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \(D_{\rm T}\) :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- \(Nb\) :
-
Brownian motion factor
- Ec :
-
Eckert number
- N :
-
Micro-rotation velocity \(\left( {{\rm s}^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(Sh_{x}\) :
-
Local Sherwood number
- \(Nu_{x}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \(Sc\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(S\) :
-
Heat source factor
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- Nt :
-
Thermophoresis factor
- \(\eta\) :
-
Similarity variable
- \(\kappa\) :
-
Micropolar fluid material property
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity \(\left( {{\rm m}^{{ - 1}}\,\Omega ^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(\sigma ^{*}\) :
-
Stefan–Boltzmann constant
- \(\tau\) :
-
Ratio of the effective heat transfer capacities of particles to liquid
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity \(\left( {{\rm kg\,m\,s}^{{ - 1}} } \right)\)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- \(\upsilon\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity \(\left( {{\rm m^{2}\,s^{{ - 1}}}} \right)\)
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity \(\left( {{\rm m^{2}\,s^{{ - 1}} }}\right)\)
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Spin gradient viscosity
- \(B_{0} ,~K,p_{0} ,~Q_{0} ,~v_{0}\) :
-
Constants
References
Eringen, C.: Theory of thermo-micro fluids. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 38, 480–496 (1972)
Jena, S.K.; Mathur, M.N.: Similarity solutions for laminar free convection flow of a thermomicropolar fluid past a non-isothermal vertical flat plate. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 19, 1431–1439 (1981)
Ahmadi, G.: Self-similar solution of incompressible micropolar boundary layer flow over a semi-infinite plate. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 14, 639–646 (1976)
Ishak, A.: Thermal boundary layer flow over a stretching sheet in a micropolar fluid with radiation effect. Meccanica 45, 367–373 (2010)
Debarati, M.; Babu, R.; Mahanthesh, B.: Theoretical and analytical analysis of convective heat transport of radiated micropolar fluid over a vertical plate under nonlinear Boussinesq approximation. Multidisc. Model. Mater. Struct. 48, 81 (2020)
Rashidi, M.M.: Analytic approximate solutions for heat transfer of a micropolar fluid through a porous medium with radiation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 16, 1874–1889 (2011)
Shit, G.C.: Unsteady flow and heat transfer of a MHD micropolar fluid over a porous stretching sheet in the presence of thermal radiation. J. Mech. 29, 559–568 (2013)
Turkyilmazoglu, M.: A note on micropolar fluid flow and heat transfer over a porous shrinking sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 72, 288–291 (2014)
Gireesha, B.J.; Mahanthesh, B.; Manjunatha, P.T.; Gorla, R.S.R.: Numerical solution for hydromagnetic boundary layer flow and heat transfer past a stretching surface embedded in non-Darcy porous medium with fluid–particle suspension. J Nig Math Soc. 34, 267–285 (2015)
Aurangzaib, M.S.; Uddin, K.; Bhattacharyya, S.: Shafie Micropolar fluid flow and heat transfer over an exponentially permeable shrinking sheet. Propul. Power Res. 5, 310–317 (2016)
Mabood, F.; Ibrahim, S.M.: Effects of Soret and non-uniform heat source on MHD non-Darcian convective flow over a stretching sheet in a dissipative micropolar fluid with radiation. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 9, 2503–2513 (2016)
Rout, P.K.; Sahoo, S.N.; Dash, G.C.; Mishra, S.R.: Chemical reaction effect on MHD free convection flow in a micropolar fluid. Alex. Eng. J. 55, 2967–2973 (2016)
Tripathy, R.S.; Dash, G.C.; Mishra, S.R.; Hoque, M.M.: Numerical analysis of hydromagnetic micropolar fluid along a stretching sheet embedded in porous medium with non-uniform heat source and chemical reaction. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 19, 1573–1581 (2016)
Swain, K.; Mahanthesh, B.; Oudina, F.M.: Heat transport and stagnation-point flow of magnetized nanoliquid with variable thermal conductivity, Brownian moment, and thermophoresis aspects. Heat Transfer (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.21902
Hsiao, K.-L.: Micropolar nanofluid flow with MHD and viscous dissipation effects towards a stretching sheet with multimedia feature. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 112, 283–290 (2017)
Senapati, M.; Parida, S.K.; Swain, K.; Ibrahim, S.M.: Analysis of variable magnetic field on chemically dissipative MHD boundary layer flow of Casson fluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet with slip conditions. Int. J. Ambient Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1831601
Lund, L.A.: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow of micropolar fluid with effects of viscous dissipation and Joule heating over an exponential shrinking sheet. Symmetry 12, 142–158 (2020)
Yousif, M.A.; Ismael, H.F.; Abbas, T.; Ellahi, R.: Numerical study of momentum and heat transfer of MHD Carreau nanofluid over an exponentially stretched plate with internal heat source/sink and radiation. Heat Transfer Res. 50(7), 649 (2019)
Rehman, S.U.; Mariam, A.; Ullah, A.; Asjad, M.I.; Bajuri, M.Y.; Pansera, B.A.; Ahmadian, A.: Numerical computation of buoyancy and radiation effects on MHD micropolar nanofluid flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet with heat source. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 25,(2021)
Ghadikolaei, S.S.; Hosseinzadeh, K.; Ganji, D.D.; Jafari, B.: Nonlinear thermal radiation effect on magneto Casson nanofluid flow with Joule heating effect over an inclined porous stretching sheet. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 12, 176–187 (2018)
Swapna, G.; Kumar, L.; Rana, P.; Kumari, A.; Singh, B.: Finite element study of radiative mixed convection magneto-micropolar flow in a porous medium with chemical reaction and convective condition. Alex. Eng. J. 57(1), 107–120 (2018)
Mishra, S.R.; Baag, S.; Mohapatra, D.K.: Chemical reaction and Soret effects on hydromagnetic micropolar fluid along a stretching sheet. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 19(4), 1919–1928 (2016)
Rout, P.K.; Sahoo, S.N.; Dash, G.C.; Mishra, S.R.: Chemical reaction effect on MHD free convection flow in a micropolar fluid. Alex. Eng. J. 55(3), 2967–2973 (2016)
Mishra, S.R.; Hoque, M.M.; Mohanty, B.; Anika, N.N.: Heat transfer effect on MHD flow of a micropolar fluid through porous medium with uniform heat source and radiation. Nonlinear Eng. 8(1), 65–73 (2019)
Shi, L.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.: Thermophysical properties of Fe3O4@ CNT nanofluid and controllable heat transfer performance under magnetic field. Energy Convers. Manage. 177, 249–257 (2018)
Shi, L.; Hu, Y.; He, Y.: Magnetocontrollable convective heat transfer of nanofluid through a straight tube. Appl. Thermal Eng. 162, 114220 (2019)
Shi, L.; Hu, Y.; He, Y.: Magneto-responsive thermal switch for remote-controlled locomotion and heat transfer based on magnetic nanofluid. Nano Energy 71, 104582 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would also like to thank the Editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, P., Mahanthesh, B., Nisar, K.S. et al. Boundary layer flow of magneto-nanomicropolar liquid over an exponentially elongated porous plate with Joule heating and viscous heating: a numerical study. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 12405–12415 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05926-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05926-8