Abstract
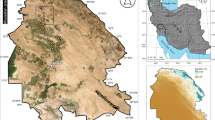
Prioritization of river basin in semi-arid to sub-humid tropical region is important in the context of natural resources conservation and management. In this paper, the Gomti River basin was prioritized for soil–water resource conservation based on analysis of morphometric parameters and land use–land cover with RS and GIS techniques. Gomti River is a monsoon and groundwater-fed river; it is a tributary of Ganga River. The basin has been divided into seventeen sub-basins. ASTER (30 m) Digital Elevation Model data and LANDSAT—8 (30 m) satellite imagery were used to analyze the morphometric parameters and to generate land-use–land-cover data for the basin through supervised image classification technique. The linear, areal, and relief aspects of each sub-basins were determined. Morphometric analysis revealed that the basin is a fifth-order drainage system with a dendritic to sub-dendritic drainage pattern. Drainage patterns indicate that sub-surface materials are homogeneous and lack structural control over topography. The circulatory ratio value indicates the basin is an elongated shape. Low values of morphometric parameters indicate good permeability, infiltration, and coarse drainage texture, low relief, and elongated shape indicated good groundwater potential in the basin. The final prioritization result shows that the sub-basin 12 is at the highest priority with the greatest shortage of groundwater potential, so immediate water conservation measures are needed. Contrary, sub-basin 3 is at low priority that indicates the highest groundwater potential. This study suggests the primary priority to improve the water resource management in semi-arid regions at the basin level.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, C. S. (1998). Study of drainage pattern through aerial data in Naugarh area of Varanasi district U.P., Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 26, pp 169175.
Abeysingha, N. S., Singh, M., Sehgal, V. K., Khanna, M., & Pathak, H. (2015). Analysis of trends in streamflow and its linkages with rainfall and anthropogenic factors in Gomti River basin of North India. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 108(12), 2202–2212.
Abrams, M., Crippen, R., & Fujisada, H. (2020). ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) and ASTER Global Water Body Dataset (ASTWBD). Remote Sens., 12, 1156.
Bhattacharyya, R., Ghosh, B., Mishra, P., Mandal, B., Rao, C., & Sarkar, D. (2015). Soil degradation in India: Challenges and potential solutions. Sustainability, 7, 3528–3570.
Bhattacharya, R. K., Chatterjee, N. D., & Das, K. (2019). Multi-criteria-based sub-basin prioritization and its risk assessment of erosion susceptibility in Kansai–Kumari catchment area India. Applied Water Science, 9(4), 1-30.
Chorley, R. J., Donal, M. E. G., & Pogorzelski, H. A. (1957). A new standard for estimating drainage basin shape. American Journal Science, 255, 138–141.
Chandniha, S. K., & Kansal, M. L. (2014). Prioritization of subwatersheds based on morphometric analysis using geospatial technique in Piperiya watershed India. Applied Water Science, 7(1), 329–338.
Clarke, J. J. (1966). Morphometric map, Essays in geomorphology, Elsvier, New York, pp 235–274
Chitra, C., Alaguraja, P., Ganeshkumari, K., Yuvaraj, D., & Manivel, M. (2011). Watershed characteristics of Kundahsubbasin using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Int J Geomatics Geosci, 2(1), 311–335.
Choudhari, P. P., Nigam, G. K., Singh, S. K., & Thakur, S. (2018). Morphometric based prioritization of watershed for groundwater potential of Mula river basin, Maharashtra, India. GeolEcol Landscapes, 9508, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1452482
Dempsey, N., Jayaraj, S. R., & Redmond, E. (2018). There’s always the river: Social and environmental equity in rapidly urbanising landscapes in India. Landscape Research, 43, 275–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/01426397.2017.1315389
Das, B., Jain, S., Singh, S., & Thakur, P. (2019). Evaluation of multisite performance of SWAT model in the Gomti River Basin India. Applied Water Science, 9, 134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1013-x
Farhan, Y., Al-shaikh, N., & Mausa, R. (2017). Prioritization of semi-arid agricultural watershed using morphometric and principal component analysis, remote sensing, and GIS techniques, the Zerqa River Watershed. AgricSci, 8, 113–148. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2017.81009
Gajbhiye, S., Mishra, S. K., & Pandey, A. (2014). Prioritizing erosion-prone area through morphometric analysis: An RS and GIS perspective. Applied Water Science, 4, 51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0129-7
Gottschalk, L. C. (1964). Reservoir Sedimentation. In: V.T. Chow (ed), Handbook of Applied Hydrology. McGraw Hill Book Company, Section 7I
Gunjan, P., Mishra, S. K., Lohani, A. K., & Chandniha, S. K. (2019). The study of morphological characteristics for best management practices over the Rampur watershed of Mahanadi River Basin using prioritization. Journal Indian Soc Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01061y
Horton, R. E. (1932). Drainage basin characteristics. Transactions-American Geophysical Union, 13, 350–361.
Horton, R. E. (1945). Erosional development of streams and their drainage density: Hydrophysical approach to quantitative geomorphology. Geological Society America Bulletin, 56, 275–370.
Javed, A., Khanday, M. Y., & Ahmed, R. (2009). Prioritization of subwatersheds based on morphometric and land use analysis using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(2), 261–274.
Javed, A., Khanday, M. Y., & Rais, S. (2011). Watershed prioritization using morphometric and land use/land cover parameters: A remote sensing and GIS based approach. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 78, 63–75.
Jhariya, D. C., Kumar, T., & Panday, H. K. (2018). Watershed prioritization based on soil and water hazard model using remote sensing, geographic information systems and multi-criteria decision analysis approach. Geocarto International. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1510039
Jones, J. A. A. (1999). Global hydrology: Processes, resources and environmental management. Longman, 399
Khare, D., Mondal, A., & Mishra, P. K. (2014). Morphometric analysis for prioritization using remote sensing and GIS technologies in a hilly catchment in the State of Uttarakhand India. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 7(10), 1650–1662.
Magesh, N. S., Jitheshlal, K. V., Chandrasekar, N., & Jini, K. V. (2012). GIS based morphometric evaluation of Chimmini and Mupily watersheds, parts of western Ghats, Thrissur District, Kerala, India. Earth SciInf, 5, 111–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-012-0101-3
Meshram, S. G., & Shrama, S. K. (2017). Prioritization of watershed through morphometric parameters: A PCA-based approach. Applied Water Science, 7, 1505–1519.
Miller, V. C. (1953). A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in the Clinch mountain area Virginia and Tennessee. New York (NY): Department of Geology, ONR, Columbia University, Virginia and Tennessee (Proj. NR 389–402, Technical Report 3).
Mundetia, N., Sharma, D., & Dubey, S. K. (2018). Morphometric assessment and sub-watershed prioritization of Khari River basin in semi-arid region of Rajasthan India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3819-5
Nautiyal, M. D. (1994). Morphometric analysis of a drainage basin, district Dehradun Uttar Pradesh. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote, 22(4), 251–261.
Prakash, K., Rawat, D., Singh, S., et al. (2019). Morphometric analysis using SRTM and GIS in synergy with depiction: A case study of the Karmanasa River basin, North central India. Applied Water Science, 9, 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0887-3
Prakash, K., Singh, S., Mohanty, T., et al. (2017). Morphometric assessment of Gomati river basin, middle Ganga plain, Uttar Pradesh, North India. Spatial Information Research, 25, 449–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41324-017-0110-x
Puno, G. R., & Puno, R. C. C. (2019). Watershed conservation prioritization using geomorphometric and land use-land cover parameters. Global J Environ Sci Manage, 5(3), 279–294.
Rao, D. P. (2000). Role of remote sensing and geographic information system in sustainable development. International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing XXXIII, B7, 1231–1251.
Reddy, V. R. (2003). Land Degradation in India. Econ PolitWkly, 38, 4700–4713.
Rai, S. K., Kumar, S., Rai, A. K., & Palsaniya, D. R. (2014). Climate change, variability and rainfall probability for crop planning in few districts of Central India. AtmosClimSci, 4, 394–403.
Rai, P. K., Chaubey, P. K., Mohan, K., Singh, P. (2017a). Geoinformatics for assessing the inferences of quantitative drainage morphometry of the Narmada Basin in India. ApplGeomat 9(3):1–23. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-017-0191-1
Rai, P. K., Mishra, V. N., & Mohan, K. (2017b). A study of morphometric evaluation of the Son basin, India using geospatial approach. Remote SensApplSoc Environ, 7, 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2017.05.001
Rai, P. K., Chandel, R. C., Mishra, V. N., & Singh, P. (2018). Hydrological inferences through morphometric analysis of lower Kosi River Basin of India for water resource management based on remote sensing data. Applied Water Science (springer), 8–15, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0660-7
Samal, D. R., Gedam, S. S., & Nagarajan, R. (2015). GIS based drainage morphometry and its influence on hydrology in parts of Western Ghats region, Maharashtra India. Geoc. Int., 30(7), 755–778.
Sangma, F., & Guru, B. (2020). Watersheds characteristics and prioritization using morphometric parameters and Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchal Process (FAHP): A part of lower subansiri sub-basin. Journal of the Indian Society Remote Sensing, 48, 473–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01091-6
Shaikh, M., & Birajdar, F. (2015). Analysis of watershed characteristics using remote sensing and gis techniques. International Journal Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology. Doi: https://doi.org/10.15680/IJIRSET.2015.0404023
Schumm, S. A. (1956). Evolution of drainage systems & slopes in badlands at Perth Anboy. New Jersey Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 67, 597–646.
Smith, K. G. (1950). Standards for grading texture of erosional topography. American Journal of Science, 248, 655–668.
Sreedevi, P. D., Subrahmanyam, K., & Ahmed, S. (2005). Integrated approach for delineating potential zones to explore for groundwater in the Pageru River basin, Kuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 13, 534–545.
Strahler, A. N. (1952). Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 63, 1117–1142.
Strahler, A. N. (1957). Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Transaction of American Geophysical Union, 38(6), 913–920.
Strahler, A. N. (1964). Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and Channel networks. In: Hand book of Applied Hydrology, Chow, V. T. (Ed.), 4: 39 - 44.
Subramanya, K. (2013). Engineering Hydrology, 4e. Tata McGraw-Hill Education
Sinha, R. K., & Eldho, T. I. (2021). Assessment of soil erosion susceptibility based on morphometric and landcover analysis: A case study of Netravati River Basin, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-021-01354-1
Tamma, Rao, G. T., Gurunadha, Rao. V.V.S., Dakate, R., et al. (2012). Remote sensing and GIS based comparative morphometric study of two subwatersheds of different physiographic conditions, west Godavari District, A.P. Journal of Geological Society India 79:383–390.
Wani, M. H., & Javed, A. (2013). Evaluation of natural resource potential in semi-arid micro-watershed, eastern Rajasthan, using remote sensing and geographic information system. Arabian Journal of Geosciences , 6, 1843–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0472-7
Verstappen, H. (1983). The applied geomorphology. International Institute for Aerial Survey and Earth Science (ITC), Enschede
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Das, B., Singh, S., Jain, S.K. et al. Prioritization of Sub-Basins of Gomti River for Soil and Water Conservation Through Morphometric and LULC Analysis Using Remote Sensing and GIS. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 49, 2503–2522 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-021-01410-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-021-01410-w