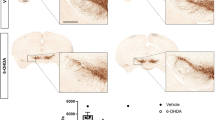
Abstract—It was shown that sphingolipids are necessary for the normal functioning of neurons, and disturbance of their metabolism accompanies the development of brain diseases, including Parkinson’s disease (PD). Since the possibilities for studying the role of sphingolipids in the pathogenesis of PD in patients are extremely limited, experimental models must be used to solve this problem. Thus, in this work, using chromatography-mass spectrometry, the content of key molecular species of sphingolipids, total ceramides, hexosylceramides, and their derivatives, sphingosine and sphinganine, with proapoptotic properties in mice were studied using a model of the clinical stage of PD for the first time. This model was obtained by systemically administering 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), which in the brain turns into MPP +, a toxin for catecholaminergic neurons. In the control, instead of MPTP, 0.9% NaCl was injected. It was shown that the total concentration of all studied sphingolipids increases in the substantia nigra, the location of dopaminergic neuron bodies, compared to the control. This occurred due to an increase in the concentration of ceramides associated with fatty acids, such as C18:1/14:0, C18:1/18:0, C18:1/24:1, and monohexosylceramides associated with fatty acids such as C18:1/18:0 and C18:1/24:1. Unlike the substantia nigra, the striatum, the site of projection of dopaminergic axons, had no changes in the content of sphingolipids. These data indicate that the death of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in the PD model is accompanied by a change in the metabolism of sphingolipids, which opens up new possibilities for studying their role in the pathogenesis of this disease and in the search for a new class of drugs that correct sphingolipid metabolism.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alessenko, A.V. and Albi, E., Front. Neurol., 2020, p. 11:437.
Gutner, U.A., Shupik, M.A., Maloshitskaya, O.A., Sokolov, S.A., Rezvykh, A.P., Funikov, S.Y., Lebedev, A.T., Ustyugov, A.A., and Alessenko, A.V., Biochemistry (Mosc.), 2019, vol. 84, no. 10, pp. 1166–1176.
Sardi, S.P., Viel, C., Clarke, J., Treleaven, C.M., and Richards, A.M., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2017, vol. 114, no. 10, pp. 2699–2704.
Wang, G. and Bieberich, E., Adv. Biol. Regul., 2018, vol. 70, pp. 51–64.
Hannun, Y.A. and Obeid, L.M., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2008, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 139–150.
Maceyka, M. and Spiegel, S., Nature, 2014, vol. 510, pp. 58–67.
Trayssac, M., Hannun, Y.A., and Obeid, L.M., J. Clin. Invest., 2018, vol. 128, no. 7, pp 2702–2712.
Alecu, I. and Bennett, S., Front. Neurosci., 2019, vol. 13, pp. 328–332.
Galvagnion, C., J. Parkinson’s Disease, 2017, vol. 7, pp. 433–450.
Xicoy, H., Wieringa, B., and Martens, G.J., Cells, 2019, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 27–33.
Indellicato, R. and Trinchera, M., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, vol. 20, p. E3304.
Gegg, M.E. and Schapira, A.H.V., FEBS J., 2018, vol. 285, pp. 3591–3603.
Rocha, E.M., Smith, G.A., Park, E., Cao, H., Graham, A.R., Brown, E., McLean, J.R., et al., Antioxid. Redox. Signal, 2015, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 550–564.
Mielke, M.M., Maetzler, W., Haughey, N.J., Bandaru, V.V., Savica, R., Deuschle, C., et al., PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 9, p. 73094.
Bligh, T.G. and Dyer, W.J., Can. J. Biochem. Physiol, 1959, vol. 37, pp. 911–917.
Hannun, Y.A. and Luberto, C., Trends. Cell. Biol., 2000, vol. 10, pp. 73–80.
Ugrumov, M.V., Khaindrava, V.G., Kozina, E.A., Kucheryanu, V.G., Bocharov, E.V., Kryzhanovsky, G.N., Kudrin, V.S., Narkevich, V.B., Klodt, P.M., Rayevsky, K.S., and Pronina, T.S., Neuroscience, 2011, vol. 181, pp. 175–188.
Kozina, E.A., Kim, A.R., Kurina, A.Y., and Ugrumov, M.V., Neurobiol. D., 2017, vol. 98, pp. 108–121.
Kozina, E.A., Khakimova, G.R., Khaindrava, V.G., Kucheryanu, V.G., Vorobyeva, N.E., Krasnov, A.N., Georgieva, S.G., Kerkerian-Le, GoffL., and Ugrumov, M.V., J. Neurol. Sci., 2014, vol. 340, pp. 198–207.
Mingazov, E.R., Khakimova, G.R., Kozina, E.A., Medvedev, A.E., Buneeva, O.A., Bazyan, A.S., and Ugrumov, M.V., Mol. Neurobiol., 2018, vol. 55, pp. 2991–3006.
Kim, A., Nigmatullina, R., Zalyalova, Z., Soshnikova, N., Krasnov, A., Vorobyeva, N., Georgieva, S., Kudrin, V., Narkevich, V., and Ugrumov, M., Mol. Neurobiol., 2019, vol. 56, pp. 3437–3450.
Nicotra, A. and Parvez, S., Neurotoxicol. Teratol., 2002, vol. 24, pp. 599–605.
Jackson-Lewis, V., Jakowec, M., Burke, R.E., and Przedborski, T., Neurodegeneration, 1995, vol. 4, pp. 257–269.
Agid, Y., Lancet, 1991, vol. 337, pp. 1321–1324.
Krown, K.A., Page, M.T., Nguyen, C., Zechner, D., Gutierrez, V., Comstock, K.L., et al., J. Clin. Invest., 1996, vol. 98, pp. 2854–2865.
Sweeney, E.A., Sakakura, C., Shirahama, T., Masamune, A., Ohta, H., Hakamori, S., and Igarashi, Y., Int. J. Cancer, 1996, vol. 66, pp. 358–366.
Cuvillier, O., Nava, V.T., Murthy, S.K., Edsall, L.C., Levade, T., Milstien, S., and Spiegel, S., Cell Death Differ., 2001, vol. 8, pp. 162–171.
Tamiya-Koizumi, K., Murate, T., Suzuki, M., Simbulan, C.M., Nakagawa, M., Takemura, M., et al., Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int., 1997, vol. 41, pp. 1179–1189.
Taguchi, Y.V., Liu, J., Ruan, J., Pacheco, J., Zhang, X., Abbasi, J., et al., J. Neurosci., 2017, vol. 37, no. 40, pp. 9617–9631.
Filippov, V., Song, M.A., Zhang, K., Vinters, H.V., Tung, S., Kirsch, W.M., Yang, J., and Duerksen-Hughes, P.J., J. Alzheimers. Dis., 2012, vol. 29, pp. 537–547.
Funding
This work was supported by the RFBR-KOMFI grant, project no. 18-00-01334.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval. All manipulations with animals were carried out in accordance with national and international requirements and rules approved by the Committee for the Protection of Animals of the Koltsov Institute of Developmental Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, protocol no. 27 from July 04, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alessenko, A.V., Blokhin, V.E., Shupik, M.A. et al. Changes in the Content of Sphingolipids in the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic System in the Brain of Mice with a Neurotoxic Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. J. 15, 175–180 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712421020021
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712421020021