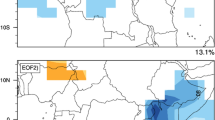
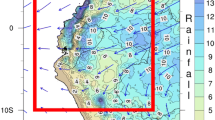
Abstract
The drivers of precipitation variability in the Ethiopian Highlands are complex, and they have considerable impact on the local rural economy of the region. While interannual variability has been studied extensively, relatively less study has focused on intra-seasonal variability in precipitation, even though this variability can be critical for agricultural activities. In this study, we examine the impacts of the Boreal Summer Intra-Seasonal Oscillation (BSISO) on precipitation variability in the Upper Blue Nile Basin (UBNB) during the rainy season (June–September). In order to optimally capture Intra-seasonal variability, we developed a customized ISO index based on leading modes of the variability in the UBNB, and found that this index shares the general character of a standard BSISO index. Analyses performed with both the customized and standard BSISO indices show that a core convective region centered on the Indian Ocean propagates to the northwest, eventually exerting significant influence on Ethiopian rainfall. The primary mechanism of influence appears to be BSISO influence on both lower and upper level tropospheric wind fields over the western Indian Ocean that influence moisture flux, convergence, and convection in the study region. This includes BSISO modulation of the East Africa Low-Level Jet and the Tropical Easterly Jet. We also find that the BSISO influence on Ethiopia is consistent with a BSISO-associated Rossby wave signal, but the magnitude of the Rossby wave signal is small relative to other mechanisms of influence.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abtew W, Melesse AM, Dessalegne T (2009) El Nino Southern Oscillation link to the Blue Nile River basin hydrology. Hydrol Process 23:3653–3660. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7367
Berhane F, Zaitchik B (2014) Modulation of daily precipitation over east Africa by the Madden–Julian oscillation. J Clim 27:6016–6034
Berhane F, Zaitchik B, Badr HS (2015) The Madden–Julian Oscillation’s influence on spring rainy season precipitation over equatorial west Africa. J Clim 28:8653–8672
Betrie GD, Mohamed YA, van Griensven A, Srinivasan R (2011) Sediment management modelling in the Blue Nile Basin using SWAT model Hydrol. Earth Syst Sci 15(3):807–818
Block P, Rajagopalan B (2007) Interannual variability and ensemble forecast of upper Blue Nile Basin Kiremt season precipitation. J Hydrometeorol 8:327–343
Chen J, Wen Z, Wu R, Chen Z, Zhao P (2015) Influences of northward propagating 25–90-day and quasi-biweekly oscillations on eastern China summer rainfall. Clim Dyn 45(1–2):105–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2334-y
Chen X, Ling J, Li C (2016) Evolution of the Madden–Julian Oscillation in two types of El Niño. J Clim 29:1919–1934
Conway D (2000) The climate and hydrology of the Upper Blue Nile River. Geogr J 166(1):49–62
De Souza EB, Ambrizzi T (2006) Modulation of the intraseasonal rainfall over tropical Brazil by the Madden Julian oscillation. Int J Climatol 26:1759–1776. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1331
DeMott CA, Klingaman NP, Woolnough SJ (2015) Atmosphere-ocean coupled processes in the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Rev Geophys 53:1099–1154
Dinku T, Funk C, Peterson P, Maidment R, Tadesse T, Gadain H, Ceccato P (2018) Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over Eastern of Africa. QJR Meteorol Soc 1:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3244
Diro GT, Grimes DIF, Black E (2011) Teleconnections between Ethiopian summer rainfall and sea surface temperature: Part I. Observation and modelling. Clim Dyn 37:103–119
Donald AM, Meinke H, Power B, Maia AHN, Wheeler MC, White N, Stone RC, Ribbe J (2006) Near-global impact of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 33:L09704. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025155
Eggen M, Ozdogan M, Zaitchik BF, Ademe D, Foltz J, Simane B (2019) Vulnerability of sorghum production to extreme, sub-seasonal weather under climate change. Environ Res Lett 14:045005
Ferranti L, Palmer TN, Molteni F, Klinker E (1990) Tropical extratropical interaction associated with the 30–60 day oscillation and its impact on medium and extended range prediction. J Atmos Sci, 47:2177–2199. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469
Ferranti L, Slingo JM, Palmer TN, Hoskins BJ (1997) Relations between interannual and intraseasonal monsoon variability as diagnosed from AMIP integrations. Q J R Meteorol Soc 123:1323–1357
Funk C, Peterson P, Landsfeld M (2015) The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci Data 2:150066. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.66
Gill AE (1980) Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 106:447–462
Gissila T, Black E, Grimes DIF, Slingo JM (2004) Seasonal forecasting of the Ethiopian summer rains. Int J Climatol 24:1345–1358
Gleixner S, Keenlyside N, Viste E, Korecha D (2017) The El Niño effect on Ethiopian summer rainfall. Clim Dyn 49(5–6):1865–1883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3421-z
Hartmann DL, Michelsen ML, Klein SA (1992) Seasonal variations of tropical intraseasonal oscillations: a 20–25 day oscillation in the Western Pacific. J Atmos Sci 49(14):1277–1289
Hidayat R, Kizu S (2010) Influence of the Madden–Julian Oscillation on Indonesian rainfall variability in austral summer. Int J Climatol 30:1816–1825. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2005
Higgins RW, Shi W (2001) Intercomparison of the principal modes of interannual and intraseasonal variability of the North American monsoon system. J Clim 14:403–417. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014%3c0403:IOTPMO%3e2.0.CO;2
Hsu P, Li T (2012) Role of the boundary layer moisture asymmetry in causing the eastward propagation of the Madden-Julian Oscillation. J Clim 25:4914–4931
Hsu PC, Lee JY, Ha KJ (2016) Influence of Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation on rainfall extremes in southern China. Int J Climatol 36(3):1403–1412. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4433
Jiang X, Li T, Wang B (2004) Structures and mechanisms of the northward-propagating Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation. J Clim 17:1022–1039
Jones C (2016) The Madden–Julian Oscillation and the monsoons. The monsoons and climate change. Springer, Berlin, pp 207–224
Jones C, Carvalho L (2011) Will global warming modify the activity of the Madden–Julian Oscillation? Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:544–552
Kemball-Cook S, Wang B (2001) Equatorial waves and air-sea interaction in the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation. J Clim 14:2923–2942
Kikuchi K, Takayabu YN (2003) Equatorial circumnavigation of moisture signal associated with the Madden-Julian Oscillation MJO during boreal winter. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 44:25–43
Kikuchi K, Wang B, Kajikawa Y (2012) Bimodal representation of the tropical intraseasonal oscillation. Clim Dyn 38:1989–2000
Kim U, Kaluarachchi JJ (2009) Climate change impacts on water resources in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. J Am Water Res Assoc 45(6):1361–1378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2009.00369.x
Klotzbach PJ (2014) The Madden–Julian oscillation’s impacts on worldwide tropical cyclone activity. J Clim 27:2317–2330. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00483.1
Knapp K, Ansari S, Bain C, Bourassa M, Dickinson M, Funk C, Huffman G (2011) Globally gridded satellite observations for climate studies. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 92:893–907. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011BAMS3039.1
Korecha D, Barnston AG (2007) Predictability of June–September rainfall in Ethiopia. Mon Weather Rev 135:628–650
Krishnamurti TN, Subramanian D (1982) The 30–50-day mode at 850 mb during MONEX. J Atmos Sci 39:2088–2095
Lau WKM, Waliser DE (eds) (2005) Intraseasonal variability of the atmosphere-ocean climate system. Springer, Heidelberg
Lavender SL, Matthews AJ (2009) Response of the West African monsoon to the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J Clim 22:4097–4116
Lee J-Y, Wang B, Wheeler MC, Fu X, Waliser DE, Kang I-S (2012) Real-time multivariate indices for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation over the Asian summer monsoon region. Clim Dyn 40(1–2):493–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1544-4
Liebmann B, Smith CA (1996) Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:1275–1277
Lin H, Frederiksen J, Straus D (2019) Sub-seasonal to seasonal prediction: tropical-extratropical interactions and teleconnections. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 143–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811714-9.00007-3
Lo F, Hendon HH (2000) Empirical extended-range prediction of the Madden–Julian Oscillation. Mon Weather Rev 128:2528–2543. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493
Madden RA (1986) Seasonal-variations of the 40–50-day oscillation in the tropics. J Atmos Sci 43:3138–3158
Madden RA, Julian PR (1971) Detection of a 40–50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical pacific. J Atmos Sci 28:702–708
Madden RA, Julian PR (1972) Description of global-scale circulation cells in tropics with a 40–50-day period. J Atmos Sci 29:1109–1123
Maloney ED, Kiehl JT (2002) MJO related SST variations over the tropical eastern Pacific during northern Hemisphere summer. J Clim 15:675–689. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442
Mao J, Wu G (2006) Intraseasonal variations of the Yangtze rainfall and its related atmospheric circulation features during the 1991 summer. Clim Dyn 27(7–8):815–830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-006-0164-2
Matthews AJ (2004) Intraseasonal variability over tropical Africa during northern summer. J Clim 17:2427–2440
Mellander PE, Gebrehiwot SG, Gärdenäs AI, Bewket W, Bishop K (2013) Summer rains and dry seasons in the Upper Blue Nile Basin: the predictability of half a century of past and future spatiotemporal patterns. PLOS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068461
Mohino E, Janicot S, Douville H, Li LZ (2012) Impact of the Indian part of the summer MJO on west Africa using nudged climate simulations. Clim Dyn 38:2319–2334
Nawaz K, Hussain K, Majeed A, Khan F, Afghan S, Ali K (2010) Fatality of salt stress to plants: morphological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Afr J Biotechnol 9(34):5475–5480
Nogués-Paegle J, Byerle LA, Mo KC (2000) Intraseasonal modulation of South American summer precipitation. Mon Weather Rev, 128:837–850. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2000)128
Pohl B, Camberlin P (2006) A typology for intraseasonal oscillations. Int J Climatol 34:430–445
Rauniyar SP, Walsh KJE (2011) Scale interaction of the diurnal cycle of rainfall over the maritime continent and Australia: influence of the MJO. J Clim 24:325–348. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3673.1
Recalde-Coronel CG, Zaitchik B, William WP (2019) Madden–Julian oscillation influence on sub-seasonal rainfall variability on the west of South America. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-05107-2
Ren H-L, Ren P (2017) Impact of Madden-Julian Oscillation upon winter extreme rainfall in Southern China: observations and predictability in CFSv2. Atmosphere 8(12):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100192
Rui H, Wang B (1990) Development characteristics and dynamic structure of tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies. J Atmos Sci 47:357–379. https://doi.org/10.1175/15200469
Shimizu MH, Ambrizzi T (2016) MJO influence on ENSO effects in precipitation and temperature over South America. Theor Appl Climatol 124:291–301
Sutcliffe JV, Parks YP (1999) The hydrology of the Nile. IAHS Special Publication 5, IAHS, Wallingford, UK
Taye MT, Willems P (2012) Temporal variability of hydroclimatic extremes in the Blue Nile Basin. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011466
Teng H, Wang B (2003) Interannual variations of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the Asian–Pacific region. J Clim 16:3572–3584
Viste E, Sorteberg A (2011) Moisture transport into the Ethiopian highlands. Int J Climatol 33:973–983
Waliser D, Sperber K, Hendon H, Kim D, Maloney E, Wheeler M, Weickmann K, Zhang C, Donner L, Gottschalck J (2008) MJO simulation diagnostics. J Clim 22:3006–3039
Wang B, Xie X (1997) A model for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Atmos Sci 54:72–86
Wang B, Webster PJ, Teng H (2005) Antecedents and self-induction of the active-break Indian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 32:L04704. doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL020996
Wang H, Wang B, Huang F, Ding Q, Lee JY (2012) Interdecadal change of the boreal summer circumglobal teleconnection (1958–2010). Geophys Res Lett 39: L12704. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL052371
Wang Y, Gozolchiani A, Ashkenazy Y, Havlin S (2016) Oceanic El-Niño wave dynamics and climate networks. New J Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/18/3/033021
Webster PJ, Magaña VO, Palmer TN, Shukla J, Tomas RA, Yanai M, Yasunari T (1998) Monsoon: processes, predictability and the prospects for prediction. J Geophys Res 103:14451–14510
Wheeler MC, Hendon HH (2004) An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Mon Weather Rev 132:1917–1932
Wheeler M, Kiladis GN (1999) Convectively coupled equatorial waves: analysis of clouds and temperature in the wavenumber-frequency domain. J Atmos Sci 56:374–399. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469
Wheeler MC, Hendon HH, Cleland S, Meinke H, Donald A (2009) Impacts of the Madden–Julian oscillation on Australian rainfall and circulation. J Clim 22:1482–1498. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2595.1
Yang J, Wang B, Bao Q (2010) Biweekly and 21–30-day variations of the subtropical summer monsoon rainfall over the lower reach of the Yangtze River basin. J Clim 23(5):1146–1159. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009jcli3005.1
Yasunari T (1979) Cloudiness fluctuations associated with the northern hemisphere summer monsoon. J Meteor Soc Jpn 57:227–242
Zaitchik BF (2017) Madden-Julian Oscillation impacts on tropical African precipitation. Atmos Res 184:88–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.10.002
Zeleke T, Giorgi F, Mengistu Tsidu G, Diro GT (2013) Spatial and temporal variability of summer rainfall over Ethiopia from observations and a regional climate model experiment. Theor Appl Climatol 111:665–681. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0700-4
Zeleke TT, Giorgi F, Diro GT, Zaitchik BF (2017) Trend and periodicity of drought over Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 37:4733–4748
Zhang CD (2005) Madden-Julian oscillation. Rev Geophys 43:RG2003. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004RG000158
Zhu B, Wang B (1993) The 30–60 day convection seesaw between the tropical Indian and western Pacific Ocean. J Atmos Sci 50:184–199
Zhu CW, Nakazawa T, Li JP, Chen LX (2003) The 30–60-day intraseasonal oscillation over the western North Pacific Ocean and its impacts on summer flooding in China during 1998. Geophys Res Lett 30(18):1952. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017817
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude and appreciation to the Department of earth and Planetary Science, John Hopkins University for hosting the first author as a visiting student and Physics Department, Bahir Dar University for their collaborations with the first author during his travel. This research was supported by U.S. National Science Foundation (NFS) award ICER-1624335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZAF: Conceived and design the experiments; Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, wrote the paper. BFZ: Writing–review and editing original draft, Fund acquisition, Resources, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Supervision, Project administration. TTZ and BDY: Supervision–review, writing and editing. CGRC: Resource, review, writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fetene, Z.A., Zaitchik, B.F., Zeleke, T.T. et al. Influence of the Boreal Summer Intra-Seasonal Oscillation on rainfall in the Blue Nile Basin. Clim Dyn 57, 3433–3445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05875-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05875-w