Abstract
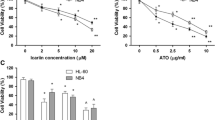
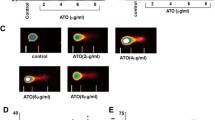
Acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL) is commonly treated with arsenic trioxide (As2O3) that has many side effects. Given the increasing trend of studies on beneficial therapeutic properties of synthetic compounds containing vanadium, the present study sought to use Schiff base oxovanadium complex to reduce the needed concentration of arsenic trioxide. The HL-60 cell line, which is a model of APL, was selected and the effects of arsenic trioxide and Schiff base oxovanadium complex were individually and simultaneously evaluated on the cell viability by the MTT assay. Flow cytometry and Real-time RT-PCR were also performed to investigate the rate of apoptosis and the expression of P53 and P21 genes, respectively. The IC50 of arsenic trioxide and Schiff base oxovanadium complex on Hl-60 cells was 8.37 ± 0.36 µM and 34.12 ± 1.52 µg/ml, respectively. At the simultaneous administration of both compounds, the maximum decrease in the cell viability was seen in co-administration of 40 µg/ml of Schiff base oxovanadium complex and 0.001 µM of arsenic trioxide. Real-time RT-PCR indicated that the co-administration of Schiff base oxovanadium complex 40 µg/ml and arsenic trioxide 0.001 µM could increase the expression of P53 and P21 genes by 3.76 ± 0.19 and 6.57 ± 1.29 fold change, respectively to the control sample. The flow cytometry studies also indicated that this co-administration could induce apoptosis up to 67% ± 0.9% significantly higher than the control sample. The use of Schiff base oxovanadium complex could significantly reduce the required dose of arsenic trioxide to induce apoptosis in HL-60 cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Yes.
References
Banerjee S, Hussain A, Prasad P, Khan I, Banik B, Kondaiah P, Chakravarty AR (2012) Photocytotoxic oxidovanadium(IV) complexes of polypyridyl ligands showing DNA-cleavage activity in near-IR light. Eur J Inorg Chem 2012(24):3899–908. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201200344
Bashash D, Safaroghli-Azar A, Delshad M, Bayati S, Nooshinfar E, Ghaffari SH (2016) Inhibitor of pan class-I PI3K induces differentially apoptotic pathways in acute leukemia cells: shedding new light on NVP-BKM120 mechanism of action. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 79:308–317
Benítez J, Guggeri L, Tomaz I, Arrambide G, Navarro M, Pessoa JC, Garat B, Gambino D (2009) Design of vanadium mixed-ligand complexes as potential anti-protozoa agents. J Inorg Biochem 103(4):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2008.10.018
Bennie RB, Livingston DJ, Joel C, Jeyanthi D, Solomon RV (2020) Crystal structure, chemical nuclease activity, and VHPO mimicking potential of oxovanadium(IV) complexes—a combined experimental and computational study. Appl Organomet Chem 35(2):e6106. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6106
Camacho LH, Soignet SL, Chanel S, Ho R, Heller G, Scheinberg DA, Ellison R, Warrell RP Jr (2000) Leukocytosis and the retinoic acid syndrome in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide. J Clin Oncol 18(13):2620–2625
Chen G-Q, Zhu J, Shi X-G, Ni J, Zhong H, Si G, Jin X, Tang W, Li X, Xong S (1996) In vitro studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4 cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and modulation of PML-RAR alpha/PML proteins. Blood 88(3):1052–1061
Chen K, Perez-Stable C, D’Ippolito G, Schiller PC, Roos BA, Howard GA (2011) Human bone marrow-derived stem cell proliferation is inhibited by hepatocyte growth factor via increasing the cell cycle inhibitors p53, p21 and p27. Bone 49(6):1194–1204
Cheng L, Huang H, Lin Z, Yang Y, Yuan Q, Hu L, Wang C, Chen Q (2021) N and O multi-coordinated vanadium single atom with enhanced oxygen reduction activity. J Colloid Interface Sci 594:466–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.074
Conte V, Bortolini O, Carraro M, Moro S (2000) Models for the active site of vanadium-dependent haloperoxidases: insight into the solution structure of peroxo vanadium compounds. J Inorg Biochem 80(1–2):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0162-0134(00)00038-6
Crans DC, Smee JJ, Gaidamauskas E, Yang L (2004) The chemistry and biochemistry of vanadium and the biological activities exerted by vanadium compounds. Chem Rev 104(2):849–902. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020607t
Crans DC, Koehn JT, Petry SM, Glover CM, Wijetunga A, Kaur R, Levina A, Lay PA (2019) Hydrophobicity may enhance membrane affinity and anti-cancer effects of Schiff base vanadium(v) catecholate complexes. Dalton Trans 48(19):6383–6395. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9DT00601J
De Abreu J, Del Carpio E, Madden W, Lubes G, Araujo ML, Lubes V, Hernández L (2021) Speciation studies of binary and ternary complexes formed with oxidovanadium(IV) ion picolinic acid and some amino acids. Phys Chem Liq 59(2):264–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319104.2019.1706176
Dejamfekr M, Khaleghian A (2019) Antioxidant properties of vanadium complexes and their anticancer effects on human gastric cancer cell line MKN45. Koomesh 21(2):331–339
Del Carpio E, Hernández L, Ciangherotti C, Villalobos Coa V, Jiménez L, Lubes V, Lubes G (2018) Vanadium: history, chemistry, interactions with α-amino acids and potential therapeutic applications. Coord Chem Rev 372:117–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.06.002
García-Rodríguez MdC, Hernández-Cortés LM, Altamirano-Lozano MA (2016) In vivo effects of vanadium pentoxide and antioxidants (ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol) on apoptotic, cytotoxic, and genotoxic damage in peripheral blood of mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6797851
Grad JM, Bahlis NJ, Reis I, Oshiro MM, Dalton WS, Boise LH (2001) Ascorbic acid enhances arsenic trioxide–induced cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 98(3):805–813
Haller JS (1975) Therapeutic mule: the use of arsenic in the nineteenth century materia medica. Pharm Hist 17(3):87–100
Huyer G, Liu S, Kelly J, Moffat J, Payette P, Kennedy B, Tsaprailis G, Gresser MJ, Ramachandran C (1997) Mechanism of inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatases by vanadate and pervanadate. J Biol Chem 272(2):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.2.843
Kalalinia F, Elahian F, Hassani M, Kasaeeian J, Behravan J (2012) Phorbol ester TPA modulates chemoresistance in the drug sensitive breast cancer cell line MCF-7 by inducing expression of drug efflux transporter ABCG2. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13(6):2979–2984
Kioseoglou E, Petanidis S, Gabriel C, Salifoglou A (2015a) The chemistry and biology of vanadium compounds in cancer therapeutics. Coord Chem Rev 301:87–105
Kioseoglou E, Petanidis S, Gabriel C, Salifoglou A (2015b) The chemistry and biology of vanadium compounds in cancer therapeutics. Coord Chem Rev 301–302:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2015.03.010
Koç E, Çelik-Uzuner S, Uzuner U, Çakmak R (2018) The detailed comparison of cell death detected by annexin V-PI counterstain using fluorescence microscope, flow cytometry and automated cell counter in mammalian and microalgae cells. J Fluoresc 28(6):1393–1404
Levina A, Lay PA (2017) Stabilities and biological activities of vanadium drugs: what is the nature of the active species? Chem Asian J 12(14):1692–1699. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201700463
Li YM, Broome JD (1999) Arsenic targets tubulins to induce apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cells. Can Res 59(4):776–780
Lo-Coco, F, Ammatuna, E, and Sanz, MA. (2007). Current treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. In. Haematologica, pp. 289–91.
Mathews C, Van Holde K, Ahern K (2000) Biochemistry. 2000. BenjaminCummings, San Francisco
Matsugo S, Kanamori K, Sugiyama H, Misu H, Takamura T (2015) Physiological roles of peroxido-vanadium complexes: leitmotif as their signal transduction pathway. J Inorg Biochem 147:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2015.02.008
Mirjalili S, Dejamfekr M, Moshtaghian A, Salehi M, Behzad M, Khaleghian A (2020) Induction of cell cycle arrest in MKN45 cells after schiff base oxovanadium complex treatment using changes in gene expression of CdC25 and P53. Drug Res (stuttg) 70(12):545–551. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1235-5565
Mistry AR, Pedersen EW, Solomon E, Grimwade D (2003) The molecular pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukaemia: implications for the clinical management of the disease. Blood Rev 17(2):71–97
Mosaffa F, Kalalinia F, Parhiz BH, Behravan J (2011) Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces stronger cytotoxicity in ABCG2-overexpressing resistant breast cancer cells compared with their drug-sensitive parental line. DNA Cell Biol 30(6):413–418
Neyshaburinezhad N, Kalalinia F, Hashemi M (2019) Encapsulation of crocetin into poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles overcomes drug resistance in human ovarian cisplatin-resistant carcinoma cell line (A2780-RCIS). Mol Biol Rep 46(6):6525–6532
Patel N, Prajapati AK, Jadeja RN, Patel RN, Patel SK, Gupta VK, Tripathi IP, Dwivedi N (2019) Model investigations for vanadium-protein interactions: synthesis, characterization and antidiabetic properties. Inorg Chim Acta 493:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2019.04.050
Pessoa JC, Etcheverry S, Gambino D (2015a) Vanadium compounds in medicine. Coord Chem Rev 301:24–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.12.002
Pessoa JC, Garribba E, Santos MF, Santos-Silva T (2015b) Vanadium and proteins: uptake, transport, structure, activity and function. Coord Chem Rev 301:49–86
Ray RS, Ghosh B, Rana A, Chatterjee M (2007) Suppression of cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest: chemopreventive activity of vanadium in vivo and in vitro. Int J Cancer 120(1):13–23
Rousselot P, Labaume S, Marolleau J-P, Larghero J, Noguera M-H, Brouet J-C, Fermand J-P (1999) Arsenic trioxide and melarsoprol induce apoptosis in plasma cell lines and in plasma cells from myeloma patients. Can Res 59(5):1041–1048
Rozzo C, Sanna D, Garribba E, Serra M, Cantara A, Palmieri G, Pisano M (2017) Antitumoral effect of vanadium compounds in malignant melanoma cell lines. J Inorg Biochem 174:14–24
Ruddon RW (2010) “Introduction to the molecular biology of cancer: translation to the clinic”. Progress in molecular biology and translational science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–8
Sanz MA (2006) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. ASH Educ Progr Book 2006(1):147–155
Sciortino G, Maréchal J-D, Garribba E (2021) Integrated experimental/computational approaches to characterize the systems formed by vanadium with proteins and enzymes. Inorg Chem Front 8(8):1951–1974. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0QI01507E
Shao W, Fanelli M, Ferrara FF, Riccioni R, Rosenauer A, Davison K, Lamph WW, Waxman S, Pelicci PG, Lo Coco F (1998) Arsenic trioxide as an inducer of apoptosis and loss of PML/RARα protein in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. JNCI 90(2):124–33
Smith A, Howell D, Patmore R, Jack A, Roman E (2011) Incidence of haematological malignancy by sub-type: a report from the haematological malignancy research network. Br J Cancer 105(11):1684
Taheri O, Behzad M, Ghaffari A, Kubicki M, Dutkiewicz G, Bezaatpour A, Nazari H, Khaleghian A, Mohammadi A, Salehi M (2014) Synthesis, crystal structures and antibacterial studies of oxidovanadium (IV) complexes of salen-type Schiff base ligands derived from meso-1, 2-diphenyl-1, 2-ethylenediamine. Transit Met Chem 39(2):253–259
Tarkanyi I, Dudognon C, Hillion J, Pendino F, Lanotte M, Aradi J, Segal-Bendirdjian E (2005) Retinoid/arsenic combination therapy of promyelocytic leukemia: induction of telomerase-dependent cell death. Leukemia 19(10):1806
Thomas D, Tyers M (2000) Transcriptional regulation: Kamikaze activators. Curr Biol 10(9):R341–R343
Treviño S, Díaz A, Sánchez-Lara E, Sanchez-Gaytan BL, Perez-Aguilar JM, González-Vergara E (2019) Vanadium in biological action: chemical, pharmacological aspects, and metabolic implications in diabetes mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res 188(1):68–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1540-6
Türkmen S, Guo G, Garshasbi M, Hoffmann K, Alshalah AJ, Mischung C, Kuss A, Humphrey N, Mundlos S, Robinson PN (2009) CA8 mutations cause a novel syndrome characterized by ataxia and mild mental retardation with predisposition to quadrupedal gait. PLoS genetics 5(5):e1000487
Yedjou CG, Tchounwou PB (2009) Modulation of p53, c-fos, RARE, cyclin A, and cyclin D1 expression in human leukemia (HL-60) cells exposed to arsenic trioxide. Mol Cell Biochem 331(1–2):207
Yedjou C, Moore P, Tchounwou P (2006) Dose-and time-dependent response of human leukemia (HL-60) cells to arsenic trioxide treatment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 3(2):136–140
Yedjou C, Tchounwou P, Jenkins J, McMurray R (2010) Basic mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (ATO)-induced apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Hematol Oncol 3(1):28
Yilmaz-Ozden T, Kurt-Sirin O, Tunali S, Akev N, Can A, Yanardag R (2014) Ameliorative effect of vanadium on oxidative stress in stomach tissue of diabetic rats. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 14(2):105
Zekri A, Ghaffari SH, Yousefi M, Ghanizadeh-Vesali S, Mojarrad M, Alimoghaddam K, Ghavamzadeh A (2013) Autocrine human growth hormone increases sensitivity of mammary carcinoma cell to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 377(1–2):84–92
Zhang T-C, Schmitt MT, Mumford JL (2003a) Effects of arsenic on telomerase and telomeres in relation to cell proliferation and apoptosis in human keratinocytes and leukemia cells in vitro. Carcinogenesis 24(11):1811–1817
Zhang Y, Cao E-H, Liang X-Q, Qin J-F (2003b) Increasing sensitivity to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis by altered telomere state. Eur J Pharmacol 474(2–3):141–147
Zhu J, Koken MH, Quignon F, Chelbi-Alix MK, Degos L, Wang ZY, Chen Z (1997) Arsenic-induced PML targeting onto nuclear bodies: implications for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(8):3978–3983
Zhu C, Guo-Qiang C, Zhi-Xiang S, Sai-Juan C, Zhen-Yi W (2001) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic compounds: in vitro and in vivo studies. Seminars in hematology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 26–36
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran, and to the Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran, for approval and financial support of this project (Grant Nos. 960748, and 1283, respectively). The results described in this paper were of Ms. Sara Mirjalili's master's thesis.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran, and to the Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan, Iran, for approval and financial support of this project (Grant Nos. 960748, and 1283, respectively).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FK conceived of the study, designed the study, and coordinated and helped to statistical analysis and draft the manuscript. SM carried out the cellular and molecular studies, performed the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. AK conceived of the study, participated in its design and drafting of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirjalili, S., Khaleghian, A. & Kalalinia, F. Effects of co-administration of arsenic trioxide and Schiff base oxovanadium complex on the induction of apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Biometals 34, 1067–1080 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00330-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00330-z