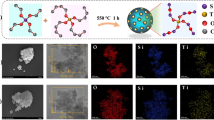
Abstract
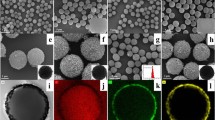
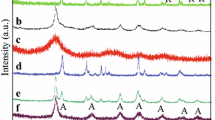
The utilization of rosin to fabricate functional polymers has attracted great attention due to its unique structure and property. Herein, we prepared a new type of carboxyl-containing cross-linked rosin microspheres (CCRMs) using a renewable-resource rosin as the raw material through the suspension polymerization. For comparative purpose, vanillin methacrylate (VMA), styrene (St) and isobornyl methacrylate (IBOMA) were separately used to replace DAGMA as monomer for the preparation of microspheres. Our results indicated that the obtained porous CCRMs showed a broad size distribution ranging from mesopores (3–50 nm) to macropores (> 50 nm), whereas the counterparts derived from VMA, St or IBOMA showed a powder state. Moreover, the CCRMs exhibited moderately high thermal stability. The integration of DAGMA into polymer microspheres provided CCRMs with excellent adsorption ability, which exhibited robust selective cationic dye (e.g., methylene blue (MB) and crystal violet (CV)) adsorption from waste aqueous solution. The adsorption process was fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The maximum adsorption capacity was observed to be 602.4 mg/g for CV at 40 °C, and 512.8 mg/g for MB at 20 °C. In general, the high dye adsorption properties suggest that CCRMs may be highly efficient in adsorption selectivity for some cationic dyes.
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang J, Liu S, Yu J, Lu C, Wang C, Chu F (2017) Rosin-derived monomers and their progress in polymer application. Sustain Polym Biomass 17:103–149
Atta AM, Mansour R, Abdou MI, Sayed AM (2004) Epoxy resins from rosin acids: synthesis and characterization. Polym Adv Technol 15:514–522
Ding W, Wang S, Yao K, Ganewatta MS, Tang C, Robertson ML (2017) Physical behavior of triblock copolymer thermoplastic elastomers containing sustainable rosin-derived polymethacrylate end blocks. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:11470–11480
Yu J, Lu C, Wang C, Wang J, Fan Y, Chu F (2017) Sustainable thermoplastic elastomers derived from cellulose, fatty acid and furfural via ATRP and click chemistry. Carbohydr Polym 176:83–90
Ganewatta MS, Ding W, Rahman MA, Yuan L, Wang Z, Hamidi N, Robertson ML, Tang C (2016) Biobased plastics and elastomers from renewable rosin via “living” ring-opening metathesis polymerization. Macromolecules 49:7155–7164
Rahman MA, Lokupitiya HN, Ganewatta MS, Yuan L, Stefik M, Tang C (2017) Designing block copolymer architectures toward tough bioplastics from natural rosin. Macromolecules 50:2069–2077
Lei YF, Wang XL, Liu BW, Ding XM, Chen L, Wang YZ (2020) Fully bio-based pressure-sensitive adhesives with high adhesivity derived from epoxidized soybean oil and rosin acid. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:13261–13270
Ganewatta MS, Miller KP, Singleton SP, Mehrpouya-Bahrami P, Chen YP, Yan Y, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti P, Decho AW, Tang C (2015) Antibacterial and biofilm-disrupting coatings from resin acid-derived materials. Biomacromolecules 16:3336–3344
Liu Y, Yao K, Chen X, Wang J, Wang Z, Ploehn HJ, Wang C, Chu F, Tang C (2014) Sustainable thermoplastic elastomers derived from renewable cellulose, rosin and fatty acids. Polym Chem 5:3170–3181
Cheng Z, Liu Y, Zhang D, Lu C, Wang C, Xu F, Wang J, Chu F (2019) Sustainable elastomers derived from cellulose, rosin and fatty acid by a combination of “graft from” RAFT and isocyanate chemistry. Int J Biol Macromol 131:387–395
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80
Yu Y, Qiao N, Wang D, Zhu Q, Fu F, Cao R, Wang R, Liu W, Xu B (2019) Fluffy honeycomb-like activated carbon from popcorn with high surface area and well-developed porosity for ultra-high efficiency adsorption of organic dyes. Bioresour Technol 285:121340
Lin Q, Gao M, Chang J, Ma H (2016) Adsorption properties of crosslinking carboxymethyl cellulose grafting dimethyldiallylammonium chloride for cationic and anionic dyes. Carbohydr Polym 151:283–294
You H, Chen J, Yang C, Xu L (2016) Selective removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution by low-cost adsorbent using phytic acid modified wheat straw. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 509:91–98
Liu S, Wang J, Huang W, Tan X, Dong H, Goodman BA, Du H, Lei F, Diao K (2019) Adsorption of phenolic compounds from water by a novel ethylenediamine rosin-based resin: interaction models and adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 214:821–829
Ruan ZH, Wu JH, Huang JF, Lin ZT, Li YF, Liu YL, Cao PY, Fang YP, Xie J, Jiang GB (2015) Facile preparation of rosin-based biochar coated bentonite for supporting α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and its application for Cr(vi) adsorption. J Mater Chem A 3:4595–4603
Tan WX, Lin ZT, Bu HT, Tian Y, Jiang GB (2012) Nano-micelles based on a rosin derivative as potent sorbents and sinking agents with high absorption capabilities for the removal of metal ions. RSC Adv 2:7279–7289
Yu C, Shan J, Chen Y, Shao J, Zhang F (2020) Preparation and adsorption properties of rosin-based bisphenol A molecularly imprinted microspheres. Mater Today Commun 24:101076
Li X, Li M, Li J, Lei F, Su X, Liu M, Li P, Tan X (2014) Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers with modified rosin as a cross-linker and selective SPE-HPLC detection of basic orange II in foods. Anal Methods 6:6397–6406
Wadhera P, Jindal R, Dogra R (2020) Insight into adsorption kinetics and isotherms for adsorption of methylene blue using gum rosin alcohol/psyllium-based green adsorbent. Iran Polym J 29:501–514
Kaith BS, Jindal R, Sharma R (2015) Synthesis of a gum rosin alcohol-poly(acrylamide) based adsorbent and its application in removal of malachite green dye from waste water. RSC Adv 5:43092–43104
Li P, Qin L, Wang T, Dai L, Li H, Jiang J, Zhou J, Li H, Cheng X, Lei F (2020) Preparation and adsorption characteristics of rosin-based polymer microspheres for berberine hydrochloride and separation of total alkaloids from coptidis rhizoma. Chem Eng J 392:123707
Shaofeng L, Chuanwei L, Chunpeng W, Jifu W, Fuxiang C (2017) Synthesis and characterization of 2-methacryloyloxyisopropanol ester of dehydroabietic acid. Chem Ind Forest Prod 37:89–94
Zhang H, Yong X, Zhou J, Deng J, Wu Y (2016) Biomass vanillin-derived polymeric microspheres containing functional aldehyde groups: preparation, characterization, and application as adsorbent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:2753–2763
Yan H, Li H, Yang H, Li A, Cheng R (2013) Removal of various cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using a kind of fully biodegradable magnetic composite microsphere. Chem Eng J 223:402–411
Fu J, Chen Z, Wang M, Liu S, Zhang J, Zhang J, Han R, Xu Q (2015) Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem Eng J 259:53–61
Fu J, Xin Q, Wu X, Chen Z, Yan Y, Liu S, Wang M, Xu Q (2016) Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution on polydopamine microspheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 461:292–304
Ai L, Zhang C, Liao F, Wang Y, Li M, Meng L, Jiang J (2011) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with magnetite loaded multi-wall carbon nanotube: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J Hazard Mater 198:282–290
Sakin Omer O, Hussein MA, Hussein BHM, Mgaidi A (2018) Adsorption thermodynamics of cationic dyes (methylene blue and crystal violet) to a natural clay mineral from aqueous solution between 293.15 and 323.15 K. Arab J Chem 11:615–623
Saeed A, Sharif M, Iqbal M (2010) Application potential of grapefruit peel as dye sorbent: kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism of crystal violet adsorption. J Hazard Mater 179:564–572
Zou J, Liao K, Xiang L, Liu M, Xie F, Liu X, Yu J, An X, Wang Y (2020) Synthesis of poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4’-diaminodiphenysulfone)microspheres and their adsorption properties for cationic dyes (methylene blue). J Inorg Org Polym Mater 30:976–985
Dotto GL, Santos JMN, Rodrigues IL, Rosa R, Pavan FA, Lima EC (2015) Adsorption of methylene blue by ultrasonic surface modified chitin. J Colloid Interface Sci 446:133–140
Zhang H, Chen L, Li L, Yang Y, Liu X (2017) Magnetic porous carbon microspheres synthesized by simultaneous activation and magnetization for removing methylene blue. J Porous Mater 24:341–353
Zhao L, Yu B, Xue F, Xie J, Zhang X, Wu R, Wang R, Hu Z, Yang ST, Luo J (2015) Facile hydrothermal preparation of recyclable S-doped graphene sponge for Cu2+ adsorption. J Hazard Mater 286:449–456
Wang B, Zhang Q, Xiong G, Ding F, He Y, Ren B, You L, Fan X, Hardacre C, Sun Y (2019) Bakelite-type anionic microporous organic polymers with high capacity for selective adsorption of cationic dyes from water. Chem Eng J 366:404–414
Zhuang S, Wang J (2019) Removal of cobalt ion from aqueous solution using magnetic graphene oxide/chitosan composite. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 38:S32–S41
Saber-Samandari S, Saber-Samandari S, Joneidi-Yekta H, Mohseni M (2017) Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gelatin-based magnetic nanocomposite beads comprising carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube. Chem Eng J 308:1133–1144
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Jiangsu Province Biomass Energy and Materials Laboratory (JSBEM-S-202009), Foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971600) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFE0106800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zenghui Cheng: investigation, designed and writing–original draft; Juan Yu and Meihong Liu: performed experiments; Daihui Zhang: analyzed the data; Chunpeng Wang: resources and methodology; Jifu Wang and Fuxiang Chu: contributed to writing–review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Z., Wang, C., Yu, J. et al. Rosin-derived porous microspheres with robust selective cationic dye adsorption. Iran Polym J 30, 1041–1052 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-00955-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-021-00955-4