Abstract
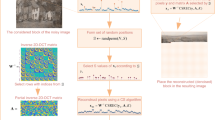
In this paper, we present an approach to the reconstruction of signals exhibiting sparsity in a transformation domain, having some heavily disturbed samples. This sparsity-driven signal recovery exploits a carefully suited random sampling consensus (RANSAC) methodology for the selection of a subset of inlier samples. To this aim, two fundamental properties are used: A signal sample represents a linear combination of the sparse coefficients, whereas the disturbance degrades the original signal sparsity. The properly selected samples are further used as measurements in the sparse signal reconstruction, performed using algorithms from the compressive sensing framework. Besides the fact that the disturbance degrades signal sparsity in the transformation domain, no other disturbance-related assumptions are made—there are no special requirements regarding its statistical behavior or the range of its values. As a case study, the discrete Fourier transform is considered as a domain of signal sparsity, owing to its significance in signal processing theory and applications. Numerical results strongly support the presented theory. In addition, the exact relation for the signal-to-noise ratio of the reconstructed signal is also presented. This simple result, which conveniently characterizes the RANSAC-based reconstruction performance, is numerically confirmed by a set of statistical examples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Ahmad, O. Kukrer, A. Hocanin, Robust recursive inverse adaptive algorithm in impulsive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(2), 703–710 (2012)
F.R. Avila, L.W.P. Biscainho, Bayesian restoration of audio signals degraded by impulsive noise modeled as individual pulses. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 20(9), 2470–2481 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2012.2203811
T. Blumensath, Sampling and reconstructing signals from a union of linear subspaces. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 57(7), 4660–4671 (2011)
M. Brajovic, S. Stankovic, I. Orovic, M. Dakovic, L. Stankovic, Sparsity-Driven Impulsive Noise Removal: A Discrete Hermite Transform Case Study 27th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR 2019) (Belgrade, Serbia, 2019)
M. Brajovic, I. Stankovic, M. Dakovic, L. Stankovic, The DCT domain sparsity-assisted detection and recovery of impulsively disturbed samples. Multimedia Tools Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09998-w
E.J. Candès, J. Romberg, T. Tao, Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(2), 489–509 (2006)
R.E. Carrillo, K.E. Barner, T.C. Aysal, Robust sampling and reconstruction methods for sparse signals in the presence of impulsive noise. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 4(2), 392–408 (2010)
M. Ciołek , M. Niedźwiecki, Detection of impulsive disturbances in archive audio signals. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA (2017), pp. 671–675. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7952240
F. Dadouchi, C. Gervaise, C. Ioana, J. Huillery, J.I. Mars, Automated segmentation of linear time-frequency representations of marine-mammal sounds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 134(3), 2546–2555 (2013)
G. Davis, S. Mallat, M. Avellaneda, Adaptive greedy approximations. Constr. Approx. 13(1), 57–98 (1997)
I. Djurovic, A WD-RANSAC instantaneous frequency estimator. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(5), 757–761 (2016)
I. Djurovic, V.V. Lukin, M. Simeunovic, B. Barkat, Quasi maximum likelihood estimator of polynomial phase signals for compressed sensed data. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 68(7), 631–636 (2014)
D.L. Donoho, Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
K. Egiazarian, A. Foi , V. Katkovnik, Compressed sensing image reconstruction via recursive spatially adaptive filtering, in 2007 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Antonio, TX, pp. 549–552 (2007), https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2007.4379013
M.J. Fadili, J.L. Starck, F. Murtagh, Inpainting and zooming using sparse representations. Comput. J. 52(1), 64–79 (2009)
R. Feng, Q. Du, X. Li, H. Shen, Robust registration for remote sensing images by combining and localizing feature- and area-based methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 151, 15–26 (2019)
P. Flandrin, P. Borgnat, Time-frequency energy distributions meet compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(6), 2974–2982 (2010)
F.E. Grubbs, Procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples. Technometrics 11(1), 1–21 (1969)
R. Hu, Y. Fu, Z. Chen, Y. Xiang, J. Tang, A Lorentzian IHT for complex-valued sparse signal recovery. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(2), 862–872 (2018)
B. Jokanovic, M.G. Amin, Y.D. Zhang, Reducing noise in the time-frequency representation using sparsity promoting kernel design, in Proceedings of SPIE 9109, Compressive Sensing III (91090B) (2014), https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2050894
V. Katkovnik, L. Stankovic, Instantaneous frequency estimation using the Wigner distribution with varying and data driven window length. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 46(9), 2315–2325 (1998)
N.A. Khan, M. Mohammadi, Reconstruction of non-stationary signals with missing samples using time-frequency filtering. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(8), 3175–3190 (2018)
T. Kim, Y.J. Im, Automatic satellite image registration by combination of matching and random sample consensus. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 41(5), 1111–1117 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2003.811994
C. Leys, C. Ley, O. Klein, P. Bernard, L. Licata, Detecting outliers: do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 49(4), 764–766 (2013)
J. Matas, O. Chum, Randomized RANSAC with T(d,d) test, in ed. D. Marshall, P. L. Rosin, Proceedings of the British Machine Conference, 43.1–43.10, (BMVA Press 2002), https://doi.org/10.5244/C.16.43.
D. Needell, J.A. Tropp, CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 26(3), 301–321 (2009)
M. Niedźwiecki, M. Ciołek, Elimination of Impulsive Disturbances From Archive Audio Signals Using Bidirectional Processing. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(5), 1046–1059 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2013.2244090
D. Nister, Preemptive RANSAC for live structure and motion estimation, in Proceedings Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Nice, France (2003), pp. 199–206, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2003.1238341
I. Orovic, V. Papic, C. Ioana, X. Li, S. Stankovic, Compressive sensing in signal processing: algorithms and transform domain formulations. Math. Probl. Eng. (2016)
Z.M. Ramadan, Efficient restoration method for images corrupted with impulse noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(4), 1397–1406 (2012)
A.A. Roenko, V.V. Lukin, I. Djurovic, Two approaches to adaptation of sample myriad to characteristics of S\(\alpha \)S distribution data. Sig. Process. 90(7), 2113–2123 (2010)
M. Ruhland, J. Bitzer, M. Brandt, S. Goetze, Reduction of gaussian, supergaussian, and impulsive noise by interpolation of the binary mask residual. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 23(10), 1680–1691 (2015)
E. Sejdic, A. Cam, L. Chaparro, C. Steele, T. Chau, Compressive sampling of swallowing accelerometry signals using time-frequency dictionaries based on modulated discrete prolate spheroidal sequences. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 101, 1–14 (2012)
H. Shen, X. Li, L. Zhang, D. Tao, C. Zeng, Compressed sensing-based inpainting of aqua moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer band 6 using adaptive spectrum-weighted sparse Bayesian dictionary learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52(2), 894–906 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2013.2245509
M. Siu, A. Chan, A Robust Viterbi algorithm against impulsive noise with application to speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 14(6), 2122–2133 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2006.872592
I. Stankovic, Recovery of images with missing pixels using a gradient compressive sensing algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1407.3695 (2014)
I. Stankovic, M. Brajovic, M. Dakovic, C. Ioana, L. Stankovic, Quantization in compressive sensing: a signal processing approach. IEEE Access 8, 50611–50625 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2979935
I. Stankovic, I. Orovic, M. Dakovic, S. Stankovic, Denoising of sparse images in impulsive disturbance environment. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(5), 5885–5905 (2018)
L. Stankovic, A measure of some time-frequency distributions concentration. Sig. Process. 81(3), 621–631 (2001)
L. Stankovic, Digital Signal Processing with Selected Topics (CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, An Amazon. Com Company, 2015)
L. Stankovic, M. Brajovic, Analysis of the reconstruction of sparse signals in the DCT domain applied to audio signals. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 26(7), 1216–1231 (2018)
L. Stankovic, M. Brajovic, I. Stankovic, C. Ioana, M. Dakovic, Reconstruction error in nonuniformly sampled approximately sparse signals. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2020.2968137
L. Stankovic, M. Dakovic, On the uniqueness of the spa rse signals reconstruction based on the missing samples variation analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. Article ID 629759 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/629759
L. Stankovic, M. Dakovic, I. Stankovic, S. Vujovic, On the errors in randomly sampled nonsparse signals reconstructed with a sparsity assumption. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 14(12), 2453–2456 (2017)
L. Stankovic, M. Dakovic, S. Vujovic, Reconstruction of Sparse signals in impulsive disturbance environments. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36, 767–794 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0334-3
L. Stankovic, D.P. Mandic, M. Dakovic, I. Kisil, Demystifying the Coherence Index in Compressive Sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 37(1), 152–162 (2020)
S. Stankovic, I. Orovic, L. Stankovic, An automated signal reconstruction method based on analysis of compressive sensed signals in noisy environment. Sig. Process. 104, 43–50 (2014)
L. Stankovic, I. Orovic, S. Stankovic, M.G. Amin, Compressive sensing based separation of nonstationary and stationary signals overlapping in time-frequency. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(18), 4562–4572 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2271752
L. Stankovic, E. Sejdic, S. Stankovic, M. Dakovic, I. Orovic, A Tutorial on Sparse Signal Reconstruction and Its Applications in Signal Processing. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38, 1206–1263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0909-2
L. Stankovic, S. Stankovic, M.G. Amin, Missing samples analysis in signals for applications to L-estimation and compressive sensing. Sig. Process. 94, 401–408 (2014)
L. Stankovic, S. Stankovic, I. Orovic, M.G. Amin, Robust time-frequency analysis based on the L-estimation and compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(5), 499–502 (2013)
C. Studer, P. Kuppinger, G. Pope, H. Bolcskei, Recovery of sparsely corrupted signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 58(5), 3115–3130 (2012)
A. Torokhti, P. Howlett, H. Laga, Estimation of stochastic signals under partially missing information. Sig. Process. 111, 199–209 (2015)
S.V. Vaseghi, Advanced Digital Signal Processing and Noise Reduction (Wiley, Hoboken, 2008)
I. Volaric, V. Sucic, On the noise impact in the L1 based reconstruction of the sparse time-frequency distributions, in 2016 International Conference on Broadband Communications for Next Generation Networks and Multimedia Applications (CoBCom), Gratz, pp. 1–6 (2016)
H. Wang, D. Suter, Robust adaptive-scale parametric model estimation for computer vision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(11), 1459–1474 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2004.109
G.H. You, T.S. Qiu, A.M. Song, Novel direction findings for cyclostationary signals in impulsive noise environments. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(6), 2939–2956 (2013)
L. Zhao, Y. Hu, Y. Liu, Stochastic gradient matching pursuit algorithm based on sparse estimation. Electronics 8(2), 165 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Croatian Science Foundation under the project IP-2020-02-4358.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Data Availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanković, L., Brajović, M., Stanković, I. et al. RANSAC-Based Signal Denoising Using Compressive Sensing. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 3907–3928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01654-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-021-01654-4