Abstract
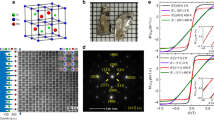
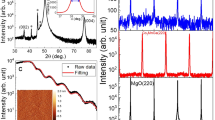
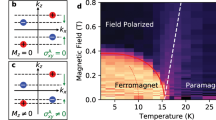
Magnetic topological materials, which combine magnetism and topology, are expected to host emerging topological states and exotic quantum phenomena. In this study, with the aid of greatly enhanced coercive fields in high-quality nanoflakes of the magnetic Weyl semimetal Co3Sn2S2, we investigate anomalous electronic transport properties that are difficult to reveal in bulk Co3Sn2S2 or other magnetic materials. When the magnetization is antiparallel to the applied magnetic field, the low longitudinal resistance state occurs, which is in sharp contrast to the high resistance state for the parallel case. Meanwhile, an exceptional Hall component that can be up to three times larger than conventional anomalous Hall resistivity is also observed for transverse transport. These anomalous transport behaviors can be further understood by considering nonlinear magnetic textures and the chiral magnetic field associated with Weyl fermions, extending the longitudinal and transverse transport physics and providing novel degrees of freedom in the spintronic applications of emerging topological magnets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Liu, Y. Sun, N. Kumar, L. Muechler, A. Sun, L. Jiao, S. Y. Yang, D. Liu, A. Liang, Q. Xu, J. Kroder, V. Süß, H. Borrmann, C. Shekhar, Z. Wang, C. Xi, W. Wang, W. Schnelle, S. Wirth, Y. Chen, S. T. B. Goennenwein, and C. Felser, Nat. Phys. 14, 1125 (2018), arXiv: 1712.06722.
Q. Wang, Y. Xu, R. Lou, Z. Liu, M. Li, Y. Huang, D. Shen, H. Weng, S. Wang, and H. Lei, Nat. Commun. 9, 3681 (2018), arXiv: 1712.09947.
D. F. Liu, A. J. Liang, E. K. Liu, Q. N. Xu, Y. W. Li, C. Chen, D. Pei, W. J. Shi, S. K. Mo, P. Dudin, T. Kim, C. Cacho, G. Li, Y. Sun, L. X. Yang, Z. K. Liu, S. S. P. Parkin, C. Felser, and Y. L. Chen, Science 365, 1282 (2019), arXiv: 1909.09580.
N. Morali, R. Batabyal, P. K. Nag, E. Liu, Q. Xu, Y. Sun, B. Yan, C. Felser, N. Avraham, and H. Beidenkopf, Science 365, 1286 (2019), arXiv: 1903.00509.
H. M. Weng, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 62, 127031 (2019).
C. Liu, J. L. Shen, J. C. Gao, C. J. Yi, D. Liu, T. Xie, L. Yang, S. Danilkin, G. C. Deng, W. H. Wang, S. L. Li, Y. G. Shi, H. M. Weng, E. K. Liu, and H. Q. Luo, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 64, 217062 (2020), arXiv: 2006.07339.
C. Z. Chang, J. Zhang, X. Feng, J. Shen, Z. Zhang, M. Guo, K. Li, Y. Ou, P. Wei, L. L. Wang, Z. Q. Ji, Y. Feng, S. Ji, X. Chen, J. Jia, X. Dai, Z. Fang, S. C. Zhang, K. He, Y. Wang, L. Lu, X. C. Ma, and Q. K. Xue, Science 340, 167 (2013), arXiv: 1605.08829.
L. Muechler, E. Liu, J. Gayles, Q. Xu, C. Felser, and Y. Sun, Phys. Rev. B 101, 115106 (2020), arXiv: 1712.08115.
K. Kobayashi, Y. Ominato, and K. Nomura, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 87, 073707 (2018), arXiv: 1802.04536.
K. Kobayashi, M. Takagaki, and K. Nomura, Phys. Rev. B 100, 161301 (2019), arXiv: 1908.02727.
S. Howard, L. Jiao, Z. Wang, P. Vir, C. Shekhar, C. Felser, T. Hughes, and V. Madhavan, arXiv: 191011205.
K. Fujiwara, J. Ikeda, J. Shiogai, T. Seki, K. Takanashi, and A. Tsukazaki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 58, 050912 (2019).
S. Li, G. Gu, E. Liu, P. Cheng, B. Feng, Y. Li, L. Chen, and K. Wu, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2, 126 (2020).
S. Y. Yang, J. Noky, J. Gayles, F. K. Dejene, Y. Sun, M. Dörr, Y. Skourski, C. Felser, M. N. Ali, E. Liu, and S. S. P. Parkin, Nano Lett. 20, 7860 (2020).
M. Tanaka, Y. Fujishiro, M. Mogi, Y. Kaneko, T. Yokosawa, N. Kanazawa, S. Minami, T. Koretsune, R. Arita, S. Tarucha, M. Yamamoto, and Y. Tokura, Nano Lett. 20, 7476 (2020), arXiv: 2009.07431.
C. X. Liu, P. Ye, and X. L. Qi, Phys. Rev. B 87, 235306 (2013), arXiv: 1204.6551.
Y. Araki, A. Yoshida, and K. Nomura, Phys. Rev. B 94, 115312 (2016), arXiv: 1607.07012.
A. G. Grushin, J. W. F. Venderbos, A. Vishwanath, and R. Ilan, Phys. Rev. X 6, 041046 (2016).
Y. Araki, and K. Nomura, Phys. Rev. Appl. 10, 014007 (2018), arXiv: 1711.03135.
Y. Araki, Ann. Der Phys. 532, 1900287 (2019), arXiv: 1910.07774.
J. Shen, Q. Zeng, S. Zhang, W. Tong, L. Ling, C. Xi, Z. Wang, E. Liu, W. Wang, G. Wu, and B. Shen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 212403 (2019), arXiv: 2002.03940.
J. M. Ziman, Electrons and Phonons: Theory of Transport Phenomena in Solids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1960).
G. Eguchi, K. Kuroda, K. Shirai, Y. Ando, T. Shinjo, A. Kimura, and M. Shiraishi, Phys. Rev. B 91, 235117 (2015), arXiv: 1505.05624.
D. Chiba, M. Yamanouchi, F. Matsukura, T. Dietl, and H. Ohno, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 096602 (2006), arXiv: cond-mat/0601464.
C. Haas, Phys. Rev. 168, 531 (1968).
M. Viret, D. Vignoles, D. Cole, J. M. D. Coey, W. Allen, D. S. Daniel, and J. F. Gregg, Phys. Rev. B 53, 8464 (1996).
J. M. D. Coey, A. E. Berkowitz, L. Balcells, F. F. Putris, and A. Barry, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 3815 (1998).
J. M. D. Coey, A. E. Berkowitz, L. Balcells, F. F. Putris, and F. T. Parker, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 734 (1998).
L. Klein, Y. Kats, A. F. Marshall, J. W. Reiner, T. H. Geballe, M. R. Beasley, and A. Kapitulnik, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 6090 (2000), arXiv: cond-mat/9912404.
M. N. Baibich, J. M. Broto, A. Fert, F. Nguyen Van Dau, F. Petroff, P. Etienne, G. Creuzet, A. Friederich, and J. Chazelas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2472 (1988).
G. Binasch, P. Grünberg, F. Saurenbach, and W. Zinn, Phys. Rev. B 39, 4828 (1989).
J. S. Moodera, L. R. Kinder, T. M. Wong, and R. Meservey, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3273 (1995).
H. R. Chang, J. Zhou, S. X. Wang, W. Y. Shan, and D. Xiao, Phys. Rev. B 92, 241103 (2015), arXiv: 1509.04741.
M. V. Hosseini, and M. Askari, Phys. Rev. B 92, 224435 (2015), arXiv: 1510.03020.
Y. Araki, and K. Nomura, Phys. Rev. B 93, 094438 (2016), arXiv: 1511.08381.
M. A. Kassem, Y. Tabata, T. Waki, and H. Nakamura, Phys. Rev. B 96, 014429 (2017), arXiv: 1702.05627.
Z. Guguchia, J. A. T. Verezhak, D. J. Gawryluk, S. S. Tsirkin, J. X. Yin, I. Belopolski, H. Zhou, G. Simutis, S. S. Zhang, T. A. Cochran, G. Chang, E. Pomjakushina, L. Keller, Z. Skrzeczkowska, Q. Wang, H. C. Lei, R. Khasanov, A. Amato, S. Jia, T. Neupert, H. Luetkens, and M. Z. Hasan, Nat. Commun. 11, 559 (2020).
A. Sugawara, T. Akashi, M. A. Kassem, Y. Tabata, T. Waki, and H. Nakamura, Phys. Rev. Mater. 3, 104421 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52088101, and 11974394), the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFA0704900), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. Z190009), the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) (Grant No. XDB33000000), the Scientific Instrument Developing Project of CAS (Grant No. ZDKYYQ20210003), Users with Excellence Program of Hefei Science Center CAS (Grant No. 2019HSC-UE009), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS (Grant No. 2013002). Shu Zhang is supported by the National Science Foundation, United States (Grant No. DMR-1742928).
Supporting Information
The supporting information is available online at phys.scichina.com and link.springer.com. The supporting materials are published as submitted, without typesetting or editing. The responsibility for scientific accuracy and content remains entirely with the authors.
Supporting Information to
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Q., Gu, G., Shi, G. et al. On the anomalous low-resistance state and exceptional Hall component in hard-magnetic Weyl nanoflakes. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 64, 287512 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1715-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1715-4