Abstract
Introduction
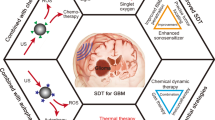
Glioma remains incurable and a life limiting disease with an urgent need for effective therapies. Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) involves systemic delivery of non-toxic chemical agents (sonosensitizers) that accumulate in tumor cells or environment and are subsequently activated by exposure to low-frequency ultrasound to become cytotoxic agents. Herein, we discuss proposed mechanisms of action of SDT and provide recommendation for future research and clinical applications of SDT for gliomas.
Methods
Review of literature of SDT in glioma cell cultures and animal models published in Pubmed/MEDLINE before January, 2021.
Results
Different porphyrin and xanthene derivatives have proven to be effective sonosensitizers. Generation of reactive oxygen species and free radicals from water pyrolysis or sonosensitizers, or physical destabilization of cell membrane, have been identified as mechanisms of SDT leading to cell death. Numerous studies across glioma cell lines using various sonosensitizers and ultrasound parameters have documented tumoricidal effects of SDT. Studies in small animal glioma xenograft models have also consistently documented that SDT is associated with improved tumor control and longer survival of animals treated with SDT while avoiding damage of surrounding brain. There are no clinical trials completed to date regarding safety and efficacy of SDT in patients harboring gliomas, but some are beginning.
Conclusions
Pre-clinical studies cell cultures and animal models indicate that SDT is a promising treatment approach for gliomas. Further studies should define optimal sonication parameters and sonosensitizers for gliomas. Clinical trials of SDT in patients harboring gliomas and other malignant brain tumors are currently underway.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Truitt G et al (2018) CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neurooncology 20:iv1–iv86. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy131
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Gilbert MR, Wang M, Aldape KD et al (2013) Dose-dense temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 31:4085–4091. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.49.6968
Stupp R, Brada M, van den Bent MJ et al (2014) High-grade glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 25 Suppl 3:iii93–i101. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu050
Nam JY, de Groot JF (2017) Treatment of Glioblastoma. JOP 13:629–638. https://doi.org/10.1200/JOP.2017.025536
Bunevicius A, Sheehan JP (2021) Radiosurgery for Glioblastoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am 32:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2020.08.007
Ostrom QT, Cote DJ, Ascha M et al (2018) Adult Glioma Incidence and Survival by Race or Ethnicity in the United States From 2000 to 2014. JAMA Oncol 4:1254–1262. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.1789
Claus EB, Walsh KM, Wiencke JK et al (2015) Survival and low-grade glioma: the emergence of genetic information. Neurosurg Focus 38:E6. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.FOCUS12367
Aldape K, Brindle KM, Chesler L et al (2019) Challenges to curing primary brain tumours. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology 16:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0177-5
Weller M, Wick W, Aldape K et al (2015) Glioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15017. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.17
McHale AP, Callan JF, Nomikou N et al (2016) Sonodynamic Therapy: Concept, Mechanism and Application to Cancer Treatment. Adv Exp Med Biol 880:429–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22536-4_22
Son S, Kim JH, Wang X et al (2020) Multifunctional sonosensitizers in sonodynamic cancer therapy. Chem Soc Rev 49:3244–3261. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00648f
Bilmin K, Kujawska T, Grieb P (2019) Sonodynamic therapy for gliomas. perspectives and prospects of selective sonosensitization of glioma cells. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111428
Bunevicius A, McDannold NJ, Golby AJ (2020) Focused ultrasound strategies for brain tumor therapy. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 19:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz374
Meng Y, Hynynen K, Lipsman N (2021) Applications of focused ultrasound in the brain: from thermoablation to drug delivery. Nat Rev Neurol 17:7–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-020-00418-z
Elias WJ, Lipsman N, Ondo WG et al (2016) A randomized trial of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor. N Engl J Med 375:730–739. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1600159
Martínez-Fernández R, Máñez-Miró JU, Rodríguez-Rojas R et al (2020) Randomized trial of focused ultrasound subthalamotomy for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 383:2501–2513. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2016311
McDannold N, Clement GT, Black P et al (2010) Transcranial magnetic resonance imaging- guided focused ultrasound surgery of brain tumors: initial findings in 3 patients. Neurosurgery 66:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000360379.95800.2F discussion 332.
Coluccia D, Fandino J, Schwyzer L et al (2014) First noninvasive thermal ablation of a brain tumor with MR-guided focused ultrasound. J Ther Ultrasound 2:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/2050-5736-2-17
Hynynen K, McDannold N, Vykhodtseva N, Jolesz FA (2001) Noninvasive MR imaging-guided focal opening of the blood-brain barrier in rabbits. Radiology 220:640–646. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2202001804
Moan J, Peng Q (2003) An outline of the hundred-year history of PDT. Anticancer Res 23:3591–3600
Abrahamse H, Hamblin MR (2016) New photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochem J 473:347–364. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20150942
Hamblin MR, Newman EL (1994) New trends in photobiology on the mechanism of the tumour-localising effect in photodynamic therapy. J Photochem Photobiol B 23:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1011-1344(94)80018-9
Tachibana K, Feril LB, Ikeda-Dantsuji Y (2008) Sonodynamic therapy. Ultrasonics 48:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2008.02.003
Song K-H, Harvey BK, Borden MA (2018) State-of-the-art of microbubble-assisted blood-brain barrier disruption. Theranostics 8:4393–4408. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.26869
Lentacker I, Cock ID, Deckers R et al (2014) Understanding ultrasound induced sonoporation: definitions and underlying mechanisms. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 72:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.11.008
Umemura S, Yumita N, Nishigaki R, Umemura K (1990) Mechanism of cell damage by ultrasound in combination with hematoporphyrin. Jpn J Cancer Res 81:962–966. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02674.x
Stride EP, Coussios CC (2010) Cavitation and contrast: the use of bubbles in ultrasound imaging and therapy. Proc Inst Mech Eng 224:171–191
Yang Y, Tu J, Yang D et al (2019) Photo- and sono-dynamic therapy: a review of mechanisms and considerations for pharmacological agents used in therapy incorporating light and sound. Curr Pharm Des 25:401–412. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666190123114107
MIŠÍK V, RIESZ P (2000) Free radical intermediates in sonodynamic therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 899:335–348. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06198.x
Rosenthal I, Sostaric JZ, Riesz P (2004) Sonodynamic therapy–a review of the synergistic effects of drugs and ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem 11:349–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2004.03.004
Lafond M, Yoshizawa S, Umemura S-I (2019) Sonodynamic therapy: advances and challenges in clinical translation. J Ultrasound Med 38:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1002/jum.14733
Costley D, Ewan CM, Fowley C et al (2015) Treating cancer with sonodynamic therapy: a review. Int J Hyperth 31:107–117. https://doi.org/10.3109/02656736.2014.992484
Zhang Q, Bao C, Cai X et al (2018) Sonodynamic therapy-assisted immunotherapy: a novel modality for cancer treatment. Cancer Sci 109:1330–1345. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13578
Hao D, Song Y, Che Z, Liu Q (2014) Calcium overload and in vitro apoptosis of the C6 glioma cells mediated by sonodynamic therapy (hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether and ultrasound). Cell Biochem Biophys 70:1445–1452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0081-7
Dai S, Hu S, Wu C (2009) Apoptotic effect of sonodynamic therapy mediated by hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether on C6 glioma cells in vitro. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151:1655–1661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0456-5
Hayashi S, Yamamoto M, Tachibana K et al (2009) Mechanism of photofrin-enhanced ultrasound-induced human glioma cell death. Anticancer Res 29:897–905
Xu Z-Y, Wang K, Li X-Q et al (2013) The ABCG2 transporter is a key molecular determinant of the efficacy of sonodynamic therapy with Photofrin in glioma stem-like cells. Ultrasonics 53:232–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2012.06.005
Xu Z-Y, Li X-Q, Chen S et al (2012) Glioma stem-like cells are less susceptible than glioma cells to sonodynamic therapy with photofrin. Technol Cancer Res Treat 11:615–623. https://doi.org/10.7785/tcrt.2012.500277
Gonzales J, Nair RK, Madsen SJ et al (2016) Focused ultrasound-mediated sonochemical internalization: an alternative to light-based therapies. J Biomed Opt 21:78002. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.21.7.078002
Sheehan K, Sheehan D, Sulaiman M et al (2020) Investigation of the tumoricidal effects of sonodynamic therapy in malignant glioblastoma brain tumors. J Neurooncol 148:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03504-w
Ju D, Yamaguchi F, Zhan G et al (2016) Hyperthermotherapy enhances antitumor effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy with activation of caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway in human glioma. Tumour Biol 37:10415–10426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4931-3
Suehiro S, Ohnishi T, Yamashita D et al (2018) Enhancement of antitumor activity by using 5-ALA-mediated sonodynamic therapy to induce apoptosis in malignant gliomas: significance of high-intensity focused ultrasound on 5-ALA-SDT in a mouse glioma model. J Neurosurg 129:1416–1428. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.6.JNS162398
Bilmin K, Kujawska T, Secomski W et al (2016) 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonosensitization of rat RG2 glioma cells in vitro. Folia Neuropathol 54:234–240. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2016.62233
Pi Z, Huang Y, Shen Y et al (2019) Sonodynamic therapy on intracranial glioblastoma xenografts using sinoporphyrin sodium delivered by ultrasound with microbubbles. Ann Biomed Eng 47:549–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-02141-9
An Y-W, Liu H-Q, Zhou Z-Q et al (2020) Sinoporphyrin sodium is a promising sensitizer for photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy in glioma. Oncol Rep 44:1596–1604. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7695
Yoshida M, Kobayashi H, Terasaka S et al (2019) Sonodynamic therapy for malignant glioma using 220-kHz transcranial magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound and 5-aminolevulinic acid. Ultrasound Med Biol 45:526–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.10.016
Wu S-K, Santos MA, Marcus SL, Hynynen K (2019) MR-guided focused ultrasound facilitates sonodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid in a rat glioma model. Sci Rep 9:10465. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46832-2
Sun Y, Wang H, Wang P et al (2019) Tumor targeting DVDMS-nanoliposomes for an enhanced sonodynamic therapy of gliomas. Biomater Sci 7:985–994. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8bm01187g
Song D, Yue W, Li Z et al (2014) Study of the mechanism of sonodynamic therapy in a rat glioma model. Onco Targets Ther 7:1801–1810. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S52426
Nonaka M, Yamamoto M, Yoshino S et al (2009) Sonodynamic therapy consisting of focused ultrasound and a photosensitizer causes a selective antitumor effect in a rat intracranial glioma model. Anticancer Res 29:943–950
Ohmura T, Fukushima T, Shibaguchi H et al (2011) Sonodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid and focused ultrasound for deep-seated intracranial glioma in rat. Anticancer Res 31:2527–2533
Inui T, Makita K, Miura H et al (2014) Case report: a breast cancer patient treated with GcMAF, sonodynamic therapy and hormone therapy. Anticancer Res 34:4589–4593
Inui T, Amitani H, Kubo K et al (2016) Case report: a non-small cell lung cancer patient treated with GcMAF, sonodynamic therapy and tumor treating fields. Anticancer Res 36:3767–3770
Jiang Y, Fan J, Li Y et al (2021) Rapid reduction in plaque inflammation by sonodynamic therapy inpatients with symptomatic femoropopliteal peripheral artery disease: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Cardiol 325:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.09.035
Beguin E, Shrivastava S, Dezhkunov NV et al (2019) Direct evidence of multibubble sonoluminescence using therapeutic ultrasound and microbubbles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:19913–19919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b07084
McEwan C, Owen J, Stride E et al (2015) Oxygen carrying microbubbles for enhanced sonodynamic therapy of hypoxic tumours. J Controlled Release 203:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.004
Kessel D, Lo J, Jeffers R et al (1995) Modes of photodynamic vs. sonodynamic cytotoxicity. J Photochem Photobiol B 28:219–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/1011-1344(94)07111-z
Prada F, Sheybani N, Franzini A et al (2020) Fluorescein-mediated sonodynamic therapy in a rat glioma model. J Neurooncol 148:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03536-2
Jeong E-J, Seo S-J, Ahn Y-J et al (2012) Sonodynamically induced antitumor effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid and fractionated ultrasound irradiation in an orthotopic rat glioma model. Ultrasound Med Biol 38:2143–2150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.07.026
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jackie Brenner for her help in the design and for the drawing of Fig. 1.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare thast they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunevicius, A., Pikis, S., Padilla, F. et al. Sonodynamic therapy for gliomas. J Neurooncol 156, 1–10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03807-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03807-6