Abstract
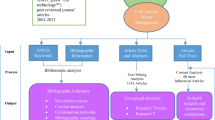
This article presents a systematic review of the literature using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) method associated with a bibliometric analysis on global perspective of technological advances in waste-to-energy (WTE). OpenRefine and VOSviewer software supported the bibliometric analysis. It was possible to establish the scientific gap through the correlation among interactions observed on co-authored countries’ analyses, cited sources of co-citation, cited authors of co-citation, and keyword of the co-occurrence author. A total of 10 papers were included for meta-analysis and categorized into 8 fields: author(s), title, published year, research areas, energy conversion technologies, wastes used for energy production, WTE products, key findings. Considering the end use of the products, the systematic literature review confirmed a limitation of research focusing on the opportunities for a cleaner transport sector. When analysing the author’s keywords, the most cited were ‘municipal solid waste’, ‘incineration’, ‘waste management’, ‘gasification’, ‘anaerobic digestion’, ‘combustion’, ‘waste-to-energy’, ‘landfill gas’, and ‘sustainability’, noting that the studies were directed at economic and sustainable development, as well as circular economy, aiming to mitigate adverse environmental impacts. As can be seen from the systematic review associated with the bibliometric analysis presented, the waste to energy technology is an important innovation way or route that finds numerous applications in the transport and energetic sector. It was evidenced that the WTE research efforts are mainly focused on the conversion of waste for end use electricity generation. The main role of WTE technologies in the circular economy is the energy recovery from biomass and non-recyclable waste, and also it was presented as a viable alternative to the decarbonization of transport and energy sectors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adami, L., Schiavon, M., & Rada, E. C. (2020). Potential environmental benefits of direct electric heating powered by waste-to-energy processes as a replacement of solid-fuel combustion in semi-rural and remote areas. Science of the Total Environment, 740, 140078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140078.
Ahamed, A., Yin, K., Ng, B. J. H., Ren, F., Chang, V. W. C., & Wang, J. Y. (2016). Life cycle assessment of the present and proposed food waste management technologies from environmental and economic impact perspectives. J Clean Prod, 131, 607–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.127.
Akrami, E., Ameri, M., & Rocco, M. V. (2020). Integration of biomass-fueled power plant and MCFC-cryogenic CO2 separation unit for low-carbon power production: Thermodynamic and exergoeconomic comparative analysis. Energy Conversion and Management, 223, 113304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113304.
Antwi-Boasiako, C., & Acheampong, B. B. (2016). Strength properties and calorific values of sawdust-briquettes as wood-residue energy generation source from tropical hardwoods of different densities. Biomass Bioenergy, 85, 144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.12.006.
Arpia, A. A., Chen, W. H., Lam, S. S., Rousset, P., & de Luna, M. D. G. (2021). Sustainable biofuel and bioenergy production from biomass waste residues using microwave-assisted heating: A comprehensive review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 403, 126233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126233.
Barbosa, F. T., Lira, A. B., de Oliveira Neto, O. B., Santos, L. L., Santos, I. O., Barbosa, L. T., et al. (2019). Tutorial for performing systematic review and meta-analysis with interventional anesthesia studies. Brazilian J Anesthesiol, 69(3), 299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjan.2018.11.007.
Casson Moreno, V., Iervolino, G., Tugnoli, A., & Cozzani, V. (2020). Techno-economic and environmental sustainability of biomass waste conversion based on thermocatalytic reforming. Waste Manag, 101, 106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.10.002.
Cucchiella, F., D’Adamo, I., & Gastaldi, M. (2017). Sustainable waste management: Waste to energy plant as an alternative to landfill. Energy Convers Manag, 131, 18–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.11.012.
Foster, W., Azimov, U., Gauthier-Maradei, P., Molano, L. C., Combrinck, M., Munoz, J., et al. (2021). Waste-to-energy conversion technologies in the UK: Processes and barriers – A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 135, 110226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110226.
Gutberlet, J., Bramryd, T., & Johansson, M. (2020). Expansion of the waste-based commodity frontier: Insights from Sweden and Brazil. Sustainability, 12(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072628.
Haaf, M., Anantharaman, R., Roussanaly, S., Ströhle, J., & Epple, B. (2020). CO2 capture from waste-to-energy plants: Techno-economic assessment of novel integration concepts of calcium looping technology. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 162, 104973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104973.
Haraguchi, M., Siddiqi, A., & Narayanamurti, V. (2019). Stochastic cost-benefit analysis of urban waste-to-energy systems. J Clean Prod, 224, 751–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.099.
Istrate, I. R., Iribarren, D., Gálvez-Martos, J. L., & Dufour, J. (2020). Review of life-cycle environmental consequences of waste-to-energy solutions on the municipal solid waste management system. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 157, 104778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104778.
Jan, N., & Ludo, V. E. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics and Informetrics, 84, 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3.
Khan, I., & Kabir, Z. (2020). Waste-to-energy generation technologies and the developing economies: A multi-criteria analysis for sustainability assessment. Renew Energy, 150, 320–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.132.
Kirchherr, J., Reike, D., & Hekkert, M. (2017). Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resources. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.005.
Kral, U., Morf, L. S., Vyzinkarova, D., & Brunner, P. H. (2019). Cycles and sinks: Two key elements of a circular economy. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 21(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0786-6.
Laso, J., Margallo, M., García-Herrero, I., Fullana, P., Bala, A., Gazulla, C., et al. (2018). Combined application of life cycle assessment and linear programming to evaluate food waste-to-food strategies: Seeking for answers in the nexus approach. Waste Manag, 80, 186–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.09.009.
Lu, J. W., Zhang, S., Hai, J., & Lei, M. (2017). Status and perspectives of municipal solid waste incineration in China: A comparison with developed regions. Waste Manag, 69, 170–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.014.
Mahmudul, H. M., Rasul, M. G., Akbar, D., Narayanan, R., & Mofijur, M. (2021). A comprehensive review of the recent development and challenges of a solar-assisted biodigester system. Science of The Total Environment, 753, 141920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141920.
Malinauskaite, J., Jouhara, H., Czajczyńska, D., Stanchev, P., Katsou, E., Rostkowski, P., et al. (2017). Municipal solid waste management and waste-to-energy in the context of a circular economy and energy recycling in Europe. Energy, 141, 2013–2044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.11.128.
Mardani, A., Zavadskas, E. K., Khalifah, Z., Zakuan, N., Jusoh, A., Nor, K. M., & Khoshnoudi, M. (2017). A review of multi-criteria decision-making applications to solve energy management problems: Two decades from 1995 to 2015. Renew Sust Energ Rev, 71(November 2016), 216–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.053.
Mukherjee, C., Denney, J., Mbonimpa, E. G., Slagley, J., & Bhowmik, R. (2020). A review on municipal solid waste-to-energy trends in the USA. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 119, 109512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109512.
Nizami, A. S., Ouda, O. K. M., Rehan, M., El-Maghraby, A. M. O., Gardy, J., Hassanpour, A., et al. (2016). The potential of Saudi Arabian natural zeolites in energy recovery technologies. Energy, 108, 162–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.07.030.
Nizami, A. S., Shahzad, K., Rehan, M., Ouda, O. K. M., Khan, M. Z., Ismail, I. M. I., et al. (2017). Developing waste biorefinery in Makkah: A way forward to convert urban waste into renewable energy. Appl Energy, 186, 189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.116.
Pizzi, S., Caputo, A., Corvino, A., & Venturelli, A. (2020). Management research and the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs): A bibliometric investigation and systematic review. J Clean Prod, 276, 124033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124033.
Ripa, M., Fiorentino, G., Vacca, V., & Ulgiati, S. (2017). The relevance of site-specific data in life cycle assessment (LCA). The case of the municipal solid waste management in the metropolitan city of Naples (Italy). J Clean Prod, 142, 445–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.149.
Satchatippavarn, S., Martinez-Hernandez, E., Leung Pah Hang, M. Y., Leach, M., & Yang, A. (2016). Urban biorefinery for waste processing. Chem Eng Res Des, 107, 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2015.09.022.
Seiple, T. E., Coleman, A. M., & Skaggs, R. L. (2017). Municipal wastewater sludge as a sustainable bioresource in the United States. J Environ Manag, 197, 673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.032.
Seruga, P., Krzywonos, M., Seruga, A., & Nied´zwiecki, Ł., Pawlak-Kruczek, H., & Urbanowska, A. (2020). Anaerobic digestion performance: Separate collected vs. mechanical segregated organic fractions of municipal solid waste as feedstock. Energies, 13, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13153768.
Sharma, S., Basu, S., Shetti, N. P., & Aminabhavi, T. M. (2020). Waste-to-energy nexus for circular economy and environmental protection: Recent trends in hydrogen energy. Sci Total Environ, 713, 136633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136633.
Soares, P. B., Carneiro, T. C. J., Calmon, J. L., & Castro, L. O. da C. de O. (2016). Análise bibliométrica da produção científica brasileira sobre Tecnologia de Construção e Edificações na base de dados Web of Science. Ambiente Construído, 16(1), 175–185. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-86212016000100067.
Świechowski, K., Syguła, E., Koziel, J. A., Stępień, P., Kugler, S., Manczarski, P., & Białowiec, A. (2020). Low-temperature pyrolysis of municipal solid waste components and refuse-derived fuel—Process efficiency and fuel properties of carbonized solid fuel. Data, 5(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/data5020048.
European Union. (2018). Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives.
Yılmaz Balaman, Ş., Wright, D. G., Scott, J., & Matopoulos, A. (2018). Network design and technology management for waste to energy production: An integrated optimization framework under the principles of circular economy. Energy, 143, 911–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.11.058.
Zhang, X., Estoque, R. C., Xie, H., Murayama, Y., & Ranagalage, M. (2019). Bibliometric analysis of highly cited articles on ecosystem services. PLoS One, 14(2), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210707.
Zhao, X., Gang, J. G., Wu, L., & A Wang, L. (2016). Economic analysis of waste-to-energy industry in China. Waste Manag, 48, 604–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.10.014.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), grant number 406789/2018-5, and was financed in part by the Brazilian Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boloy, R.A.M., da Cunha Reis, A., Rios, E.M. et al. Waste-to-Energy Technologies Towards Circular Economy: a Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 306 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05224-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05224-x