Abstract
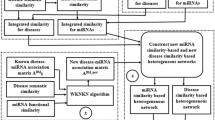
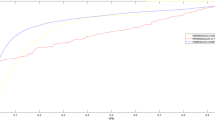
With the rapid development of biotechnology and computer technology, increasing studies have shown that the occurrence of many diseases in the human body is closely related to the dysfunction of miRNA, and the relationship between them has become a new research hotspot. Exploring disease-related miRNAs information provides a new perspective for understanding the etiology and pathogenesis of diseases. In this study, we proposed a new method based on similarity constrained learning (RSCMDA) to infer disease-associated miRNAs. Considering the problems of noise and incomplete information in current biological datasets, we designed a new framework RSCMDA, which can learn a new disease similarity network and miRNA similarity network based on the existing biological information, and then update the predicted miRNA–disease associations using robust similarity constraint learning method. Consequently, the AUC scores obtained in the global and local cross-validation of RSCMDA are 0.9465 and 0.8494, respectively, which are superior to the other methods. Besides, the prediction performance of RSCMDA is further confirmed by the case study on lung Neoplasms, because 94% of the top 50 miRNAs predicted by the RSCMDA method are confirmed from the existing biological databases or research results. All the results show that RSCMDA is a reliable and effective framework, which can be used as new technology to explore the relationship between miRNA and disease.
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu X, Wang X, Zhao H, Pei T, Wang LJFG (2020) BHCMDA: a new biased heat conduction based method for potential MiRNA–disease association prediction. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00384
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75(5):843–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-Y
Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, Lemon SM, Sarnow P (2005) Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific MicroRNA. Science 309(5740):1577–1581. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113329
Usha S, Jyothi MN, Suchithra B, Dixit R, Rai DV, Nagesh babu R (2017) Computational identification of MicroRNAs and their targets from finger millet (Eleusine coracana). Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 9(1):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0130-y
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75(5):855–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90530-4
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J, Song E (2007) let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131(6):1109–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.054
Liu JT, Chen ZY, Xiang JB, Gu XD (2018) MicroRNA-155 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting CTHRC1 in vitro. Oncol Lett 15(4):5561–5568. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8069
Jiang QH, Hao YY, Wang GH, Juan LR, Zhang TJ, Teng MX, Liu YL, Wang YD (2010) Prioritization of disease microRNAs through a human phenome-microRNAome network. BMC Syst Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-4-S1-S2
Xu J, Li CX, Lv JY, Li YS, Xiao Y, Shao TT, Huo X, Li X, Zou Y, Han QL, Li X, Wang LH, Ren H (2011) Prioritizing candidate disease miRNAs by topological features in the miRNA target-dysregulated network: case study of prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 10(10):1857–1866. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0055
Shi HB, Xu J, Zhang GD, Xu LD, Li CQ, Wang L, Zhao Z, Jiang W, Guo Z, Li X (2013) Walking the interactome to identify human miRNA–disease associations through the functional link between miRNA targets and disease genes. BMC Syst Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-7-101
Mork S, Pletscher-Frankild S, Caro AP, Gorodkin J, Jensen LJ (2014) Protein-driven inference of miRNA–disease associations. Bioinformatics 30(3):392–397. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt677
Xu CH, Ping YY, Li X, Zhao HY, Wang L, Fan HH, Xiao Y, Li X (2014) Prioritizing candidate disease miRNAs by integrating phenotype associations of multiple diseases with matched miRNA and mRNA expression profiles. Mol Biosyst 10(11):2800–2809. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mb00353e
Bandyopadhyay S, Mitra R, Maulik U, Zhang MQ (2010) Development of the human cancer microRNA network. Silence 1(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-907X-1-6
Sun DD, Li A, Feng HQ, Wang MH (2016) NTSMDA: prediction of miRNA–disease associations by integrating network topological similarity. Mol Biosyst 12(7):2224–2232. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00049e
You ZH, Huang ZA, Zhu ZX, Yan GY, Li ZW, Wen ZK, Chen X (2017) PBMDA: a novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA–disease association prediction. Plos Comput Biol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005455
Chen X, Guan NN, Li JQ, Yan GY (2018) GIMDA: graphlet interaction-based MiRNA–disease association prediction. J Cell Mol Med 22(3):1548–1561. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13429
Chen X, Wang LY, Huang L (2018) NDAMDA: network distance analysis for MiRNA–disease association prediction. J Cell Mol Med 22(5):2884–2895. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13583
Zeng XX, Liu L, Lu LY, Zou Q (2018) Prediction of potential disease-associated microRNAs using structural perturbation method. Bioinformatics 34(14):2425–2432. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty112
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang XT, Li ZH, Deng LX, Zhang YD, Dai QH (2015) RBMMMDA: predicting multiple types of disease-microRNA associations. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13877
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang X, You ZH, Huang YA, Yan GY (2016) HGIMDA: heterogeneous graph inference for miRNA–disease association prediction. Oncotarget 7(40):65257–65269. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11251
Chen X, Huang L (2017) LRSSLMDA: laplacian regularized sparse subspace learning for MiRNA–disease association prediction. Plos Comput Biol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005912
Chen X, Niu YW, Wang GH, Yan GY (2017) MKRMDA: multiple kernel learning-based Kronecker regularized least squares for MiRNA–disease association prediction. J Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1340-3
Chen X, Wu QF, Yan GY (2017) RKNNMDA: ranking-based KNN for MiRNA–disease association prediction. RNA Biol 14(7):952–962. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2017.1312226
Chen X, Huang L, Xie D, Zhao Q (2018) EGBMMDA: extreme gradient boosting machine for MiRNA–disease association prediction. Cell Death Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0003-x
Qu Y, Zhang HX, Liang C, Ding PJ, Luo JW (2018) SNMDA: a novel method for predicting microRNA–disease associations based on sparse neighbourhood. J Cell Mol Med 22(10):5109–5120. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13799
Yu SP, Liang C, Xiao Q, Li GH, Ding PJ, Luo JW (2018) GLNMDA: a novel method for miRNA–disease association prediction based on global linear neighborhoods. RNA Biol 15(9):1215–1227. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2018.1521210
Zheng K, You ZH, Wang L, Li YR, Zeng HT (2020) MISSIM: an incremental learning-based model with applications to the prediction of miRNA–disease association. IEEE Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2020.3013837
Li HY, You ZH, Li ZW, Zhou JR, Hu PW (2020) A network embedding-based method for predicting miRNA–disease associations by integrating multiple information. BMC Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60796-8_31
Li W, Cheng ZJBRI (2021) Prediction of miRNA–disease association using deep collaborative filtering. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6652948
Li Y, Qiu C, Tu J, Geng B, Yang J, Jiang T, Cui Q (2014) HMDD v20: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1070–D1074. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1023
Wang D, Wang JA, Lu M, Song F, Cui QH (2010) Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13):1644–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241
Wang M, Zhu PJB (2021) MRWMDA: a novel framework to infer miRNA–disease associations. Biosystems. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2020.104292
Xie J, Yin Y, Yang F, Sun J, Wang J (2021) Differential network analysis reveals regulatory patterns in neural stem cell fate decision. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.19445/v1
Singh NK (2017) microRNAs databases: developmental methodologies, structural and functional annotations. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 9(3):357–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-016-0166-7
Qu Y, Zhang HX, Liang C, Dong X (2018) KATZMDA: prediction of miRNA–disease associations based on KATZ Model. IEEE Access 6:3943–3950. https://doi.org/10.1109/Access.2017.2754409
Huang H, Yan J, Nie F, Huang J, Cai W, Saykin AJ, Shen L (2013) A new sparse simplex model for brain anatomical and genetic network analysis. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 16(Pt 2):625–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_77
Wong TT (2015) Performance evaluation of classification algorithms by k-fold and leave-one-out cross validation. Pattern Recogn 48(9):2839–2846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2015.03.009
Li JQ, Rong ZH, Chen X, Yan GY, You ZH (2017) MCMDA: matrix completion for MiRNA–disease association prediction. Oncotarget 8(13):21187–21199. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15061
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang X, You ZH, Deng L, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Dai Q (2016) WBSMDA: within and between score for MiRNA–disease association prediction. Sci Rep 6:21106. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21106
Xuan P, Han K, Guo M, Guo Y, Huang YJPO (2013) Prediction of microRNAs associated with human diseases based on weighted k most similar neighbors. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070204
Chen X, Yan GYJSR (2014) Semi-supervised learning for potential human microRNA–disease associations inference. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05501
Uddin A, Chakraborty S (2018) Role of miRNAs in lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26607
Claude P, Julien G (2016) Prediction of mirna-disease associations with a vector space model. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27036
Li Y, Qiu CX, Tu J, Geng B, Yang JC, Jiang TZ, Cui QH (2014) HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D1070–D1074. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1023
Yang Z, Wu L, Wang A, Tang W, Zhao Y, Zhao H, Teschendorff AE (2017) dbDEMC 2.0: updated database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D812–D818. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1079
Jiang Q, Wang Y, Hao Y, Juan L, Teng M, Zhang X, Li M, Wang G, Liu Y (2009) miR2Disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D98–D104. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn714
Das SS, Saha P, Chakravorty N (2018) miRwayDB: a database for experimentally validated microRNA-pathway associations in pathophysiological conditions. Database Oxf. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bay023
Ruepp A, Kowarsch A, Schmidl D, Buggenthin F, Brauner B, Dunger I, Fobo G, Frishman G, Montrone C, Theis FJ (2010) PhenomiR: a knowledgebase for microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-1-r6
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 61672329, 62072290) in part by the Project of the Shandong Provincial Project of Education Scientific Plan (No. SDYY18058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ShengPeng, Y., Hong, W. RSCMDA: Prediction of Potential miRNA–Disease Associations Based on a Robust Similarity Constraint Learning Method. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 13, 559–571 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00459-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-021-00459-y