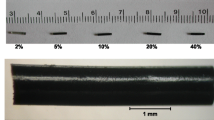
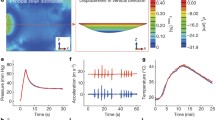
Abstract
(1) Summarize revisions made to the implantable resonator (IR) design and results of testing to characterize biocompatibility; (2) Demonstrate safety of implantation and feasibility of deep tissue oxygenation measurement using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) oximetry. In vitro testing of the revised IR and in vivo implantation in rabbit brain and leg tissues. Revised IRs were fabricated with 1–4 OxyChips with a thin wire encapsulated with two biocompatible coatings. Biocompatibility and chemical characterization tests were performed. Rabbits were implanted with either an IR with 2 oxygen sensors or a biocompatible-control sample in both the brain and hind leg. The rabbits were implanted with IRs using a catheter-based, minimally invasive surgical procedure. EPR oximetry was performed for rabbits with IRs. Cohorts of rabbits were euthanized and tissues were obtained at 1 week, 3 months, and 9 months after implantation and examined for tissue reaction. Biocompatibility and toxicity testing of the revised IRs demonstrated no abnormal reactions. EPR oximetry from brain and leg tissues were successfully executed. Blood work and histopathological evaluations showed no significant difference between the IR and control groups. IRs were functional for up to 9 months after implantation and provided deep tissue oxygen measurements using EPR oximetry. Tissues surrounding the IRs showed no more tissue reaction than tissues surrounding the control samples. This pre-clinical study demonstrates that the IRs can be safely implanted in brain and leg tissues and that repeated, non-invasive, deep-tissue oxygen measurements can be obtained using in vivo EPR oximetry.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the results reported in the article are available upon request.
References
S. Rockwell, I. Dobrucki, E. Kim, S. Marrison, V. Vu, Hypoxia and radiation therapy: past history, ongoing research, and future promise. Curr Mol Med 9, 442–458 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2174/156652409788167087
B.S. Sørensen, M.R. Horsman, Tumor hypoxia: impact on radiation therapy and molecular pathways. Front Oncol 10, 562 (2020)
M.R. Horsman, J. Overgaard, The impact of hypoxia and its modification of the outcome of radiotherapy. J Radiat Res 57(S1), i90–i98 (2016)
J.M. Brown, The hypoxic cell: a target for selective cancer therapy—eighteenth Bruce F. Cain Memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 59(23), 5863–5870 (1999)
D.M. Brizel, G.S. Sibley, L.R. Prosnitz, R.L. Scher, M.W. Dewhirst, Tumor hypoxia adversely affects the prognosis of carcinoma of the head and neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 38, 285–289 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(97)00101-6
P. Vaupel, Hypoxia and aggressive tumor phenotype: implications for therapy and prognosis. Oncologist 13(Suppl 3), 21–26 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.13-S3-21;10.1634/theoncologist.13-S3-21
M. Höckel, K. Schlenger, B. Aral, M. Mitze, U. Schäffer, P. Vaupel, Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res 56, 4509–4515 (1996)
K. Begg, M. Tavassoli, Inside the hypoxic tumour: reprogramming of the DDR and radioresistance. Cell Death Discov. 6, 1234567890 (2020)
T.G. Graeber, C. Osmanian, T. Jacks, D.E. Housman, C.J. Koch, S.W. Lowe, A.J. Giaccia, Hypoxia-mediated selection of cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours. Nature 379, 88–91 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379088a0
H.M. Swartz, A.B. Flood, P.E. Schaner, H. Howard, B.B. Williams, B.W. Pogue, B. Gallez, How best to interpret measures of levels of oxygen in tissues to make them effective clinical tools for care of patients with cancer and other oxygen-dependent pathologies. Physiol Rep 8, 14541 (2020)
H.M. Swartz, A.B. Flood, B.B. Williams, B.W. Pogue, P.E. Schaner, P. Vaupel, What is the meaning of an oxygen measurement?, in Oxygen Transport to Tissue XLII. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol. 1269, ed. by E.M. Nemoto, E.M. Harrison, S.C. Pias, D.E. Bragin, D.K. Harrison, J.C. LaManna (Springer, Cham, 2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48238-1_48
W.R. Wilson, M.P. Hay, Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 11, 393–410 (2011)
V.L. Codony, M. Tavassoli, Hypoxia-induced therapy resistance: available hypoxia-targeting strategies and current advances in head and neck cancer. Transl Oncol 14, 101017 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101017
K. Pinker, P. Andrzejewski, P. Baltzer, S.H. Polanec, A. Sturdza, D. Georg, T.H. Helbich, G. Karanikas, C. Grimm, S. Polterauer, R. Poetter, W. Wadsak, M. Mitterhauser, P. Georg, Multiparametric [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose/[18F]fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography/ magnetic resonance imaging of locally advanced cervical cancer for the non-invasive detection of tumor heterogeneity: a pilot study. PLoS ONE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155333
Z. Xu, X.F. Li, H. Zou, X. Sun, B. Shen, 18F-Fluoromisonidazole in tumor hypoxia imaging. Oncotarget 8(55), 94969 (2017)
J.P.B. O’Connor, S.P. Robinson, J.C. Waterton, Imaging tumour hypoxia with oxygen-enhanced MRI and BOLD MRI. Br J Radiol (2019). https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20180642
J.V. Gaustad, A. Hauge, C.S. Wegner, T.G. Simonsen, K.V. Lund, L.M.K. Hansem, E.K. Rofstad, DCE-MRI of tumor hypoxia and hypoxia-associated aggressiveness. Cancers (Basel) 12, 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071979
H. Lyng, K. Sundfør, E.K. Rofstad, Oxygen tension in human tumours measured with polarographic needle electrodes and its relationship to vascular density, necrosis and hypoxia. Radiother Oncol 44, 163–169 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8140(97)01920-8
M. Nordsmark, S.M. Bentzen, J. Overgaard, Measurement of human tumour oxygenation status by a polarographic needle electrode: an analysis of inter- and intratumour heterogeneity. Acta Oncol (Madr) 33, 383–389 (1994). https://doi.org/10.3109/02841869409098433
M. Höckel, C. Knoop, K. Schlenger, B. Vorndran, E. Baußnann, M. Mitze, P.G. Knapstein, P. Vaupel, Intratumoral pO2 predicts survival in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Radiother Oncol 26, 45–50 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8140(93)90025-4
N. Khan, H. Hou, S. Hodge, M. Kuppusamy, E.Y. Chen, A. Eastman, P. Kuppusamy, H.M. Swartz, Recurrent low-dose chemotherapy to inhibit and oxygenate head and neck tumors, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXVI. ed. by H.M. Swartz, D.K. Harrison, D.F. Bruley (Springer, New York, 2014), pp. 105–111
N. Khan, H. Hou, C.J. Eskey, K. Moodie, S. Gohain, G. Du, S. Hodge, W.C. Culp, P. Kuppusamy, H.M. Swartz, Deep-tissue oxygen monitoring in the brain of rabbits for stroke research. Stroke 46, e62–e66 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007324
H. Hou, O. Grinberg, B. Williams, S. Grinberg, H. Yu, D.L. Alvarenga, H. Wallach, J. Buckey, H.M. Swartz, The effect of oxygen therapy on brain damage and cerebral pO2 in transient focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Physiol Meas 28, 963–976 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/28/8/017
M.A. Polacco, H. Hou, P. Kuppusamy, E.Y. Chen, Measuring flap oxygen using electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry. Laryngoscope 129, E415–E419 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28043
H. Hou, S.P. Mupparaju, J.P. Lariviere, S. Hodge, J. Gui, H.M. Swartz, N. Khan, Assessment of the changes in 9L and C6 glioma pO2 by EPR oximetry as a prognostic indicator of differential response to radiotherapy. Radiat Res 179, 343–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1667/RR2811.1;10.1667/RR2811.1
A.B. Flood, V.A. Wood, H.M. Swartz, Using India ink as a sensor for oximetry: evidence of its safety as a medical device, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXIX. ed. by H.J. Halpern, J.C. LaManna, D.K. Harrison, B. Epel (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2017), pp. 297–312
P.E. Schaner, J.R. Pettus, A.B. Flood, B.B. Williams, L.A. Jarvis, E.Y. Chen, D.A. Pastel, R.A. Zuurbier, R.M. DiFlorio-Alexander, H.M. Swartz, P. Kuppusamy, OxyChip implantation and subsequent electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry in human tumors is safe and feasible: first experience in 24 patients. Front Oncol (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.572060
H.M. Swartz, B.B. Williams, H. Hou, N. Khan, L.A. Jarvis, E.Y. Chen, P.E. Schaner, A. Ali, B. Gallez, P. Kuppusamy, A.B. Flood, Direct and repeated clinical measurements of pO2 for enhancing cancer therapy and other applications, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXVIII. ed. by Q. Luo, L.Z. Li, D.K. Harrison, H. Shi, D.F. Bruley (Springer, Cham, 2016), pp. 95–104
G. Meenakshisundaram, E. Eteshola, R.P. Pandian, A. Bratasz, S.C. Lee, P. Kuppusamy, Fabrication and physical evaluation of a polymer-encapsulated paramagnetic probe for biomedical oximetry. Biomed Microdevices 11, 773–782 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9292-x
G. Meenakshisundaram, R.P. Pandian, E. Eteshola, S.C. Lee, P. Kuppusamy, A paramagnetic implant containing lithium naphthalocyanine microcrystals for high-resolution biological oximetry. J Magn Reson 203, 185–189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2009.11.016
H. Hou, N. Khan, M. Nagane, S. Gohain, E.Y. Chen, L.A. Jarvis, P.E. Schaner, B.B. Williams, A.B. Flood, H.M. Swartz, P. Kuppusamy, Skeletal muscle oxygenation measured by EPR oximetry using a highly sensitive polymer-encapsulated paramagnetic sensor, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXVIII. ed. by Q. Luo, L.Z. Li, D.K. Harrison, H. Shi, D.F. Bruley (Springer, Cham, 2016), pp. 351–357
Sergey Petryakov, Wilson Schreiber, Maciej Kmiec, Harold M. Swartz, Philip E. Schaner, Benjamin Williams (2021) Flexible, segmented surface coil resonator for in vivo EPR oximetry. Appl Magn Reson (special issue)
H.J. Halpern, D.P. Spencer, J. Van Polen, M.K. Bowman, A.C. Nelson, E.M. Dowey, B.A. Teicher, Imaging radio frequency electron-spin-resonance spectrometer with high resolution and sensitivity for in vivo measurements. Rev Sci Instrum 60, 1040–1050 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1140314
Y. Deng, G. He, S. Petryakov, P. Kuppusamy, J.L. Zweier, Fast EPR imaging at 300 MHz using spinning magnetic field gradients. J Magn Reson 168, 220–227 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2004.02.012
G.A. Rinard, R.W. Quine, S.S. Eaton, G.R. Eaton, Frequency dependence of EPR signal intensity, 250 MHz to 9.1 GHz. J Magn Reson 156, 113–121 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/jmre.2002.2530
S. Subramanian, K.I. Matsumoto, J.B. Mitchell, M.C. Krishna, Radio frequency continuous-wave and time-domain EPR imaging and Overhauser-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of small animals: Instrumental developments and comparison of relative merits for functional imaging. NMR Biomed. 17, 263–294 (2004)
B. Epel, S.V. Sundramoorthy, E.D. Barth, C. Mailer, H.J. Halpern, Comparison of 250 MHz electron spin echo and continuous wave oxygen EPR imaging methods for in vivo applications. Med Phys 38, 2045–2052 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3555297
B. Epel, S.V. Sundramoorthy, C. Mailer, H.J. Halpern, A versatile high speed 250-MHz pulse imager for biomedical applications. Concepts Magn Reson Part B Magn Reson Eng 33, 163–176 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/cmr.b.20119
H. Hirata, S. Petryakov, W. Schreiber, Resonators for clinical electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), in measuring oxidants and oxidative stress in biological system. ed. by L. Berliner, N. Parinandi (Springer, Cham, 2020), pp. 189–219
S. Petryakov, A. Samouilov, M. Chzhan-Roytenberg, E. Kesselring, Z. Sun, J.L. Zweier, Segmented surface coil resonator for in vivo EPR applications at 1.1 GHz. J Magn Reson 198, 8–14 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2008.12.014
H. Li, H. Hou, A. Sucheta, B. Williams, J. Lariviere, M. Khan, P. Lesniewski, B. Gallez, H. Swartz, Implantable resonators-a technique for repeated measurement of oxygen at multiple deep sites with in vivo EPR, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXI. (Springer, Boston, 2010), pp. 265–272
R.M. Caston, W. Schreiber, H. Hou, B.B. Williams, E.Y. Chen, P.E. Schaner, L.A. Jarvis, A.B. Flood, S.V. Petryakov, M.M. Kmiec, P. Kuppusamy, H.M. Swartz, Development of the implantable resonator system for clinical EPR oximetry. Cell Biochem Biophys 75, 275–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0809-2
H. Hou, R. Dong, H. Li, B. Williams, J.P. Lariviere, S.K. Hekmatyar, R.A. Kauppinen, N. Khan, H. Swartz, Dynamic changes in oxygenation of intracranial tumor and contralateral brain during tumor growth and carbogen breathing: a multisite EPR oximetry with implantable resonators. J Magn Reson 214, 22–28 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2011.09.043
H. Hou, H. Li, R. Dong, S. Mupparaju, N. Khan, H. Swartz, Cerebral oxygenation of the cortex and striatum following normobaric hyperoxia and mild hypoxia in rats by EPR oximetry using multi-probe implantable resonators, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXII. ed. by J.C. LaManna, M.A. Puchowicz, K. Xu, D.K. Harrison, D.F. Bruley (Springer, Boston, 2011), pp. 61–67
H. Hou, N. Khan, J. Lariviere, S. Hodge, E.Y. Chen, L.A. Jarvis, A. Eastman, B.B. Williams, P. Kuppusamy, H.M. Swartz, Skeletal muscle and glioma oxygenation by carbogen inhalation in rats: a longitudinal study by EPR oximetry using single-probe implantable oxygen sensors, in Oxygen transport to tissue XXXVI. ed. by H.M. Swartz, D.K. Harrison, D.F. Bruley (Springer, New York, 2014), pp. 97–103
H.M. Swartz, R.B. Clarkson, The measurement of oxygen in vivo using EPR techniques. Phys Med Biol 43, 1957–1975 (1998)
N. Khan, B.B. Williams, H. Hou, H. Li, H.M. Swartz, Repetitive tissue pO2 measurements by electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry: current status and future potential for experimental and clinical studies. Antioxid Redox Signal 9, 1169–1182 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.1635
H.M. Swartz, S. Boyer, P. Gast, J.F. Glockner, H. Hu, K.J. Liu, M. Moussavi, S.W. Norby, N. Vahidi, T. Walczak, M. Wu, R.B. Clarkson, Measurements of pertinent concentrations of oxygen in vivo. Magn Reson Med 20, 333–339 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910200217
H.M. Swartz, T. Walczak, Developing in vivo EPR oximetry for clinical use, in Oxygen transport to tissue XX. ed. by A.G. Hudetz, D.F. Bruley (Springer, Boston, 1998), pp. 243–252
H. Hou, N. Khan, S. Gohain, C.J. Eskey, K.L. Moodie, K.J. Maurer, H.M. Swartz, P. Kuppusamy, Dynamic EPR oximetry of changes in intracerebral oxygen tension during induced thromboembolism. Cell Biochem Biophys 75, 285–294 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0798-1
Schreiber W, Petryakov S V., Kmiec MM, Flood AB, Swartz HM, Schaner PE, Williams. BB (2021) In vivo cw-epr spectrometer systems for dosimetry and oximetry in preclinical and clinical applications. Appl Magn Reson (special issue)
O.Y. Grinberg, H. Hou, S.A. Grinberg, K.L. Moodie, E. Demidenko, B.J. Friedman, M.J. Post, H.M. Swartz, pO2 and regional blood flow in a rabbit model of limb ischemia. Physiol Meas 25(3), 659 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Robyn Mosher for her assistance during the execution of this study, including technical and lab managerial aspects. We also acknowledge Karen Moodie and Kirk Maurer for their veterinary expertise and Sassan Hodge for his histopathological evaluations.
Funding
This study was supported by NIH grants P01 CA190193 and EB004031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EYC, PK, HMS, and BBW contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Harold Swartz is a co-owner of Clin-EPR, LLC which manufactures clinical and preclinical EPR spectrometers for investigational use only. No other authors have any conflicts of interest or competing interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, E.Y., Tse, D., Hou, H. et al. Evaluation of a Refined Implantable Resonator for Deep-Tissue EPR Oximetry in the Clinic. Appl Magn Reson 52, 1321–1342 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01376-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01376-5