Abstract
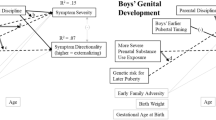
The current study leveraged the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) cohort (n = 4504 White boys, n = 4287 White girls assessed from the prenatal period through 18.5 years of age) to test a developmental cascade from genetic and prenatal substance use through pubertal timing and parenting to the severity of (regardless of type) and directionality (i.e., differentiation) of externalizing and internalizing problems to adolescent substance use. Limited associations of early pubertal timing with substance use outcomes were only observable via symptom directionality, differently for girls and boys. For boys, more severe exposure to prenatal substance use influenced adolescent substance use progression via differentiation towards relatively more pure externalizing problems, but in girls the associations were largely direct. Severity and especially directionality (i.e., differentiation towards relatively more pure externalizing problems) were key intermediaries in developmental cascades from parental harsh discipline with substance use progressions for girls and boys.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data for the current study is available from the ALSPAC study: http://www.bristol.ac.uk/alspac/researchers/access/.
Code availability
Derived variables and associated code for variables created in this study are returned to the ALSPAC Executive Team, and are available/distributed by ALSPAC. Data analytic scripts or additional details are freely available upon author request.
Notes
We also considered a more restrictive measure of harsh discipline that included only the slapped/hit item, averaged across the 9.5 and 11.5 year assessments. Results (available on author request) were practically identical when using this more restrictive measure; we elected to present findings from the more psychometrically sound four-item measure.
References
Bailey JA, Hill KG, Oesterle S, Hawkins JD (2009) Parenting practices and problem behavior across three generations: monitoring, harsh discipline, and drug use in the intergenerational transmission of externalizing behavior. Dev Psychol 45(5):1214–1226
Beltz AM, Corley RP, Wadsworth SJ, DiLalla LF, Berenbaum SA (2020) Does puberty affect the development of behavior problems as a mediator, moderator, or unique predictor? Dev Psychopathol 32(4):1473–1485
Bender HL, Allen JP, McElhaney KB, Antonishak J, Moore CM, Kelly HOB, Davis SM (2007) Use of harsh physical discipline and developmental outcomes in adolescence. Dev Psychopathol 19(1):227
Boyd A, Golding J, Macleod J, Lawlor DA, Fraser A, Henderson J, Molloy L, Ness A, Ring S, Davey Smith G (2013) Cohort Profile: The ‘Children of the 90s’—the index offspring of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children. Int J Epidemiol 42(1):111–127
Bowen E, Heron J, Waylen A, Wolke D, & ALSPAC Study Team (2005) Domestic violence risk during and after pregnancy: findings from a British longitudinal study. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynaecol 112(8):1083–1089
Brenner V, Fox RA (1998) Parental discipline and behavior problems in young children. J Genet Psychol 159(2):251–256
Buckingham-Howes S, Mazza D, Wang Y, Granger DA, Black MM (2016) Prenatal drug exposure and adolescent cortisol reactivity: association with behavioral concerns. J Dev Behav Pediatr 37(7):565–572
Button TMM, Lau JYF, Maughan B, Eley TC (2008) Parental punitive discipline, negative life events and gene–environment interplay in the development of externalizing behavior. Psychol Med 38(1):29–39
Colder CR, Scalco M, Trucco EM, Read JP, Lengua LJ, Wieczorek WF, Hawk LW Jr (2013) Prospective associations of internalizing and externalizing problems and their co-occurrence with early adolescent substance use. J Abnormal Child Psychol 41(4):667–677
Conradt E, Abar B, Lester BM, LaGasse LL, Shankaran S, Bada H, Bauer CR, Whitaker TM, Hammond JA (2014) Cortisol reactivity to social stress as a mediator of early adversity on risk and adaptive outcomes. Child Dev 85(6):2279–2298
Copeland WE, Worthman C, Shanahan L, Costello EJ, Angold A (2019) Early pubertal timing and testosterone associated with higher levels of adolescent depression in girls. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 58(12):1197–1206
Corley RP, Beltz AM, Wadsworth SJ, Berenbaum SA (2015) Genetic influences on pubertal development and links to behavior problems. Behav Genet 45(3):294–312
Day FR, Thompson DJ, Helgason H, Chasman DI, Finucane H, Sulem P, Ruth KS, Whalen S, Sarkar AK, Albrecht E (2017) Genomic analyses identify hundreds of variants associated with age at menarche and support a role for puberty timing in cancer risk. Nat Genet. https://doi.org/10.1530/ey.15.7.5
Deardorff J, Marceau K, Johnson M, Reeves J, Biro FM, Kubo A, Greenspan LC, Laurent C, Windham GC, Pinney SM, Kushi LH, Hiatt RA (2021) Girls’ timing and tempo and mental health: a longitudinal examination in an ethnically-diverse sample. J Adolesc Health 68(6):1197–1203
Dick DM, Rose RJ, Viken RJ, Kaprio J (2000) Pubertal timing and substance use: associations between and within families across late adolescence. Dev Psychol 36(2):180–189
Dodge KA, Malone PS, Lansford JE, Miller S, Pettit GS, Bates JE (2009) A dynamic cascade model of the development of substance-use onset. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev 74(3):vii–119
Donaldson CD, Handren LM, Crano WD (2016) The enduring impact of parents’ monitoring, warmth, expectancies, and alcohol use on their children’s future binge drinking and arrests: a longitudinal analysis. Prev Sci 17(5):606–614
Dorn LD, Dahl RE, Woodward HR, Biro F (2006) Defining the boundaries of early adolescence: a user’s guide to assessing pubertal status and pubertal timing in research with adolescents. Appl Dev Sci 10(1):30–56
Edwards AC, Latendresse SJ, Heron J, Cho SB, Hickman M, Lewis G, Dick DM, Kendler KS (2014) Childhood internalizing symptoms are negatively associated with early adolescent alcohol use. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(6):1680–1688
Ekblad MO, Marceau K, Rolan E, Palmer RH, Todorov A, Heath AC, Knopik VS (2020) The effect of smoking during pregnancy on severity and directionality of externalizing and internalizing symptoms: a genetically informed approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(21):7921
Elam KK, Chassin L, Pandika D (2018) Polygenic risk, family cohesion, and adolescent aggression in Mexican American and European American families: developmental pathways to alcohol use. Dev Psychopathol 30(5):1715–1728
Ellis BJ, Essex MJ (2007) Family environments, adrenarche, and sexual maturation: a longitudinal test of a life history model. Child Dev 78(6):1799–1817
Eriksson C, Kaprio J, Pulkkinen L, Rose R (2005) Testosterone and alcohol use among adolescent male twins: testing between-family associations in within-family comparisons. Behav Genet 35(3):359–368
Essex MJ, Klein MH, Cho E, Kraemer HC (2003) Exposure to maternal depression and marital conflict: gender differences in children’s later mental health symptoms. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42(6):728–737
Essex MJ, Shirtcliff EA, Burk LR, Ruttle PL, Klein MH, Slattery MJ, Kalin NH, Armstrong JM (2011) Influence of early life stress on later hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and its covariation with mental health symptoms: a study of the allostatic process from childhood into adolescence. Dev Psychopathol 23:1039–1058. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579411000484
Fraser A, Macdonald-Wallis C, Tilling K, Boyd A, Golding J, Davey Smith G, Henderson J, Macleod J, Molloy L, Ness A (2013) Cohort profile: the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children: ALSPAC mothers cohort. Int J Epidemiol 42(1):97–110
Ge X, Natsuaki MN (2009) In search of explanations for early pubertal timing effects on developmental psychopathology. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 18(6):327–331
Goodman R (1997) The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: a research note. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discipl 38(5):581–586
Goodman R, Meltzer H, Bailey V (1998) The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: a pilot study on the validity of the self-report version. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 7(3):125–130
Grumbach MM, Styne DM (2003) Puberty: ontogeny, neuroendocrinology, physiology, and disorders. In: Larsen PR, Kronenberg HM, Melmed S, Polonsky KS (eds) Williams textbook of endocrinology, vol 10. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1115–1286
Hicks BM, Schalet BD, Malone SM, Iacono WG, McGue M (2011) Psychometric and genetic architecture of substance use disorder and behavioral disinhibition measures for gene association studies. Behav Genet 41(4):459–475
Hopfer CJ, Crowley TJ, Hewitt JK (2003) Review of twin and adoption studies of adolescent substance use. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42(6):710–719
Horvath G, Knopik VS, Marceau K (2020) Polygenic influences on pubertal timing and tempo and depressive symptoms in boys and girls. J Res Adolesc 30(1):78–94
Hummel A (2014) Substance use in adolescent girls: the interplay of pubertal timing, family and peer influence. Cardiff University, Cardiff
Hussong AM, Jones DJ, Stein GL, Baucom DH, Boeding S (2011) An internalizing pathway to alcohol and substance use disorders. Psychol Addict Behav J Soc Psychol Addict Behav 25(3):390–404
Hussong AM, Ennett ST, Cox MJ, Haroon M (2017) A systematic review of the unique prospective association of negative affect symptoms and adolescent substance use controlling for externalizing symptoms. Psychol Addict Behav J Soc Psychol Addict Behav 31(2):137–147
Irner TB (2012) Substance exposure in utero and developmental consequences in adolescence: a systematic review. Child Neuropsychol J Normal Abnormal Dev Child Adolesc 18(6):521–549
Khoury JE, Jamieson B, Milligan K (2018) Risk for childhood internalizing and externalizing behavior problems in the context of prenatal alcohol exposure: a meta-analysis and comprehensive examination of moderators. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 42(8):1358–1377
Lansford JE, Erath S, Yu T, Pettit GS, Dodge KA, Bates JE (2008) The developmental course of illicit substance use from age 12 to 22: links with depressive, anxiety, and behavior disorders at age 18. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discipl 49(8):877–885
Lansford JE (2010) The special problem of cultural differences in effects of corporal punishment. Law Contemp Probl 73(2):89–106
Lansford JE, Criss MM, Laird RD, Shaw DS, Pettit GS, Bates JE, Dodge KA (2011) Reciprocal relations between parents’ physical discipline and children’s externalizing behavior during middle childhood and adolescence. Dev Psychopathol 23(01):225–238
Legleye S, Karila L, Beck F, Reynaud M (2007) Validation of the CAST, a general population Cannabis Abuse Screening Test. J Subst Use 12(4):233–242
Lougheed JP (2020) Parent–adolescent dyads as temporal interpersonal emotion systems. J Res Adolesc 30(1):26–40
Maier R, Visscher P, Robinson M, Wray N (2018) Embracing polygenicity: a review of methods and tools for psychiatric genetics research. Psychol Med 48(7):1055–1067
Maisonet M, Christensen KY, Rubin C, Holmes A, Flanders WD, Heron J, Ong KK, Golding J, McGeehin MA, Marcus M (2010) Role of prenatal characteristics and early growth on pubertal attainment of British girls. Pediatrics 126(3):e591–e600
Marceau K, Neiderhiser J, Lichtenstein P, Reiss D (2012) Genetic and environmental influences on the association between pubertal maturation and internalizing symptoms. J Youth Adolesc 41(9):1111–1126
Marceau K, Abar C, Jackson K (2015a) Parental knowledge is a contextual amplifier of associations of pubertal maturation and substance use. J Youth Adolesc 44(9):1720–1734
Marceau K, Laurent H, Neiderhiser J, Reiss D, Shaw D, Natsuaki M, Fisher P, Leve L (2015b) Combined influences of genes, prenatal environment, cortisol, and parenting on the development of children’s internalizing versus externalizing problems. Behav Genet 45:268–282
Marceau K, Zahn-Waxler C, Shirtcliff EA, Schreiber JE, Hastings P, Klimes-Dougan B (2015c) Adolescents’, mothers’, and fathers’ gendered coping strategies during conflict: youth and parent influences on conflict resolution and psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol 27(4pt1):1025–1044
Marceau K, De Arujo-Greecher M, Miller ES, Massey SH, Mayes LC, Ganiban JM, Reiss D, Shaw DS, Leve LD, Neiderhiser JM (2016) The Perinatal Risk Index: early risks experienced by domestic adoptees in the united states. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150486
Marceau K, Jackson K (2017) Deviant peers as a mediator of pubertal timing–substance use associations: the moderating role of parental knowledge. J Adolesc Health 61(1):53–60
Marceau K, Kirisci L, Tarter RE (2019a) Correspondence of pubertal neuroendocrine and Tanner stage changes in boys and associations with substance use. Child Dev 90(6):e763–e782
Marceau K, Rolan E, Leve LD, Ganiban JM, Reiss D, Shaw DS, Natsuaki MN, Egger H, Neiderhiser JM (2019b) Parenting and prenatal risk as moderators of genetic influences on conduct problems during middle childhood. Dev Psychol 55:1164–1181. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000701
Marceau K, Brick L, Knopik VS, Reijneveld SA (2020a) Developmental pathways from genetic, prenatal, parenting and emotional/behavioral risk to cortisol reactivity and adolescent substance use: a TRAILS study. J Youth Adolesc 49:17–31
Marceau K, Nair N, Rogers ML, Jackson KM (2020b) Lability in parent- and child-based sources of parental monitoring is differentially associated with adolescent substance use. Prev Sci 21(4):1–12
Marceau K, Neiderhiser J (2020) Generalist genes and specialist environments for adolescent internalizing and externalizing problems: a test of severity and directionality. Dev Psychopathol. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579420001108
Masten AS, Roisman GI, Long JD, Burt KB, Obradović J, Riley JR, Boelcke-Stennes K, Tellegen A (2005) Developmental cascades: linking academic achievement and externalizing and internalizing symptoms over 20 years. Dev Psychol 41(5):733
McNeil TF, Cantor-Graae E, Sjöström K (1994) Obstetric complications as antecedents of schizophrenia: empirical effects of using different obstetric complication scales. J Psychiatr Res 28(6):519–530
Mendle J, Turkheimer E, Emery RE (2007) Detrimental psychological outcomes associated with early pubertal timing in adolescent girls. Dev Rev 27(2):151–171
Mendle J, Ferrero J (2012) Detrimental psychological outcomes associated with pubertal timing in adolescent boys. Dev Rev 32(1):49–66
Mendle J (2014) Beyond pubertal timing: new directions for studying individual differences in development. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 23(3):215–219
Min MO, Albert JM, Lorincz-Comi N, Minnes S, Lester B, Momotaz H, Powers G, Yoon D, Singer LT (2020) Prenatal substance exposure and developmental trajectories of internalizing symptoms: toddlerhood to preadolescence. Drug Alcohol Depend 218:108411
Morris NM, Udry JR (1980) Validation of a self-administered instrument to assess stage of adolescent development. J Youth Adolesc 9(3):271–280
Neiderhiser JM, Marceau K, De Araujo-Greecher M, Ganiban JM, Mayes LC, Shaw DS, Reiss D, Leve LD (2016) Estimating the roles of genetic risk, perinatal risk, and marital hostility on early childhood adjustment: medical records and self-reports. Behav Genet 46:334–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-016-9788-0
Neiderhiser JM, Marceau K, Reiss D (2013) Four factors for the initiation of substance use by young adulthood: a 10-year follow-up twin and sibling study of marital conflict, monitoring, siblings, and peers. Dev Psychopathol 25(Special Issue 01):133–149
Patterson G (1982) Coercive family process: a social learning approach. Castalia, Eugene
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, De Bakker PI, Daly MJ (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81(3):559–575
Rhee SH, Lahey BB, Waldman ID (2015) Comorbidity among dimensions of childhood psychopathology: converging evidence from behavior genetics. Child Dev Perspect 9(1):26–31
Riggins-Caspers KM, Cadoret RJ, Knutson JF, Langbehn D (2003) Biology–environment interaction and evocative biology–environment correlation: contributions of harsh discipline and parental psychopathology to problem adolescent behaviors. Behav Genet 33(3):205–220
Rose J, Roman N, Mwaba K, Ismail K (2018) The relationship between parenting and internalizing behaviours of children: a systematic review. Early Child Dev Care 188(10):1468–1486
Rosseel Y (2012) lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling. J Stat Softw 48(2):36
Sartor CE, Jackson KM, McCutcheon VV, Duncan AE, Grant JD, Werner KB, Bucholz KK (2016) Progression from first drink, first intoxication, and regular drinking to alcohol use disorder: a comparison of African American and European American youth. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 40(7):1515–1523
Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, De la Fuente JR, Grant M (1993) Development of the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-II. Addiction (abingdon Engl) 88(6):791–804
Scalco MD, Colder CR, Read JP, Lengua LJ, Wieczorek WF, Hawk LW (2020) Testing alternative cascades from internalizing and externalizing symptoms to adolescent alcohol use and alcohol use disorder through co-occurring symptoms and peer delinquency. Dev Psychopathol 33(1):1–18
Schelleman-Offermans K, Knibbe RA, Kuntsche E (2013) Are the effects of early pubertal timing on the initiation of weekly alcohol use mediated by peers and/or parents? A Longitudinal Study. Dev Psychol 49(7):1277–1285
Shirtcliff EA, Essex MJ (2008) Concurrent and longitudinal associations of basal and diurnal cortisol with mental health symptoms in early adolescence. Dev Psychobiol 50(7):690–703
Shirtcliff EA, Dahl RE, Pollak SD (2009) Pubertal development: correspondence between hormonal and physical development. Child Dev 80(2):327–337
Silveira F, Shafer K, Dufur MJ, Roberson M (2021) Ethnicity and parental discipline practices: a cross-national comparison. J Marriage Fam 83(3):644–666
Stice E, Presnell K, Bearman SK (2001) Relation of early menarche to depression, eating disorders, substance abuse, and comorbid psychopathology among adolescent girls. Dev Psychol 37(5):608
Trucco EM, Hicks BM, Villafuerte S, Nigg J, Burmeister M, Zucker RA (2016) Temperament and externalizing behavior as mediators of genetic risk on adolescent substance use. J Abnormal Psychol 125(4):565–575
Trucco EM, Villafuerte S, Hussong A, Burmeister M, Zucker RA (2018) Biological underpinnings of an internalizing pathway to alcohol, cigarette, and marijuana use. J Abnormal Psychol 127(1):79–91
Ullsperger JM, Nikolas MA (2017) A meta-analytic review of the association between pubertal timing and psychopathology in adolescence: are there sex differences in risk? Psychol Bull 143(9):903
Vaughan EB, Van Hulle CA, Beasley WH, Rodgers JL, D’Onofrio BM (2015) Clarifying the associations between age at menarche and adolescent emotional and behavioral problems. J Youth Adolesc 44(4):922–939
Weigard AS, Hardee JE, Zucker RA, Heitzeg MM, Beltz AM (2020) The role of pubertal timing in the link between family history of alcohol use disorder and late adolescent substance use. Drug Alcohol Depend 210:107955
Weymouth BB, Fosco GM, Feinberg ME (2019) Nurturant-involved parenting and adolescent substance use: examining an internalizing pathway through adolescent social anxiety symptoms and substance refusal efficacy. Dev Psychopathol 31(1):247
Zheng J, Erzurumluoglu AM, Elsworth BL, Kemp JP, Howe L, Haycock PC, Hemani G, Tansey K, Laurin C, Pourcain BS (2017) LD Hub: a centralized database and web interface to perform LD score regression that maximizes the potential of summary level GWAS data for SNP heritability and genetic correlation analysis. Bioinformatics 33(2):272–279
Acknowledgements
We are extremely grateful to all the families who took part in this study, the midwives for their help in recruiting them, and the whole ALSPAC Team, which includes interviewers, computer and laboratory technicians, clerical workers, research scientists, volunteers, managers, receptionists and nurses.
Funding
The UK Medical Research Council and Wellcome (Grant Ref. 217065/Z/19/Z) and the University of Bristol provide core support for ALSPAC. This publication is the work of the authors, who will serve as guarantors for the contents of this paper. A comprehensive list of grants funding is available on the ALSPAC website (http://www.bristol.ac.uk/alspac/external/documents/grant-acknowledgements.pdf). GWAS data was generated by Sample Logistics and Genotyping Facilities at Wellcome Sanger Institute and LabCorp (Laboratory Corporation of America) using support from 23andMe. This research was specifically funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (K01 DA039288, Marceau).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KM conceived of the study, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. GH and AL were instrumental in construction of key study variables. VK was instrumental in conceptualizing the study. All authors edited the manuscript and approved of the final manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Kristine Marceau, Gregor Horvath, Amy Loviska, and Valerie Knopik declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the ALSPAC Ethics and Law Committee and the Local Research Ethics Committees. Ethical approval for the present data analysis was also obtained from the Purdue University IRB.
Informed consent
Informed consent for the use of data collected via questionnaires and clinics was obtained from participants following the recommendations of the ALSPAC Ethics and Law Committee at the time.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marceau, K., Horvath, G., Loviska, A.M. et al. Developmental Cascades from Polygenic and Prenatal Substance Use to Adolescent Substance Use: Leveraging Severity and Directionality of Externalizing and Internalizing Problems to Understand Pubertal and Harsh Discipline-Related Risk. Behav Genet 51, 559–579 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-021-10068-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-021-10068-6