Abstract
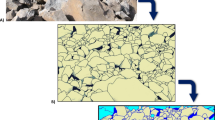
Application of the image processing techniques (IPT) to identify rock mass geometry provides more fast information about discontinuity properties used in geo-engineering characteristics. In this regard, the field survey can be improved using IPT. This study has utilised the IPT to identify the discontinuity and block volume characteristics in a discontinuous rock mass. For this purpose, a visual evaluation of the rock mass outcrop with discontinuities from a road slope cut located in the South Pars Special Zone, Assalouyeh, Iran, was considered. A three-step IPT analysis (i.e. pre-processing, main processing, and post-processing) was conducted to extract the features through the Python programming language. Regarding the IPT methodology, the studied rock mass characteristics consist of four major discontinuity sets and rock block volumes between the intersections of the discontinuities, as confirmed with a scan-line field survey. The evaluated data indicated that the maximum, minimum, and average block volumes processed by the IPT were 1.068, 0.479, and 1.055 m3, and their field measurement results were 1.092, 0.479, and 1.065 m3, respectively. Additionally, the orientations of the estimated discontinuity properties and their spacings determined by IPT for the rock mass ranging between 32 and 69.9° and 0.5 and 2.18 m, respectively. Similarly, the orientations of the field measurement results were also obtained between 33 and 71° and 0.58 and 2.25 m, respectively. The results of the IPT and the field survey were close, which revealed that the IPT is a reliable method for determining discontinuity spacing and rock block volume along large cut slopes. This approach provided rapid data processing with spatial extensions in a short period, making it possible to achieve accurate results in discontinuity network characteristics.




(Adapted from the Geological Survey of Iran 2009)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai D, Zho Y, Xie B, Li C (2019) Experimental study of fracture characterizations of rocks under dynamic tension test with image processing. Shock Vib 2019:6352609. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6352609
Azarafza M, Asghari-Kaljahi E, Akgün H (2017) Numerical modeling of discontinuous rock slopes utilizing the 3DDGM (three-dimensional discontinuity geometrical modeling) method. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76(3):989–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0879-1
Azarafza M, Akgün H, Asghari-Kaljahi E (2018) Stochastic geometry model of rock mass fracture network in tunnels. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 51(3):379–386. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2017-136
Azarafza M, Ghazifard A, Akgün H, Asghari-Kaljahi E (2019) Development of a 2D and 3D computational algorithm for discontinuity structural geometry identification by artificial intelligence based on image processing techniques. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:3371–3383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1298-2
Balakrishnan N, Basu AP (1996) Exponential distribution: theory, methods and applications. CRC Press, Florida
Ban L, Du W, Qi C, Zhu C (2021) Modified 2D roughness parameters for rock joints at two different scales and their correlation with JRC. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 137:104549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104549
Basirat R, Goshtasbi K, Ahmadi M (2019) Determination of the fractal dimension of the fracture network system using image processing technique. Fractal Fract 3(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3020017
Brady BHG, Brown ET (2007) Rock mechanics: for underground mining. Springer, Heidelberg
Burger W, Burge MJ (2009) Principles of digital image processing: fundamental techniques. Springer, Heidelberg
Buyer A, Aichinger S, Schubert W (2020) Applying photogrammetry and semi-automated joint mapping for rock mass characterization. Eng Geol 264:105332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105332
Cacciari PP, Futai MM (2016) Mapping and characterization of rock discontinuities in a tunnel using 3D terrestrial laser scanning. Bull Eng Geol Environ 75(1):223–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0748-3
Chityala R, Pudipeddi S (2014) Image processing and acquisition using Python. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Florida
Chu Z, Wu Z, Liu Q, Liu B (2020) Analytical solutions for deep-buried lined tunnels considering longitudinal discontinuous excavation in rheological rock mass. J Eng Mech 146(6):04020047. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001784
Deb D, Hariharan S, Rao UM, Ryn CH (2008) Automatic detection and analysis of discontinuity geometry of rock mass from digital images. Comput Geosci 34(2):115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2007.03.007
Fattah H, Moradi A (2018) A new approach for estimation of the rock mass deformation modulus: a rock engineering systems-based model. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:363–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-1000-5
Geological Survey of Iran (2009) Geological map of Kangan and Assalouyeh-scale. Geological Survey of Iran Press, Tehran (in Persian)
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2017) Digital image processing, 4th edn. Pearson, London
Goodman RE (1989) Introduction to rock mechanics. Wiley & Sons, New York
Gue J, Li S, Zhang P, Wu L, Zhou W, Yu Y (2017) Towards semi-automatic rock mass discontinuity orientation and set analysis from 3D point clouds. Comput Geosci 103:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.03.017
Guo J, Lin Y, Wu L, Yang T, Zhu W, Zhang Z (2019) A geometry- and texture-based automatic discontinuity trace extraction method for rock mass point cloud. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 124:104132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104132
Hoek E (2006) Practical rock engineering. Rocscience press, p 341
Hong K, Han H, Kang K (2017) Determination of geological strength index of jointed rock mass based on image processing. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 9(4):702–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2017.05.001
Hudson JA, Harrison JP (1997) Engineering rock mechanics—an introduction to the principles. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Iran Meteorological Organization (2018) Climatological data from Assalouyeh station. The Iran Meteorological Organization. http://www.irimo.ir/. Accessed 5 Aug 2018
ISRM (1981) Rock characterization, testing and monitoring. In: Brown ET (ed) ISRM suggested methods. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Jinhai Z, Liming Y, Weijia G (2018) Influence of three-dimensional roughness of rock fracture on seepage characteristics based on the digital image technology. Arab J Geosci 11:778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4121-2
Karakaş A (2008) Book reviews: practical rock engineering. Environ Eng Geosci 14(1):55–57. https://doi.org/10.2113/gseegeosci.14.1.55
Kemeny J, Post R (2003) Estimating three-dimensional rock discontinuity orientation from digital images of fracture traces. Comput Geosci 29(1):65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-3004(02)00106-1
Kim BH, Cai M, Kaiser PK, Yang HS (2007) Estimation of block sizes for rock masses with non-persistent joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 40(2):169–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-006-0093-8
Kumar R, Choudhury D, Bhargava K (2016) Determination of blast-induced ground vibration equations for rocks using mechanical and geological properties. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 8:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.10.009
Lawal AI, Kwon S (2021) Application of artificial intelligence to rock mechanics: an overview. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13:248–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.05.010
Li X, Chen J, Zhu H (2016) A new method for automated discontinuity trace mapping on rock mass 3D surface model. Comput Geosci 89:118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.12.010
Mahmoodzadeh A, Zare S (2016) Probabilistic prediction of expected ground condition and construction time and costs in road tunnels. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 8:734–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.07.001
Menegoni N, Giordan D, Perotti C, Tannant DD (2019) Detection and geometric characterization of rock mass discontinuities using a 3D high-resolution digital outcrop model generated from RPAS imagery—Ormea rock slope, Italy. Eng Geol 252:145–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.02.028
Meng Q, Wang H, Xu W, Zhang Q (2018) A coupling method incorporating digital image processing and discrete element method for modeling of geomaterials. Eng Comput 35(1):411–431. https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-11-2016-0390
Min SY, Kim TK, Lee JS, Einstein HH (2008) Design and construction of a road tunnel in Korea including application of the decision aids for tunneling—a case study. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 23:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2007.01.003
Moret Y, Einstein HH (2016) Construction cost and duration uncertainty model: application to high-speed rail line project. J Constr Eng Manag 142:05016010. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001161
Palmstrom A (1995) RMi—a rock mass characterization system for rock engineering purposes. PhD Thesis, University of Oslo, Department of Geology, p 400
Palmstrom A (2001) Chapter 2 of Measurement and characterization of rock mass jointing. In: Sharma VM, Saxena KR (eds) In-situ characterization of rocks. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Rotterdam, pp 1–40
Palmstrom A (2005) Measurements and correlations between block size and rock quality designation (RQD). Tunn Undergr Space Technol 20(4):362–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2005.01.005
Palmstrom A, Stille H (2015) Rock engineering, 2nd edn. ICE Publishing, Westminster
Porsani JL, Sauck WA, Junior AO (2006) GPR for mapping fractures and as a guide for the extraction of ornamental granite from a quarry: a case study from southern Brazil. J Appl Geophys 58(3):177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2005.05.010
Priest S (1993) Discontinuity analysis for rock engineering. Chapman & Hall, London
Prost GL (2013) Remote sensing for geoscientists: image analysis and integration, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Baton Rouge
Reid TR, Harrison JP (2000) A semi-automated methodology for discontinuity trace detection in digital images of rock mass exposures. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37(7):1073–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00041-1
Reynolds JM (2011) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics, 2nd edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Rives T, Razack M, Petit JP, Rawnsley D (1992) Joint spacing: analogue and numerical simulations. J Struct Geol 14(8/9):925–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8141(92)90024-Q
Rocscience (2018) DIPS—stereographic projection program for the analysis and presentation of orientation based data. Rocscience Inc. https://www.rocscience.com/software/dips
Saricam T, Ozturk H (2018) Estimation of RQD by digital image analysis using a shadow-based method. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 112:253–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.10.032
Skea C, Rezagholilou A, Far PB, Gholami R, Sarmadivleh M (2018) An approach for wellbore failure analysis using rock cavings and image processing. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 10(5):865–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.04.011
Tao R, Sharifzadeh M, Zhang Y, Teng XT (2020) Analysis of mafic rocks microstructure damage and failure process under compression test using quantitative scanning electron microscopy and digital images processing. Eng Fract Mech 231:107019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107019
Thomopoulos NT (2017) Probability distributions: with truncated, log and bivariate extensions. Springer, Heidelberg
Tong YL (2011) The multivariate normal distribution. Springer, Heidelberg
Umili G, Ferrero A, Einstein HH (2013) A new method for automatic discontinuity traces sampling on rock mass 3D model. Comput Geosci 51:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.07.026
Vöge M, Lato MJ, Diederichs MS (2013) Automated rock mass discontinuity mapping from 3-dimensional surface data. Eng Geol 164:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.07.008
Xu W, Zhang Y, Li X, Wang X, Ma F, Zhao J, Zhan Y (2020) Extraction and statistics of discontinuity orientation and trace length from typical fractured rock mass: a case study of the Xinchang underground research laboratory site. China Eng Geol 269:105553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105553
Yan L, Meng Q, Xu W, Wang H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Wang R (2017) A numerical method for analyzing the permeability of heterogeneous geomaterials based on digital image processing. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 18:124–137. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1500335
Zhang K, Wu W, Zhu H, Zhang L, Li X, Zhang H (2020a) A modified method of discontinuity trace mapping using three-dimensional point clouds of rock mass surfaces. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 12(3):571–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.10.006
Zhang W, Lan Z, Ma Z, Tan C, Que J, Wanf F, Cao C (2020b) Determination of statistical discontinuity persistence for a rock mass characterized by non-persistent fractures. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 126:104177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104177
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to sincerely thank Tamara George for her support during the editing of the manuscript. We would also specifically like to thank Professor Haluk Akgün for his valuable comments throughout the manuscript. Finally, the authors would like to express their gratitude to Editor-in-chief Olaf Kolditz and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions that helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azarafza, M., Koçkar, M.K. & Faramarzi, L. Spacing and block volume estimation in discontinuous rock masses using image processing technique: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 80, 471 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09768-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09768-3