Abstract
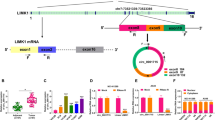
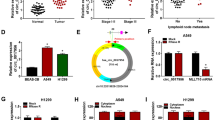
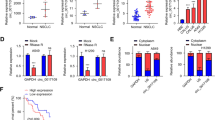
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a significant role in the progression of diverse malignancies. Here, we aimed to probe the function and mechanism of circ_0069244 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In the present study, circ_0069244 was selected from the circRNA microarray datasets (GSE112214). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was applied to examine circ_0069244, miR-346 and XPC complex subunit, DNA damage recognition and repair factor (XPC) expression levels. Kaplan–Meier curve was employed to analyze the association between circ_0069244 expression and overall survival of NSCLC patients. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-Bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) experiments were utilized to examine the proliferation of NSCLC cells. Scratch healing and Transwell experiments were executed to examine the migration of NSCLC cells. Western blot was conducted to detect XPC expression at protein level in NSCLC cells. Bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter gene and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) experiments predicted and validated the targeting relationships of circ_0069244 and miR-346, as well as miR-346 and 3'untranslated region (UTR) of XPC mRNA, respectively. We reported that circ_0069244 was remarkably down modulated in NSCLC and was linked to shorter survival and poor tumor histological grade in NSCLC patients. Functionally, circ_0069244 repressed NSCLC cell proliferation and migration. Furthermore, miR-346-5p was unveiled to be a downstream target of circ_0069244, and miR-346-5p specifically modulated XPC expression. Rescue experiments indicated that the inhibitory effect of circ_0069244 was abolished by co-expression of miR-346-5p mimics. Taken together, circ_0069244 restrained NSCLC progression by modulating the miR-346-5p/XPC axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Nasim F, Sabath BF, Eapen GA. Lung cancer. Med Clin North Am. 2019;103(3):463–73.
Lee SS, Cheah YK. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and cellular components of tumour microenvironment (TME) on non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:3046379.
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446–54.
Chen Z, Fillmore CM, Hammerman PS, Kim CF, Wong KK. Non-small-cell lung cancers: a heterogeneous set of diseases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14(8):535–46.
Verduci L, Strano S, Yarden Y, Blandino G. The circRNA-microRNA code: emerging implications for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(4):669–80.
Wu J, Qi X, Liu L, Hu X, Liu J, Yang J, Yang J, Lu L, Zhang Z, Ma S, et al. Emerging epigenetic regulation of circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;16:589–96.
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC, Ji ZL. CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer. 2018;25(1):1–7.
Liu Z, Zhou Y, Liang G, Ling Y, Tan W, Tan L, Andrews R, Zhong W, Zhang X, Song E, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_001783 regulates breast cancer progression via sponging miR-200c-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(2):55.
Tang Q, Chen Z, Zhao L, Xu H. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000515 acts as a miR-326 sponge to promote cervical cancer progression through up-regulation of ELK1. Aging. 2019;11(22):9982–99.
Afonso-Grunz F, Müller S. Principles of miRNA-mRNA interactions: beyond sequence complementarity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(16):3127–41.
Zhang M, Shi H, Zhang C, Zhang SQ. MiRNA-621 inhibits the malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer via targeting SIX4. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(11):4807–14.
Jin X, Chen Y, Chen H, Fei S, Chen D, Cai X, Liu L, Lin B, Su H, Zhao L, et al. Evaluation of tumor-derived exosomal miRNA as potential diagnostic biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer using next-generation sequencing. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(17):5311–9.
Sun CC, Li SJ, Yuan ZP, Li DJ. MicroRNA-346 facilitates cell growth and metastasis, and suppresses cell apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer by regulation of XPC/ERK/Snail/E-cadherin pathway. Aging. 2016;8(10):2509–24.
Xiong DD, Dang YW, Lin P, Wen DY, He RQ, Luo DZ, Feng ZB, Chen G. A circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):220.
Chen D, Ma W, Ke Z, Xie F. CircRNA hsa_circ_100395 regulates miR-1228/TCF21 pathway to inhibit lung cancer progression. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(16):2080–90.
Zhang G, Li S, Lu J, Ge Y, Wang Q, Ma G, Zhao Q, Wu D, Gong W, Du M, et al. LncRNA MT1JP functions as a ceRNA in regulating FBXW7 through competitively binding to miR-92a-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0829-6.
Patop IL, Kadener S. circRNAs in Cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018;48:121–7.
Patop IL, Wüst S, Kadener S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J. 2019;38(16):e100836.
Hsiao KY, Sun HS, Tsai SJ. Circular RNA - New member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(11):1136–41.
Ma X, Liu C, Gao C, Li J, Zhuang J, Liu L, Li H, Wang X, Zhang X, Dong S, et al. circRNA-associated ceRNA network construction reveals the circRNAs involved in the progression and prognosis of breast cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3973–83.
Li X, Yang B, Ren H, Xiao T, Zhang L, Li L, Li M, Wang X, Zhou H, Zhang W. Hsa_circ_0002483 inhibited the progression and enhanced the Taxol sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-182-5p. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(12):953.
Chen T, Yang Z, Liu C, Wang L, Yang J, Chen L, Li W. Circ_0078767 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer by protecting RASSF1A expression via sponging miR-330–3p. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12548.
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:287–314.
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(4):1202–7.
Mishra S, Yadav T, Rani V. Exploring miRNA based approaches in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;98:12–23.
Del Vescovo V, Denti MA. microRNA and lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;889:153–77.
Li W, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Tang L, Liu X, Dai Y, Xiao L, Huang S, Chen L, Guo Z, et al. MicroRNA-486 as a biomarker for early diagnosis and recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8):e0134220.
Xie WB, Liang LH, Wu KG, Wang LX, He X, Song C, Wang YQ, Li YH. MiR-140 expression regulates cell proliferation and targets PD-L1 in NSCLC. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):654–63.
Chen Y, Min L, Zhang X, Hu S, Wang B, Liu W, Wang R, Gu X, Shen W, Lv H, et al. Decreased miRNA-148a is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor clinical outcomes and functions as a suppressor of tumor metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2013;30(4):1832–40.
Yan HL, Li L, Li SJ, Zhang HS, Xu W. miR-346-5p promotes migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via targeting BRMS1. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016;30(12):602–7.
Guo Z, Li J, Sun J, Sun L, Zhou Y, Yu Z. miR-346-5p promotes HCC progression by suppressing breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 expression. Oncol Res. 2018;26(7):1073–81.
Dupuy A, Sarasin A. DNA damage and gene therapy of xeroderma pigmentosum, a human DNA repair-deficient disease. Mutat Res. 2015;776:2–8.
Yang J, Xu Z, Li J, Zhang R, Zhang G, Ji H, Song B, Chen Z. XPC epigenetic silence coupled with p53 alteration has a significant impact on bladder cancer outcome. J Urol. 2010;184(1):336–43.
Teng X, Fan XF, Li Q, Liu S, Wu DY, Wang SY, Shi Y, Dong M. XPC inhibition rescues cisplatin resistance via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in A549/DDP lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1875–82.
Sears CR. DNA repair as an emerging target for COPD-lung cancer overlap. Respir Investig. 2019;57(2):111–21.
Zhang R, Jia M, Xue H, Xu Y, Wang M, Zhu M, Sun M, Chang J, Wei Q. Genetic variants in ERCC1 and XPC predict survival outcome of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based therapy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10702.
Cui T, Srivastava AK, Han C, Yang L, Zhao R, Zou N, Qu M, Duan W, Zhang X, Wang QE. XPC inhibits NSCLC cell proliferation and migration by enhancing E-Cadherin expression. Oncotarget. 2015;6(12):10060–72.
Wu YH, Cheng YW, Chang JT, Wu TC, Chen CY, Lee H. Reduced XPC messenger RNA level may predict a poor outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2007;110(1):215–23.
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the technical support provided by Hubei Yican Health Industry Co., Ltd.
Funding
This study is supported by the Youth Research Funding of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: JS, HW, WF, JJ, Performed the experiments: JS, WF, SH, JA, LW, JJ. Analyzed the data: JS, JA, LW, JJ. Wrote the paper: JS, JJ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Our study was approved by the Ethics Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (approval number: 201900012).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., Wang, H., Feng, W. et al. Hsa_circ_0069244 acts as the sponge of miR-346 to inhibit non-small cell lung cancer progression by regulating XPC expression. Human Cell 34, 1490–1503 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00573-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00573-5