Abstract
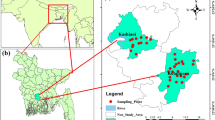
Groundwater from the Mocorito River aquifer in Mexico has been historically employed for both human consumption and irrigation of its overlaying agriculture fields. The aim of this research was to investigate the levels and distribution of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in the aquifer to determine their sources and to assess their potential health risks. Groundwater samples were collected from wells at eighteen sites in two climatic seasons. In the dry season, mean dissolved concentrations (µg L−1) of As, Pb, Cd, and Cr were 3.19, 0.05, 0.02, and 0.15, respectively, and their total (unfiltered) concentrations were 4.10, 0.47, 0.05, and 0.52, respectively. While in the rainy season, their dissolved concentrations were 4.60, 0.03, 0.01, and 0.06, respectively, and their total concentrations were 5.58, 0.25, 0.01, and 0.12, respectively. On average, concentrations of the four PTEs were below national and international guidelines for drinking water. Concentrations of As exceeded the WHO (2007) guidelines (10 µg L−1) at three sites and had yielded relatively high values of both chronic daily intake and hazard quotient. Lifetime cancer risk for As indicated the probability for developing this disease of 1 in 10, 000 inhabitants. Pearson’s correlation and principal component analysis (PCA-Varimax) were carried out. According to these, all the PTE concentrations were mainly derived from natural lithogenic sources. Arsenic concentrations constitute potential human health concerns for both direct consumption and its bioaccumulation in local crops. Finally, due to high As concentrations in some sites in the aquifer, the implementation of a sustainable groundwater management plan in the MORCA, that include a monitoring of PTE levels, is recommended.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Afzal, M., Shabir, G., Iqbal, S., Mustafa, T., Khan, Q. M., & Khalid, Z. M. (2014). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil and groundwater at leather industrial area of Kasur, Pakistan. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 42(8), 1133–1139. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201100715
Aullón-Alcaine, A., Schulz, C., Bundschuh, J., Jacks, G., Thunvik, R., Gustafsson, J. P., Mörth, C. M., Sracek, O., Ahmad, A., & Bhattacharya, P. (2020). Hydrogeochemical controls on the mobility of arsenic, fluoride and other geogenic co-contaminants in the shallow aquifers of northeastern La Pampa Province in Argentina. Science of the Total Environment, 715, 136671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136671
Arkoc, O. (2014). Heavy metal concentrations of groundwater in the east of Ergene Basin, Turkey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 93, 429–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1347-x
Ayedun, H., Gbadebo, A. M., Idowu, O. A., & Arowolo, T. A. (2015). Toxic elements in groundwater of Lagos and Ogun States, Southwest, Nigeria and their human health risk assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 351–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4319-7
Armienta, M. A., Rodríguez, R., Ceniceros, N., Cruz, O., Aguayo, A., Morales, P., & Cienfuegos, E. (2014). Groundwater quality and geothermal energy. The case of Cerro PrietoGeothermal Field. México. Renewable Energy., 63, 236–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.09.018
Armienta, M. A., & Segovia, N. (2008). Arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of Mexico. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30, 345–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9167-8
Armienta, M. A., Villaseñor, R., Rodriguez, R., Ongley, L. K., & Mango, H. (2001). The role of arsenic-bearing rocks in groundwater pollution at Zimapán Valley. México. Environmental Geology, 40(4–5), 571–581.
Barzegar, R., Moghaddam, A. A., Soltani, S., Fijani, E., Tziritis, E., & Kazemian, N. (2019). Heavy metal(loid)s in the groundwater of Shabestar Area (NW Iran): Source identification and health risk assessment. Exposure and Health, 11, 251–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0267-5
Bawa, R., & Dwivedi, P. (2019). Impact of land cover on groundwater quality in the Upper Floridan Aquifer in Florida. United States. Environmental Pollution, 252, 1828–1840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.054
Bodrud-Doza, M., Islam, S. M. D., Hasan, M. T., Alam, F., Haque, M. M., Rakib, M. A., Asad, M. A., & Rahman, M. A. (2019). Groundwater pollution by trace metals and human health risk assessment in central west part of Bangladesh. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 9, 100219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100219
Buragohain, M., Bhuyan, B., & Sarma, H. P. (2010). Seasonal variations of lead, arsenic, cadmium and aluminium contamination of groundwater in Dhemaji district, Assam. India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170, 345–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1237-6
Cao, X., Lu, Y., Wang, Ch., Zhang, M., Yuan, J., Zhang, A., Song, Sh., Baninla, Y., Khan, K., & Wang, Y. (2019). Hydrogeochemistry and quality of surface water and groundwater in the drinking water source area of an urbanizing region. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 186, 109628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109628
Chen, J., Qian, H., Gao, Y., Wang, H., & Zhang, M. (2020). Insights into hydrological and hydrochemical processes in response to water replenishment for lakes in arid regions. Journal of Hydrology, 581, 124386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124386
Chen, J., Wu, H., Qian, H., & Gao, Y. (2017). Assessing nitrate and fluoride contaminants in drinking water and their health risk of rural residents living in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Exposure and Health, 9(3), 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0231-9
Chen, J., Wu, H., & Qian, H. (2016). Groundwater nitrate contamination and associated health risk for the rural communities in an agricultural area of Ningxia, northwest China. Exposure and Health, 8(3), 349–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0208-8
Comisión Nacional de Agua (CONAGUA). (2020). Actualización de la disponibilidad medial anual de agua en el acuífero Río Mocorito (2503), Estado de Sinaloa. Diario Oficial de la Federación, 04 de enero de 2018, Gobierno Federal de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos, pp. 2–30. https://sigagis.conagua.gob.mx/gas1/Edos_Acuiferos_18/sinaloa/DR_2503.pdf (accessed 25 November 2020)
Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). (2014). Información histórica, temporada de ciclones 2014. Servicio Meteorologico Nacional. https://smn.conagua.gob.mx/tools/DATA/Climatolog%C3%ADa/Pron%C3%B3stico%20clim%C3%A1tico/Temperatura%20y%20Lluvia/PREC/2013.pdf. Accessed 24 June 2021
Coyte, R. M., Singh, A., Furst, K. E., Mitch, W. A., & Vengosh, A. (2019). Co-occurrence of geogenic and anthropogenic contaminants in groundwater from Rajasthan Indian. Science of the Total Environment, 688(20), 1216–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.334
David, N., Bell, D., Gold, J. (2001). Field sampling manual for the regional monitoring program for trace substances. https://www.sfei.org/sites/default/files/biblio_files/FOM2001_0.pdf (accessed: 30 august 2020).
De Paiva-Magalhães, D., da Costa-Marques, M. R., Fernandes-Baptista, D., & Forsin-Buss, D. (2015). Metal bioavailability and toxicity in freshwaters. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 13, 69–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0491-9
Dhaliwal, S. S., Singh, J., Taneja, P. K., & Mandal, A. (2020). Remediation techniques for removal of heavy metals from the soil contaminated through different sources: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 1319–1333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06967-1
Edet, A., Nganje, T. N., Ukpong, A. J., & Ekwere, A. S. (2011). Groundwater chemistry and quality of Nigeria: A status review. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(13), 1152–1169. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJESTX11.011
Erickson, M. L., Yager, R. M., Kauffman, L. J., & Wilson, J. T. (2019). Drinking water quality in the glacial aquifer system, northern USA. Science of the Total Environment, 694(1), 133735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133735
Fitzgerald, W.F. (1999). Clean hands, dirty hands: Clair Patterson and the aquatic biogeochemistry of mercury. In: Davidson, C.I. (Ed.), Clean Hands, Clair Patterson’s Crusade against Environmental Lead Contamination. Nova Science, Commack, NY, pp. 119–137.
Flegal, A. R., & Smith, D. R. (1995). Measurements of environmental lead contamination and human exposure. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 143, 1–45.
Garau, M., Garau, G., Diquattro, S., Roggero, P. P., & Castaldi, P. (2019). Mobility, bioaccessibility and toxicity of potentially toxic elements in a contaminated soil treated with municipal solid waste compost. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 186, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109766
García-Beltrán, A.N. (2008). Metodología para la generación y evaluación de políticas de operación en sistemas de recursos hídricos. Aplicación a un sistema en México. PhD Thesis. Universitat Politècnica de València. https://doi.org/10.4995/Thesis/10251/1970. (accessed, 17 February 2020).
García, E. (1964). Modificaciones al sistema de clasificación climática de Koppen. Offset Larios, Mexico City.
García-Gutiérrez, C., & Rodríguez-Meza, G. D. (2012). Problemática y riesgo ambiental por el uso de plaguicidas en Sinaloa. Ra Ximhai Revista De Sociedad Cultura y Desarrollo Sustentable, 8(3), 1–10.
Ghezzi, L., D’Orazio, M., Doveri, M., Lelli, M., Petrini, R., & Giannecchini, R. (2019). Groundwater and potentially toxic elements in a dismissed mining area: Thallium contamination of drinking spring water in the Apuan Alps (Tuscany, Italy). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 197, 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.11.009
Ghobadi, A., Cheraghi, M., Sobhanardakani, S., Lorestani, B., & Merrikhpour, H. (2020). Hydrogeochemical characteristics, temporal, and spatial variations for evaluation of groundwater quality of Hamedan-Bahar Plain as a major agricultural region. West of Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 79, 428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09177-y
Health Canada. (2004). Federal contaminated site risk assessment in Canada. Part II: Health Canada toxicological reference values (TRVs). Health Canada, Ottawa.
Huq, M. E., Fahad, S., Shao, Z., Sarven, M. S., Khan, I. A., Alam, M., Saeed, M., Ullah, H., Adnan, M., Saud, S., Cheng, Q., Ali, S., Wahid, F., Zamin, M., Raza, M. A., Saeed, B., Riaz, M., & Khan, W. U. (2020). Arsenic in a groundwater environment in Bangladesh: Occurrence and mobilization. Journal of Environmental Management, 262, 110318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110318
Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarias (INIFAP). (2000). Guía para la asistencia técnica agrícola. Área de influencia del campo experimental. Fundación Produce Sinaloa. Consejo consultivo zona norte, pp 284.
Karam-Quiñones, C. (2002). Los agroquímicos: una perspectiva jurídica-ambiental. Análisis del caso Sinaloa. Colegio de Sinaloa. Culiacán, Sinaloa, México. P.p. 404.
Krieger, P., & Hagner, A. F. (1943). Gold-nickel mineralization at Alistos Sinaloa, Mexico. American Mineralogist: Journal of Earth and Planetary Materials, 28(4), 257–271.
Lenntech. (2015). Iron in groundwater. Lenntech water treatment and purification holding B.V, Rotterdamseweg, Netherlands. https://www.lenntech.com/groundwater/iron.htm (accessed: 9 March 2020)
Leyva-Morales, J. B., García de la Parra, L. M., Bastidas Bastidas, P. J., Astorga Rodríguez, J. E., Bejarano Trujillo, J., Cruz Hernández, A., et al. (2014). Pesticide use in a technified agricultural valley in Northwest Mexico [Uso de plaguicidas en un valle agrícola tecnificado en el Noroeste de México]. Revista Internacional De Contaminación Ambiental, 30(3), 247–261.
Liang, B., Han, G., Liu, M., Yang, K., Li, X., & Liu, J. (2018). Distribution, sources, and water quality assessment of dissolved heavy metals in the Jiulongjiang river water, Southeast China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122752
Liang, Y., Yi, X., Dang, Z., Wang, Q., Luo, H., & Tang, J. (2017). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of a tailing pond in Guangdong, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121557
McDonough, L. K., O’Carrolla, D. M., Meredith, K., Andersen, M. S., Brügger, C., Huang, H., Rutlidge, H., Behnke, M. I., Spencer, R. G. M., McKenna, A., Marjo, C. E., Oudone, P., & Baker, A. (2020). Changes in groundwater dissolved organic matter character in a coastal sand aquifer due to rainfall recharge. Water Research, 169, 115201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115201
Mora, A., Mahlknecht, J., Rosales-Lagarde, L., & Hernández-Antonio, A. (2017). Assessment of major ions and trace elements in groundwater supplied to the Monterrey metropolitan area, Nuevo León. Mexico. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189, 394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6096-y
Morales-Zepeda, F. (2007). El impacto de la biotecnología en la formación de redes institucionales en el sector hortofrutícola de Sinaloa, México. PhD Thesis, Departamento de geografía física y análisis geográfico regional, Universidad de Barcelona. España, pp 441.
Páez-Osuna, F., Ramírez, G., Ruíz-Fernández, A.C., Soto-Jiménez, M.F. (2007). La contaminación por nitrógeno y fosforo en Sinaloa: flujos, fuentes, efectos y opciones de manejo. Serie lagunas costeras de Sinaloa. Primera edición. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Instituto de Ciencias del Mar y Limnología, Unidad Académica Mazatlán.
Peinado-Guevara, H. J., Green-Ruiz, C. R., Herrera-Barrientos, J., Escolero-Fuentes, O. A., Delgado-Rodríguez, O., Belmonte-Jiménez, S. I., & Ladrón de Guevara, M. Á. (2011). Calidad y aptitud de uso agrícola y doméstico del agua del acuífero del río Sinaloa, porción costera. Hidrobiologica, 21(1), 63–76.
Qian, H., Chen, J., & Howard, K. W. F. (2020). Assessing groundwater pollution and potential remediation processes in a multi-layer aquifer system. Environmental Pollution, 263, 114669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114669
Qiao, D., Wang, G., Li, X., Wang, S., & Zhao, Y. (2020). Pollution, sources and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface AMD water, sediments and surface soils around unexploited Rona Cu deposit, Tibet. China. Chemosphere, 248, 125988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125988
Rajkumar, H., Naik, P. K., & Rishi, M. S. (2020). A new indexing approach for evaluating heavy metal contamination in groundwater. Chemosphere, 245, 125598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125598
Rakib, M. A., Sasaki, J., Matsuda, H., Quraishi, S. B., Mahmud, M. J., Bodrud-Doza, M., Ullah, A. K. M. A., Fatema, K. J., Newaz, M. A., & Bhuiyan, M. A. H. (2020). Groundwater salinization and associated co-contamination risk increase severe drinking water vulnerabilities in the southwestern coast of Bangladesh. Chemosphere, 246, 125646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125646
Ravindra, K., & Mor, S. (2019). Distribution and health risk assessment of arsenic and selected heavy metals in Groundwater of Chandigarh. India. Environmental Pollution, 250, 820–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.080
Razo, I., Carrizales, L., Castro, J., Díaz-Barriga, F., & Monroy, M. (2004). Arsenic and heavy metal pollution of soil, water and sediments in a semi-arid climate mining area in Mexico. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 152, 129–152.
Rehman, A., Bukhari, S. M., Andleeb, Sh., Mahmood, A., Erinle, K. O., Naeem, M. M., & Imran, Q. (2019). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in vegetables irrigated with groundwater and wastewater: The particular case of Sahiwal district in Pakistan. Agricultural Water Management, 226, 105816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105816
Rivera-Hernández, J. R., Alvarado-Zambrano, D., Gonzales, L. A., & Green-Ruiz, C. (2019). Subtotal content and geochemical fractionation of potential toxic elements in agricultural soils from Mocorito River basin in NW Mexico: Environmental and health implications. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 1, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2019.1700939
Rivera-Hernández, J. R., Green-Ruiz, C., Pelling-Salazar, L. E., & Trejo-Alduenda, A. (2017). Hidroquímica del acuífero costero del Río Mocorito, Sinaloa, México: Evaluación de la calidad del agua para consumo humano y agricultura. Hidrobiologica, 27(1), 103–113.
Robles-Camacho, J., & Armienta, M. A. (2000). Natural chromium contamination of groundwater at León Valley México. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 68, 167–181.
Rodriguez, R., Armienta, M. A., Berlin, J., & Mejia, J. A. (2002). Arsenic and lead pollution of the Salamanca aquifer, Mexico: Origin, mobilization and restoration alternatives. Groundwater Quality: Natural and Enhanced Restoration of Groundwater Pollution, 275, 561–565.
Rosales, L., Carranza, A., Álvarez, U. (1986). Sedimentological and chemical studies in sediments from Alvarado lagoon system, Veracruz, Mexico. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Anuario Instituto de Ciencias del Mar y Limnología 13(3), 19–28.
Rubio, B., Nombela, M., & Vilas, F. (2000). Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ría Vigo: Assessment of metal pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(11), 968–980.
Rubio, B., Nombela, M., Vilas, F., Alejo, I., García-Gil, S., García-Gil, E., & Pazos, O. (1995). Distribución y enriquecimiento de metales pesados en sedimentos actuales de la parte interna de la Ría de Pontevedra. Thalassas, 11(3), 968–980.
Rubio, B., Pye, K., Rae, J., & Rey, D. (2001). Sedimentological characteristics, heavy metal distribution and magnetic properties in subtidal sediments, Ría de Pontevedra. Sedimentology, 48, 1–20.
Salvador, G. A. (2010). Iron in neuronal function and dysfunction. BioFactors, 36(2), 103–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.80
Sanjrani, M. A., Zhou, B., Zhao, H., Bhutto, S. A., Muneer, A. S., & Xia, S. B. (2019). Arsenic contaminated groundwater in China and its treatment options, a review. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17(2), 1655–1683. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1702_16551683
Santra, D., Mandal, S., Santra, A., & Ghorai, U. K. (2018). Cost-effective, wireless, portable device for estimation of hexavalent chromium, fluoride, and iron in drinking water. Analytical Chemistry, 90, 12815–12823. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03337
Sarti, G., Sammartino, I., & Amorosi, A. (2020). Geochemical anomalies of potentially hazardous elements reflect catchment geology: An example from the Tyrrhenian coast of Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 714, 136870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136870
Secretaria de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural (SADER) and Servicio Nacional de Sanidad, Inocuidad y Calidad Agroalimentaria (SENASICA). (2019). Manual para el buen uso y manejo de plaguicidas en campo, first ed. SENASICA, Mexico City. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/452645/MANUAL_PARA_EL_BUEN_USO_Y_MANEJO_DE_PLAGUICIDAS_EN_CAMPO.pdf. (accessed: 17 February 2020).
Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT). (2015). Acuerdo por el que se da a conocer el resultado de los estudios técnicos de aguas nacionales subterráneas del Acuífero Río Mocorito, Clave 2503, en el Estado de Sinaloa, Región Hidrológico-Administrativa Pacífico Norte. Diario Oficial de la Federación, 26 de agosto de 2015, Gobierno Federal de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos, Primera sección. http://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5405188&fecha=26/08/2015 (accessed: 6 February 2020).
Secretaría de Salud (SSA). (2000). Modificación a la Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-127-SSA1–1994, Salud ambiental. Agua para uso y consumo humano. Límites permisibles de calidad y tratamientos a que debe someterse el agua para su potabilización. Diario Oficial de la Federación, 22 de noviembre de 2000, Gobierno Federal de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos, Primera sección, 248–55. http://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=2063863&fecha=22/11/2000 (accessed: 17 February 2020).
Servicio Geológico Mexicano (SGM). (2015a). Carta geoquímica por Fe, escala: 1: 250,000, Pericos, Sinaloa, México. https://mapserver.sgm.gob.mx/Cartas_Online/geoquimica/39_G13-7_fe.pdf (accessed: 17 February 2020).
Servicio Geológico Mexicano (SGM). (2015b). Carta geoquímica por As, escala: 1: 250,000, Pericos, Sinaloa, México. https://mapserver.sgm.gob.mx/Cartas_Online/geoquimica/39_G13-7_as.pdf (accessed: 17 February 2020).
Servicio Geológico Mexicano (SGM). (2015c). Carta geoquímica por Pb, escala: 1: 250,000, Pericos, Sinaloa, México. https://mapserver.sgm.gob.mx/Cartas_Online/geoquimica/39_G13-7_pb.pdf (accessed: 17 February 2020).
Servicio Geológico Mexicano (SGM). (2015d). Carta geoquímica por Cd, escala: 1: 250,000, Pericos, Sinaloa, México. https://mapserver.sgm.gob.mx/Cartas_Online/geoquimica/39_G13-7_cd.pdf (accessed: 17 February 2020).
Setia, R., Dhaliwal, S.S., Kumar, V., Singh, R., Kukal, S.S., Pateriya, B. (2020). Impact assessment of metal contamination in surface water of Sutlej River (India) on human health risks. Environmental Pollution. 114907https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114907
Sobhanardakani, S. (2017a). Potential health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of caviar of Persian sturgeon. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 123, 34–38.
Sobhanardakani, S. (2017b). arsenic health risk assessment through groundwater drinking (case study: Qaleeh Shahin Agricultural Region, Kermanshah Province, Iran). Pollution, 4(1), 77–82. https://doi.org/10.22059/poll.2017.236875.291
Sobhanardakani, S. (2018). Health risk assessment of inorganic arsenic through groundwater drinking pathway in some agricultural districts of Hamedan, West of Iran. Avicenna Journal of Environmental Health Engineering, 5(2), 73–77. https://doi.org/10.15171/ajehe.2018.10
Sobhanardakani, S., Tayebi, L., & Hosseini, S. V. (2018). Health risk assessment of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Cu Co, Pb, and Sn) through consumption of caviar of Acipenser persicus from Southern Caspian Sea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 2664–2671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0705-8
Soto-Jimenez, M. F., Hibdon, S. A., Rankin, Ch. W., Aggarawl, J., Ruiz-Fernandez, A. C., Paez-Osuna, F., & Flegal, A. R. (2006). Chronicling a century of lead pollution in Mexico: Stable lead isotopic composition analyses of dated sediment cores. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(3), 764–770. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048478g
Tang, D., Warnken, K. W., & Santschi, H. (2002). Distribution and partitioning of trace metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in Galveston Bay waters. Marine Chemistry, 78, 29–45.
Thuyet, D. Q., Saito, H., Saito, T., Moritani, S., Kohgo, Y., & Komatsu, T. (2016). Multivariate analysis of trace elements in shallow groundwater in Fuchu in western Tokyo metropolis. Japan. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5170-4
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (1989). Risk assessment guidance for superfund. Human health evaluation manual, (part a) (Vol. 1). Washington, D.C.: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (1999a). Guidance for performing aggregate exposure and risk assessments, Office of Pesticide Programs, Washington, DC. https://archive.epa.gov/scipoly/sap/meetings/web/pdf/guidance.pdf (accessed: 9 March 2020)
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (1999b). A risk assessment–multi way exposure spread sheet calculation tool. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2001). Parameters of water quality: Interpretation and standards. Ireland. 133 pp. https://www.epa.ie/pubs/advice/water/quality/Water_Quality.pdf (accessed: 2 March 2020).
Upadhyaya, D., Survaija, M. D., Basha, S., Mandal, S. K., Thorat, R. B., Haldar, S., Goel, S., Dave, H., Baxi, K., Trivedi, R. H., & Mody, K. H. (2014). Occurrence and distribution of selected heavy metals and boron in groundwater of the Gulf of Khambhat region, Gujarat. India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 3880–3890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2376-4
Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM). (1978). Atlas geológico y evaluación geológica minera del Estado de Sinaloa. Rodríguez R., Cordoba D. (eds). Instituto de Geología. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Hojas I ‘‘Mocorito’’; II ‘‘Culiacán’’; III ‘‘Tamazula’’ y IV ‘‘La Peña’’, México.
Wang, Z.-L., & Liu, C.-Q. (2003). Distribution and partition behavior of heavy metals between dissolved and acid-soluble fractions along a salinity gradient in the Changjiang Estuary, eastern China. Chemical Geology, 202, 383–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2002.05.001
Wuana, R., & Okieimen, F. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best strategies for remediation. International Scholarly Research Network Ecology, 402647, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/402647
World Health Organization (WHO). (2017). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: Fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. Geneva, 541 pp. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254637/9789241549950-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed 2 March 2020).
Xiong, X., Liu, X., Yu, I. K. M., Wang, L., Zhou, J., Sun, X., Rinklebe, J., Shaheen, S. M., Ok, Y. S., Lin, Z., & Tsang, D. C. W. (2019). Potentially toxic elements in solid waste streams: Fate and management approaches. Environmental Pollution, 253, 680–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.012
Zgheib, S., Moilleron, R., Saad, M., & Chebbo, G. (2011). Partition of pollution between dissolved and particulate phases: What about emerging substances in urban stormwater catchments? Water Research, 45, 913–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.032
Zhou, M., Liao, B., Shu, W., Yang, B., & Lan, C. (2015). Pollution assessment and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils around four Pb/Zn mines of Shaoguan City, China. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 24(1), 76–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2014.914152.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sharon Hibdon† and Rob Frank of the University of California at Santa Cruz, for their support in the treatment, processing, and chemical analysis in the ICP-MS. In addition, they extend their appreciation to Francisco Montes of the National Water Commission (CONAGUA) in Guamuchil, Sinaloa, and to Alejandra Trejo Alduenda, Nuria Alonso, and Hernán Quiroga for their invaluable support during the fieldwork.
Funding
This research was supported by the Programa de Apoyo para la Superación del Personal Académico (PASPA) and Programa de Apoyo a Proyectos de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica (PAPPIT-IN107813) of the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. J. R. Rivera-Hernández and L. Pelling-Salazar had doctorate and master scholarship, respectively, from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivera-Hernández, J.R., Green-Ruiz, C.R., Pelling-Salazar, L.E. et al. Monitoring of As, Cd, Cr, and Pb in Groundwater of Mexico’s Agriculture Mocorito River Aquifer: Implications for Risks to Human Health. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 291 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05238-5