Abstract
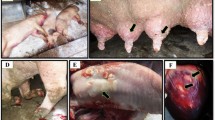
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is highly infectious, limits live animal trade, and affects ranchers owing to the loss of animal yield. The present study was designed to perform vaccine matching for field FMD virus isolates from clinically diseased cattle and assess the antigenic properties of the field isolates against the current vaccine strains used for vaccine production at the National Veterinary Institute, Ethiopia. Both sequencing and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reactions were used for distinguishing between the viral strains. To evaluate the serological relationship of the vaccine strain with these field isolates (r1 value), in vitro cross-neutralization was performed using ETH/6/2000 and ETH/38/2005 antisera. Infectious field FMD viral samples represented serotypes A and O. Sequence analysis showed that serotype A VP1/1D possessed amino acid variability at positions 28 and 42 to 48, 138, 141, 142, 148, 156, 173, and 197 compared with the ETH/6/2000 vaccine strain, whereas serotype O possessed amino acid variability at positions 45, 48, 138, 139, 140, 141, and 197 compared with the ETH/38/2005 vaccine strain. Based on the one-dimensional virus neutralization test, serotypes A and O demonstrated antigenic matching of up to 13/17 (76.47%) with the vaccine strain, except for the isolates ETH/40/2018, ETH/48/2018, ETH/55/2018, and ETH/61/2018, which had r-values less than 0.3. Therefore, the currently used vaccine strains ETH/38/2005 for serotype O and ETH/6/2000 for serotype A protected against all and most field viruses characterized as serotypes O and A, respectively, and amino acid residue variation was observed in different FMD virus B-C loops, G-H loops, and C-termini of VP1 at sites 1 and 3 in both serotypes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data related to the present study are included in the manuscript.
References
Acharya R, Fry E, Stuart D, Fox G, Rowlands D, Brown F (1989) The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 Å resolution. Nature 337:709–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/337709a0
Asfor A, Upadhyaya S, Knowles N, King D, Paton D, Mahapatra M (2014) Novel antibody binding determinants on the capsid surface of serotype O foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol 95:1104–1116. https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.060939-0
Ayelet G, Mahapatra M, Gelaye E, Egziabher BG, Rufeal T, Sahle M, Ferris NP, Wadsworth J, Hutchings GH, Knowles NJ (2009) Genetic characterization of foot-and-mouth disease viruses, Ethiopia, 1981–2007. Emerg Infect Dis 15:1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1509.090091
Ayelet G, Soressa M, Sisay T, Belay A, Gelaye E, Jembere S, Skjerve E, Asmare K (2013) FMD virus isolates: the candidate strains for polyvalent vaccine development in Ethiopia. Acta trop 126:244–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.02.005
Bari FD, Parida S, Tekleghiorghis T, Dekker A, Sangula A, Reeve R, Haydon DT, Paton DJ, Mahapatra M (2014) Genetic and antigenic characterisation of serotype A FMD viruses from East Africa to select new vaccine strains. Vaccine 32:5794–5800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.08.033
Barnett PV, Samuel AR, Pullen L, Ansell D, Butcher RN, Parkhouse RM (1998) Monoclonal antibodies, against O1 serotype foot-and-mouth disease virus, from a natural bovine host, recognize similar antigenic features to those defined by the mouse. J Gen Virol 79:1687–1697. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-79-7-1687
Baxt B, Vakharia V, Moore DM, Franke AJ, Morgan DO (1989) Analysis of neutralising antigenic sites on the surface of the type A12 foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol 63:2143–2151
Brehm KE, Kumar N, Thulke HH, Haas B (2008) High potency vaccines induce protection against heterologous challenge with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vaccine 26:1681–1687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.01.038
Carrillo C, Tulman ER, Delhon G, Lu Z, Carreno A, Vagnozzi A, Kutish GF, Rock DL (2005) Comparative genomics of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol 79:6487–6504. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.10.6487-6504.2005
Crowther JR, Farias S, Carpenter WC, Samuel AR (1993) Identification of a fifth neutralizable site on type O foot-and-mouth disease virus following characterization of single and quintuple monoclonal antibody escape mutants. J Gen Virol 74(8):1547–1553. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-74-8-1547
Central Statistical Agency (2019) Livestock and livestock characteristics report for 2018/2019, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Statistical bulletin 588, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Retrieved from https://www.statsethiopia.gov.et/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Crop-And-Livestock-Product-Utilization-Private-Peasant-Holdings-Meher-Season-2018-19-2011-E.C..pdf. Accessed 20 Nov 2020
Das B, Sanyal A, Subramaniam S, Mohapatra J, Pattniak B (2012) Field outbreak strains of serotype O foot-and-mouth disease virus from India with a deletion in the immune dominant βG-βH loop of the VP1 protien. Arch Virol 157:1967–1970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1380-1
Ding YZ, Chein J, Zhang JH, Zhou LN, Ma L, Zhang Y (2013) An overview of control strategy and diagnostic technology for foot-and-mouth disease in China. Virol J 10:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-10-78
Doel TR (2003) FMD vaccines. Virus Res 91:81–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1702(02)00261-7
Garcia-Boronat M, Diez-Rivero CM, Reinherz EL, Reche PA (2008) PVS: a web server for protein sequence variability analysis tuned to facilitate conserved epitope discovery. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W35-41. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn211
Gorna K, Houndje E, Romey A, Remly A, Blaise-Boisseau S, Kpodekon M, Saegerman C, Moutou F, Zientara S, Kassimi L (2014) First isolation and molecular characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus in Benin. Vet Microbiol 171:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.03.003
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Series 41:95–98
Haydon DT, Bastos AD, Knowles NJ, Samuel AR (2001) Evidence for positive selection in foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid genes from field isolates. Genet 157:7–15
Huang X, Li Y, Fang H, Zheng C (2011) Establishment of persistent infection with foot-and-mouth disease virus in BHK-21 cells. Virol J 8:169–169. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-8-169
Jemberu WT, Mourits MC, Sahle M, Siraw B, Vernooij JC, Hogeveen H (2016) Epidemiology of foot and mouth disease in Ethiopia: a retrospective analysis of district level outbreaks, 2007–2012. Transbound Emerg Dis 63:e246–e259. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12338
Kabat E, Wu T, Bilofsky H (1977) Unusual distributions of amino acids in complementarity-determining (hypervariable) segments of heavy and light chains of immunoglobulins and their possible roles in specificity of antibodycombining sites. J Biol Chem 252(19):6609–6616
Kitson JD, McCahon D, Belsham GJ (1990) Sequence analysis of monoclonal antibody resistant mutants of type O foot and mouth disease virus: evidence for the involvement of the three surface exposed capsid proteins in four antigenic sites. Virol 179:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-6822(90)90269-w
Knowles NJ, Samuel AR (2003) Molecular epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Res 91:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1702(02)00260-5
Knowles NJ, Wadsworth J, Bachanek-Bankowska K, King DP (2016) VP1 sequencing protocol for foot and mouth disease virus molecular epidemiology. Rev Sci et Tech (International Office of Epizootics) 35:741–755. https://doi.org/10.20506/rst.35.3.2565
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lea S, Abu-Ghazaleh R, Blakemore W, Curry S, Fry E, Jackson T, King A, Logan D, Newman J, Stuart D (1995) Structural comparison of two strains of foot-and-mouth disease virus subtype O1 and a laboratory antigenic variant, G67. Structure (London, England: 1993) 3(6):571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00191-5
Liu W, Yanga B, Wanga M, Wanga H, Yanga D, Mab W, Zhoua G, Yu L (2017) Identification of a conformational neutralizing epitope on the VP1 protein of type A foot-and-mouth disease virus. Res Vet Sci 115:374–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2017.07.001
Lloyd-Jones K, Mahapatra M, Upadhyaya S, Paton DJ, Babu A, Hutchings G, Parida S (2017) Genetic and antigenic characterization of serotype O FMD viruses from East Africa for the selection of suitable vaccine strain. Vaccine 35:6842–6849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.10.040
Longjam N, Deb R, Sarmah AK, Tayo T, Awachat VB, Saxena VK (2011) A brief review on diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease of livestock: conventional to molecular tools. Vet Med Inter 2011:905768–905768. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/905768
Mahapatra M, Seki C, Upadhyaya S, Barnett P, La Torre J, Paton DJ (2011) Characterisation and epitope mapping of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to A24 Cruzeiro strain of FMDV. Vet Microbiol 149:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.11.003
Mahapatra M, Statham B, Li Y, Hammond J, Paton D, Parida S (2016) Emergence of antigenic variants within serotype A FMDV in the Middle East with antigenically critical amino acid substitutions. Vaccine 34:3199–3206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.02.057
Mahapatra M, Yuvaraj S, Madhanmohan S, Subramaniam M, Pattnaik B, Paton D, Srinivasan V, Paridaa S (2015) Antigenic and genetic comparison of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O Indian vaccine strain, O/IND/R2/75 against currently circulating viruses. Vaccine 33(5):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.11.058
Mateu MG, Camarero JA, Giralt E, Andreu D, Domingo E (1995) Direct evaluation of the immuodominance of a major antigenic site of foot-and-mouth disease virus in a natural host. Virol 206(1):298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6822(95)80045-X
Mittal M, Tosh C, Hemadri D, Sanyal A, Bandyopadhyay S (2005) Phylogeny, genome evolution, and antigenic variability among endemic foot-and-mouth disease virus type A isolates from India. Arch Virol 150:911–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-004-0469-6
Momtaz S, Rahman A, Sultana M, Hossain MA (2014) Evolutionary analysis and prediction of peptide vaccine candidates for foot-and-mouth-disease virus types A and O in Bangladesh. Evol Bioinform 10:187–196. https://doi.org/10.4137/EBO.S17027
Negussie H, Kyule MN, Yami M, Ayelet G, Jenberie S (2011) Outbreak investigations and genetic characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus in Ethiopia in 2008/2009. Trop Anim Health Prod 43:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9683-2
Paton D, Reeve R, Capozzo A, Ludi A (2019) Estimating the protection afforded by foot-and-mouth disease vaccines in the laboratory. Vaccine 37(37):5515–5524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.07.102
Ramakrishnan M (2016) Determination of 50% endpoint titer using a simple formula. World J Virol 5(2):85–86. https://doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v5.i2.85
Reid SM, Ferris NP, Hutchings GH, Samuel AR, Knowles NJ (2000) Primary diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods 89(1–2):167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-0934(00)00213-5
Rieder E, Henry T, Duque H, Baxt B (2005) Analysis of a foot-and-mouth disease virus type A24 isolate containing an SGD receptor recognition site in vitro and its pathogenesis in cattle. J Virol 79(20):12989–12998. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.20.12989-12998.2005
Rweyemamu MM (1984) Antigenic variation in foot-and-mouth disease: studies based on the virus neutralization reaction. J Biol Stand 12(3):323–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-1157(84)80013-x
Rweyemamu MM, Hingley PJ (1984) Foot and mouth disease virus strain differentiation: analysis of the serological data. J Biol Stand 12(2):225–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-1157(84)80057-8
Samuel AR, Knowles NJ (2001) Foot-and-mouth disease type O viruses exhibit genetically and geographically distinct evolutionary lineages (topotypes). J Gen Virol 82:609–621. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-82-3-609
Sarangi L, Mohapatra J, Subramaniam S, Sanyal A, Pattnaik B (2013) Antigenic site variation in foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O grown under vaccinal serum antibodies in-vitro. Virus Res 176(1–2):272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2013.07.003
Subramaniam S, Mohapatra J, Das B, Sanyal A, Pattnaik B (2015) Genetic and antigenic analysis of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O responsible for outbreak in India during 2013. Infect Gen Evol 30:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2014.12.009
Tesfaye Y, Khan F, Yami M, Wadsworth J, Knowles N, King D, Gelaye E (2020) A vaccine-matching assessment of different genetic variants of serotype O foot-and-mouth disease virus isolated in Ethiopia between 2011 and 2014. Arch Virol 165:1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04662-y
Thomas A, Woortmeijer RJ, Puijk W, Barteling SJ (1988) Antigenic sites on foot-and-mouth disease virus type A10. J Virol 62(8):2782–2789. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.62.8.2782-2789.1988
Tosh C, Hemadri D, Sanyal A, Bandyopadhyay S (2003) Genetic and antigenicanalysis of two recently circulating genotypes of type A foot-and-mouth disease virus in India: evidence for positive selection in the capsid-encoding genes. Arch Virol 148:853–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-002-0968-2
Upadhyaya S, Ayelet G, Paul G, Donald PK, Paton DJ, Mahapatra M (2014) Genetic basis of antigenic variation in foot-and-mouth disease serotype A viruses from the Middle East. Vaccine 32:631–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.102
Acknowledgements
Colleagues from the World Reference Laboratory for Foot-and-Mouth Disease at The Pirbright Institute, United Kingdom, were acknowledged for sequencing the virus samples. The opinions expressed thus can no approach be taken to disclose the authorized attitude of the European Union and the National Veterinary Institute of Ethiopia additionally acknowledges for delivery of research facility and reagents with the authors. Authors additionally acknowledge the Department of Biotechnology, School of Engineering and Technology, Sharda University, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YT experimented. YT, EG, and FK structured the analysis and examined the information. All writers engaged with composing and adjustment of the original copy.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval and consent were obtained from AAU College of VMA Review Committee and Minutes of Animal Research Ethics (Reference VM/ERC/01/06/10/2018). Oral permission was additionally acquired from the animal proprietor to take samples from their cattle and for additional examination utilization of the samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tesfaye, Y., Khan, F. & Gelaye, E. Vaccine matching and antigenic variability of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotypes O and A from 2018 Ethiopian isolates. Int Microbiol 25, 47–59 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-021-00178-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-021-00178-w