Abstract
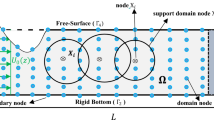
A numerical wave tank (NWT) is developed by employing the local radial point interpolation collocation method, mixed Eulerian–Lagrangian approach, and the fourth-order Runge–Kutta method. The potential theory is used for a mathematical explanation of the wave-propagation problem. The Laplace equation in the Eulerian manner and the free surface conditions in the Lagrangian manner are used to simulate the fully nonlinear water waves. The incident waves are generated by imposing analytic forms of the potential on the upstream boundary. To avoid any reflection of the waves at the end of the tank, a damping zone is placed on the free surface before the downstream wall boundary. In order to demonstrate the efficiency and accuracy of the meshless NWT, the first-, second-, third-, and fifth-order Stokes waves are simulated and the numerical results are compared with the analytical solutions. In addition, the wave propagation of water waves in uneven bottom NWT is investigated. Fairly good agreements between the numerical results, the analytical solutions, and experimental data are observed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bojanowski, C.: Numerical modeling of large deformations in soil structure interaction problems using FE, EFG, SPH, and MM-ALE formulations. Arch. Appl. Mech. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0830-5
Murčinková, Z., Novák, P., Kompiš, V., Žmindák, M.: Homogenization of the finite-length fibre composite materials by boundary meshless type method. Arch. Appl. Mech. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-018-1342-5
Cui, X., Liu, G., Li, G.: A smoothed Hermite radial point interpolation method for thin plate analysis. Arch. Appl. Mech. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-009-0392-0
Monaghan, J.J.: Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J. Comput. Phys. (1994). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1994.1034
Wen, H., Ren, B., Dong, P., Wang, Y.: A SPH numerical wave basin for modeling wave-structure interactions. Appl. Ocean Res. 56, 366–377 (2016)
Altomare, C., Tagliafierro, B., Dominguez, J.M., Suzuki, T., Viccione, G.: Improved relaxation zone method in SPH-based model for coastal engineering applications. Appl. Ocean Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2016.06.012
Ramli, M.Z., Temarel, P., Tan, M.: Hydrodynamic coefficients for a 3-D uniform flexible barge using weakly compressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-018-0044-2
Wu, N.-J., Tsay, T.-K., Young, D.L.: Meshless numerical simulation for fully nonlinear water waves. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.1051
Wu, N.-J., Tsay, T.-K.: Applicability of the method of fundamental solutions to 3-D wave–body interaction with fully nonlinear free surface. J. Eng. Math. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-008-9250-2
Xiao, L.-F., Yang, J.-M., Peng, T., Li, J.: A meshless numerical wave tank for simulation of nonlinear irregular waves in shallow water. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.1954
Xiao, L., Yang, J., Peng, T., Tao, L.: A free surface interpolation approach for rapid simulation of short waves in meshless numerical wave tank based on the radial basis function. J. Comput. Phys. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2015.12.003
Zhang, T., Ren, Y.-F., Yang, Z.-Q., Fan, C.-M., Li, P.-W.: Application of generalized finite difference method to propagation of nonlinear water waves in numerical wave flume. Ocean Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.07.038
Fan, C.-M., Chu, C.-N., Šarler, B., Li, T.-H.: Numerical solutions of waves-current interactions by generalized finite difference method. Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2018.01.010
Senturk, U.: Modeling nonlinear waves in a numerical wave tank with localized meshless RBF method. Comput. Fluids (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2018.01.010
Gholamipoor, M., Ghiasi, M.: A meshless numerical wave tank for simulation of fully nonlinear wave–wave and wave–current interactions. J. Eng. Math. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-019-10021-x
Gobbi, M.F., Kirby, J.T.: Wave evolution over submerged sills: tests of a high-order Boussinesq model. Coast. Eng. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3839(99)00015-0
Bayona, V., Moscoso, M., Kindelan, M.: Optimal variable shape parameter for multiquadric based RBF-FD method. J. Comput. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2011.11.036
Sarra, S.A., Sturgill, D.: A random variable shape parameter strategy for radial basis function approximation methods. Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2009.07.003
Liu, G.R., Zhang, G.Y., Gu, Y.T., Wang, Y.Y.: A meshfree radial point interpolation method (RPIM) for three-dimensional solids. Comput. Mech. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-005-0657-6
Liu, X., Liu, G.R., Tai, K., Lam, K.Y.: Radial point interpolation collocation method (RPICM) for partial differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2005.02.019
Liu, G.-R., Gu, Y.-T.: An Introduction to Meshfree Methods and Their Programming. Springer Science & Business Media (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3468-7
Ma, R., Li, G.: Spectral analysis of Stokes waves. Ocean Eng. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(01)00034-8
Mueller, A.: Novel two-way artificial boundary condition for 2D vertical water wave propagation modelled with radial-basis-function collocation method. J. Comput. Phys. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0029-8018(01)00034-8
Luth, H.R., Klopman, G., Kitou, N.: Kinematics of waves breaking partially on an offshore bar; LDV measurements of waves with and without a net onshore current. Technical Report H-1573, Delft Hydraulics, Delft vol 40 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholamipoor, M., Ghiasi, M. Simulation of fully nonlinear water wave propagation over the flat bottom and uneven bottom by meshless numerical wave tank. Arch Appl Mech 91, 4329–4341 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02010-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02010-3