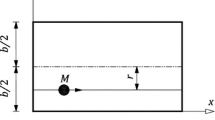
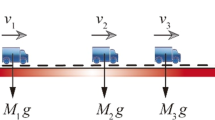
Abstract
Background
Dynamic analysis of structures under moving load excitation has been one of the most critical challenges for engineers during the last few years. The vast applications of this type of loading in many fields of the industry have intensified the importance of evaluating the dynamic response of vibrant structures under moving loads.
Purpose
This paper investigates the dynamic response of stiffened bridge decks subjected to moving loads for various constant velocities. The plates’ strength is improved by the placement of the stiffeners either concentrically or eccentrically. The stiffeners’ orientation, size, and shape play an important role in strengthening the plates, keeping the structure's weight low. Also, the number of loads and load traversing paths significantly affect the plate's response behaviour. Hence, an attempt has been made to present a parametric study for the dynamic response characteristics of stiffened bridge decks under single and multiple moving loads considering all the aforementioned parameters.
Methods
An in-house finite element MATLAB code is developed for the dynamic response study of the stiffened bridge decks. The plate and stiffener elements’ stiffness and mass matrices have been obtained separately and assembled to form the entire structure’s global matrices. Newmark integration method is used for computing the displacement, velocity, and acceleration for each time step. Some example results have been verified with previously published results and the FEAST (Finite Element Analysis of STructures) software to show the method’s efficacy.
Results
The frequency and the dynamic deflection results of bridge decks with various eccentrically and concentrically attached stiffeners are reported. The dynamic responses under single and multiple loads moving with different constant velocities are also addressed. The dynamic deflection results at various points of the bridge deck and the deflections due to the load moving in an arbitrary path are also assessed.
Conclusions
The attachment of I-beam stiffeners makes the bridge deck stiffer and depicts higher frequencies and lesser deflections than the attachment of T-beam or R-beam type stiffeners. The central deflection of the stiffened bridge deck is directly proportional to the distance traversed by the load. The maximum deflection value increases with an increment of dimension and load velocity.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harik IE, Guo M (1993) Finite element analysis of eccentrically stiffened plates in free vibration. Comput Struct 49(6):1007–1015
Liew KM, Xiang Y, Kitipornchai S, Lim MK (1994) Vibration of rectangular Mindlin plates with intermediate stiffeners. J Vib Acoust 116(4):529–535
Chen CJ, Liu W, Chern SM (1994) Vibration analysis of stiffened plates. Comput Struct 50(4):471–480
Barik M, Mukhopadhyay M (1998) Finite element free flexural vibration analysis of arbitrary plates. Finite Elem Anal Des 29(2):137–151
Barik M, Mukhopadhyay M (1999) Free flexural vibration analysis of arbitrary plates with arbitrary stiffeners. J Vib Control 5(5):667–683
Barik M, Mukhopadhyay M (2002) A new stiffened plate element for the analysis of arbitrary plates. Thin Walled Struct 40(7–8):625–639
Ahmad N, Kapania RK (2016) Free vibration analysis of integrally stiffened plates with plate-strip stiffeners. AIAA J 54(3):1107–1119
Nayak AN, Satpathy L, Tripathy PK (2018) Free vibration characteristics of stiffened plates. Int J Adv Struct Eng 10(2):153–167
Yang YB, Yang JP (2018) State-of-the-art review on modal identification and damage detection of bridges by moving test vehicles. Int J Struct Stab Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219455418500256
Yang JP, Chen BH (2018) Two-mass vehicle model for extracting bridge frequencies. Int J Struct Stab Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219455418500566
Yang YB, Wang ZL, Shi K, Xu H, Wu YT (2020) State-of-the-art of the vehicle-based methods for detecting the various properties of highway bridges and railway tracks. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 20:13. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219455420410047
Yang YB, Yang JP, Zhang B, Wu Y (2019) Vehicle scanning method for bridges. Wiley Publisher, Hoboken (ISBN: 978-1-119-53958-2)
Yang JP, Sun JY (2020) Pitching effect of a three-mass vehicle model for analyzing vehicle-bridge interaction. Eng Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.111248
Yang JP, Lee WC (2018) Damping effect of a passing vehicle for indirectly measuring bridge frequencies by EMD technique. Int J Struct Stab Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219455418500086
Sahoo PR, Barik M (2020) Free vibration analysis of stiffened plates. J Vib Eng Technol 8(6):869–882
Sahoo PR, Barik M (2020) A numerical investigation on the dynamic response of stiffened plated structures under moving loads. Structures 28:1675–1686
Sahoo PR, Barik M (2021) Free vibration analysis of stiffened curved plates. J Vib Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-021-00284-z
Mishra BP, Barik M (2021) Free flexural vibration of thin stiffened plates using NURBS-augmented finite element method. Structures 33:1620–1632
Wilson EN, Tsirk A (1967) Dynamic behavior of rectangular plates and cylindrical shells. National Aeronautics and Space Administration Report No. NGR-33-016-067
Wu JJ, Lee ML, Lai TS (1987) The dynamic analysis of a flat plate under a moving load by the finite element method. Int J Numer Eng Methods Eng 24:743–762
Raske TF, Schlack AL (1967) Dynamic response of plates due to moving loads. J Acoust Soc Am 42(3):625–635
Dobyns AL (1981) Analysis of simply-supported orthotropic plates subject to static and dynamic loads. AIAA J 19(5):642–650
Ratzlaff KP, Kennedy DJL (1985) Analysis of continuous steel plates subjected to uniform transverse loads. Can J Civ Eng 12(3):685–699
Ratzlaff KP, Kennedy DJL (1985) Behaviour and ultimate strength of continuous steel plates subjected to uniform transverse loads. Can J Civ Eng 13(1):76–85
Taheri MR, Ting EC (1989) Dynamic response of plate to moving loads: structural impedance method. Comput Struct 33(6):1379–1393
Taheri MR, Ting EC (1990) Dynamic response of plates to moving loads: Finite element method. Comput Struct 34(3):509–521
Humar JL, Kashif AH (1993) Dynamic response of bridges under travelling loads. Can J Civ Eng 20(2):287–298
Humar JL, Kashif AH (1995) Dynamic response analysis of slab-type bridges. J Struct Eng 121(1):48–62
Henchi K, Fafard M, Dhatt G, Talbot M (1997) Dynamic behaviour of multi-span beams under moving loads. J Sound Vib 199(1):33–50
Takabatake H (1998) Dynamic analysis of rectangular plates with stepped thickness subjected to moving loads including additional mass. J Sound Vib 213(5):829–842
Wu JJ, Whittaker AR, Cartmell MP (2000) The use of finite element techniques for calculating the dynamic response of structures to moving loads. Comput Struct 78(6):789–799
Sun L (2001) Dynamic displacement response of beam type structures to moving line loads. Int J Solids Struct 38(48–49):8869–8878
Wu JJ (2005) Dynamic analysis of a rectangular plate under a moving line load using scale beams and scaling laws. Comput Struct 83:1646–1658
Song Q, Shi J, Liu Z, Wan Y (2016) Dynamic analysis of rectangular thin plates of arbitrary boundary conditions under moving loads. Int J Mech Sci 117:16–29
Shirmohammadi F, Bahrami S, Saadatpour MM (2017) Dynamic response of rectangular plate subjected to moving loads using spectral finite strip method. Asian J Civ Eng 18(5):703–718
Esmaeilzadeh M, Kadkhodayan M (2019) Dynamic analysis of stiffened bi-directional functionally graded plates with porosities under a moving load by dynamic relaxation method with kinetic damping. Aerosp Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.105333
Yang DS, Wang CM, Pan WH (2020) Further insights into moving load problem on inclined beam based on 305 semi-analytical solution. Structures 26:247–256
Mizusawa T, Kajita Y, Naruoka M (1979) Vibration of skew plates by using B-spline functions. J Sound Vib 62(2):301–308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
The torsional stiffness matrix is given by:
The stiffness matrix is given by
where
The mass matrix is given by
where
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, P.R., Barik, M. Dynamic Response of Stiffened Bridge Decks Subjected to Moving Loads. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 9, 1983–1999 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-021-00344-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-021-00344-4