Abstract
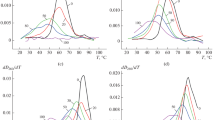
In this study, we compared the effects of gamma and high-energy proton radiation (1000 MeV) on DNA in aqueous saline solutions (5 and 150 mM NaCl) at doses of 30 and 50 Gy. We used spectral methods (the ultraviolet absorption method, spectrophotometric methods for nucleic acid quantification, spectrophotometric DNA melting, and circular dichroism) for the estimation of the number of damaged nitrogenous bases and damage of the secondary DNA structure. It was found that under these conditions, proton radiation causes more severe destruction of nitrogenous bases and the secondary DNA structure than exposure to gamma rays at the same dose. In DNA irradiated with protons, the formation of crosslinks is possible and the probability for crosslinking increases with the increase of the ionic strength of the irradiated solution.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yu. B. Kudryashov, Radiation Biophysics: Ionizing Radiation (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2004) [in Russian].
H. Murshed, Fundamentals of Radiation Oncology: Physical, Biological and Clinical Aspects (Elsevier, London, 2019).
M. Beyzadeoglu, G. Ozyigit, and C. Ebruli, Basic Radiation Oncology (Springer, Berlin, 2010).
G. E. Trufanov, M. A. Asaturyan, andi G. M. Zharinov, Radiation Therapy (GEOTAR-Media, Moscow, 2010) [in Russian].
O. Desouky and G. Zhou, J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 10, 187 (2016).
C. Cao, D. Wang, C. Chung, et al., J. Thoracic Cardiovasc. Surg. 157 (1), 362 (2019).
R. W. Gao, K. R. Olivier, S. S. Park, et al., Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 4, 314 (2019).
S. Falk, Surgery 27, 4 (2009).
A. P. Chernyaev, G. I. Klenov, A. Yu. Bushmanov, et al., Med. Radiol. Radiats. Bezopasn. 64 (2), 11 (2019).
A. S. Samoilov, Zh. Zh. Smirnova, V. A. Klimanov i dr., Med. Radiol. Radiats. Bezopasn. 64 (2), 41 (2019).
V. S. Khoroshkov, Med. Radiol. Radiats. Bezopasn. 64 (2), 52 (2019).
I. A. Gulidov, Radiats. Onkol. Yadern. Med., No. 1, 34 (2013)..
V. E. Balakin, A. E. Shemyakov, S. I. Zaichkina, et al., Biophysics (Moscow) 62 (1), 138 (2017).
L. L. Gol’din, V. P. Dzhelepov, M. F. Lomanov, et al., Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 16 (3), 402 (1973).
M. Durante and H. Paganetti, Rep. Prog. Phys. 79, 096702 (2016).
16. L. Brewster, R. Mohan, G. Mageras, et al., Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 33, 1081 (1995).
N. K. Abrosimov, A. A. Vorob’ev, V. A. Eliseev, et al., Med. Radiol. 32 (8), 10 (1987).
N. K. Abrosimov, Yu. A. Gavrikov, E. M. Ivanov, et al., J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 41, 424 (2006).
N. I. Ryabchenko, Radiation and DNA (Atomizdat, Moscow, 1979) [in Russian].
J. E. Coggle, Biological Effects of Radiation (Taylor & Francis, London, 1983).
C. Allen, T. B. Borak, H. Tsujii, and J. A. Nickoloff, Mutat. Res. 711, 150 (2011).
E. Surdutovich, E. Scifoni, and A. V. Solov’yov, Mutat. Res. 704, 206 (2010).
R. A. Mitteer Jr, Y. Wang, J. Shah, and S. Gordon, Sci. Rep. 5, 13961 (2015).
J. Kobierski and E. Lipiec, J. Mol. Struct. 1178, 162 (2019).
T. K. Gaisser, Astroparticle Phys. 35, 801 (2012).
A. S. Spirin, Biokhimiya 23, 656 (1958).
S. A. Tankovskaia, O. M. Kotb, O. A. Dommes, and S. V. Paston, J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1038, 012027 (2018).
S. A. Tankovskaia, O. M. Kotb, O. A. Dommes, and S. V. Paston, Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 200, 85 (2018).
C. R. Cantor and P. R. Schimmel, Biophysical Chemistry (Freeman, San Francisco, 1980), Parts 2, 3.
A. A. Vedenov, A. M. Dykhne, and M. D. Frank-Kamenetsky, Usp. Fiz. Nauk 107 (3), 479 (1971).
D. Y. Lando, A. S. Fridman, C.-L. Chang, et al., Anal. Biochem. 479, 28 (2015).
D. S. Ershov, S. V. Paston, L. A. Kartsova, et al., Struct. Chem. 22 (2), 475 (2011).
S. V. Paston and V. V. Zamotin, J. Struct. Chem. 50 (5), 970 (2009).
S. V. Paston, O. A. Dommes, and A. E. Tarasov, in Circular Dichroism: Theory and Spectroscopy, Ed. by D. S. Rodgers (Nova Science Publ., New York, 2011), pp. 301–319.
E. V. Chikhirzhina, T. Yu. Starkova, E. I. Kostyleva, et al., Cell Tissue Biol. 5, 536 (2011).
N. A. Kasyanenko, S. F. Bartoshevich, and E. V. Frisman, Mol. Biol. (Moscow) 19 (5), 13, (1985).
E. I. Ramm, V. I. Vorob’ev, T. M. Birshtein, et al., Eur. J. Biochem. 25, 245 (1972).
D. Y. Lando, A. S. Fridman, A. G. Kabak, and A. A. Akhrem, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 15, 141 (1997).
N. A. Kas’yanenko, J. Struct. Chem. 47, 163 (2006).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was carried out using the equipment of the Research park of St.Petersburg State University at “Center for Optical and Laser Research” and “Center for Nanofabrication of Photoactive Materials (Nanophotonics)”.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-08-01500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Statement of the welfare of animals
No studies on animals were carried out.
Additional information
Translated by A. Boutanaev
Abbreviations: LET is linear energy transfer, CD is circular dichroism.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotb, O.M., Brozhik, D.S., Verbenko, V.N. et al. Investigation of DNA Damage Induced by Proton and Gamma Radiation. BIOPHYSICS 66, 202–208 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350921020123
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350921020123