Abstract
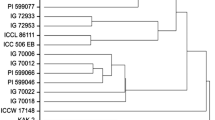
Host plant resistance mechanisms play an important role in developing cultivars with resistance to the target pests; information regarding morphological and biochemical factors contributing to the resistance is essential for developing pest-resistant cultivars. As a result, we investigated the contribution of various morphological and biochemical characters in forty-two eggplant genotypes against Leucinodes orbonalis Guenée, in Himachal Pradesh, India. Out of all the phenotypic parameters evaluated, pericarp thickness (r = 0.89) has significantly positive correlation with fruit infestation, whereas trichome density had significantly negative correlation (r = − 0.89). Analysis of the biochemical compounds in the eggplant genotypes revealed that total phenols (r = − 0.71), polyphenol oxidase (r = − 0.63), peroxidases (r = − 0.35), phenylalanine ammonium lyase (r = − 0.71) and solasodine (r = − 0.81) had significantly negative correlation with the per cent fruit infestation by L. orbonalis while the reducing sugars (r = 0.66) and non-reducing sugars (r = 0.62) showed a significantly positive correlation. Molecular characterization by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers also revealed the presence of high genetic diversity among different eggplant genotypes, where 17 polymorphic RAPD primers produced a total of 167 amplicons, among which 144 amplicons were polymorphic and 23 monomorphic bands. PCR-amplified DNA fragment size ranged from 100 to 2500 bp, mean polymorphism was 86.42% and the average PIC value was 0.444. Jaccards coefficient–based dendrogram grouped 40 eggplant genotypes into two major clusters. Results also revealed that the resistant genotypes accumulated higher levels of defensive biochemical enzymes such as phenols, PO, PPO, PAL and solasodine to confer insect resistance. Molecular characterization also revealed that genotypes in the present study were genetically diverse and could be used in future breeding and improvement programmes in this crop. Genotypes, IC411485 and IC090951, in particular, can be used as varied parents in breeding programmes to generate improved lines in terms of resistance to L. orbonalis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin SMR, Alam MZ, Rahman MM, Hossain MM, Mian IH (2014) Study on morphological characteristics of leaves, shoots and fruits of selected eggplant varieties/lines influencing eggplant shoot and fruit borer infestation. Int J EconPlants 1:1–8
Bhattacharya A, Mazumdar D, Das AK, Hazra P, Pal S (2009) Peroxidase and polyphenoloxidase activities and phenol content in fruit of eggplant and their relationship to infestation by shoot and fruit borer. Int J Veg Sci 15:316–324
Chang JC, Ponnath DW, Ramasamy S (2014) Phylogeographical structure in mitochondrial DNA of eggplant fruit and shoot borer, LeucinodesorbonalisGuenée (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in South and Southeast Asia. Mitochondrial DNA 27:198–204
Chen NC, Kalb T, Talekar NS, Wang JF, Ma CH (2001) Suggested cultural practices for eggplant. In: AVRDC Training Guide. AVRDC – The World Vegetable Center, Shanhua, p 8
Dempsey DA, Vlot AC, Wildermuth MC, Klessig DF (2011) Salicylic acid biosynthesis and metabolism. Arabidopsis Book 9:e0156
Devi P, Gawde P, Koshta VK (2015) Screening of some eggplant cultivars for resistance to shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee). Bioscan 10:247–251
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Ghananand T, Prasad CS, Nath L (2011) Effect of insecticides, bio-pesticides and botanicals on the population of natural enemies in brinjal ecosystem. Vegetos. 24:40–44
Haseeb M, Sharma DK, Qamar M (2009) Estimation of the losses caused by shoot and fruit borer, LeucinodesorbonalisGuen. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in brinjal. Trends Biosci 2:68–69
Islam T, Roknuzzaman A, HassanK UMS (2020) Temperature impacts on the eggplant shoot and fruit borer Leucinodes orbonalis: a life table approach. Int J Trop Insect Sci 40:351–360
Jin R, Ming S, Chao F, Ming LW, Xiao JL, Du CL, Jian YL (2007) Analysis of genetic diversity in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Southwest China J Agric Sci 20:694–697
Kaiser HF (1958) The varimax criteria for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychomethka 23:187–200
Kariyanna B, Prabhuraj A, Asokan R, Babu P, Jalali SK, Venkatesan T, GracyRG MM (2020) Identification of suitable reference genes for normalization of RT-qPCR data in eggplant fruit and shoot borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenée). Biologia 75:289–297
Khorsheduzzaman AKM, Alam MZ, Mian IH (2010) Biochemical basis of resistance in eggplant (Solanum melongena. L) to Leucinodes orbonalis Guen. and their correlation with shoot and fruit infestation. Bangladesh J Agric Res 35:149–155
Krishna A, Dubey VK, Agale SV, Rana DK (2017) Biophysical mechanism of resistance to Eggplant shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee in Eggplant. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 6:121–126
Laila R, Siddiqua MK, Khalil I, Robin AHK, Meah MB (2012) Molecular characterization of Solanum melongena L. using RAPD marker for collar rot resistance. Int J Adv Life Sci 1:1839–1899
Mannan MA, Begum A, Rahman MM, Hossain MM (2003) Screening of local and exotic brinjal varieties/cultivars for resistance to brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guen. Pak J Biol Sci 6:488–492
Mannan MA, Islam KS, Jahan M (2015) Brinjal shoot and fruit borer infestation in relation to plant age and season. Bangladesh J Agric Res 40:399–407
Mishra PN, Singh YV, Nautiyal MC (1988) Screening of brinjal varieties for resistance to shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guen.) (Pyralidae: Lepidoptera). South Indian Hortric 36:188–192
Mishra K, Keshav S, Tripathi CPM (2014) Management of infestation of pod borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee) and productivity enhancement of brinjal (Solanum melogena) through vermiwash with biopesticide. Int J Adv Res 2:780–789
Mitchell C, Brennan RM, Graham J, Karley AJ (2016) Plant defense against herbivorous pests: exploiting resistance and tolerance traits for sustainable crop protection. Front Plant Sci 7:1132
Mukherjee I (2003) Pesticide residues in vegetables in and around Dehli. Environ Monit Assess 86:265–271
Niranjana RF, Devi M, Shanika W, Sridhar PR (2015) Influence of biophysical characteristics of Eggplant varieties on the infestation of eggplant shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee. J Univ Ruhuna 1:21–28
Nirmala N, Vethamoni PI, Natarajan N (2017) Association of biochemical characters on shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis G.) resistance in green fruited brinjal. Int J Chem Stud 5:212–214
Onda Y, Mochida K (2016) Exploring genetic diversity in plants using high-throughput sequencing techniques. Curr Genomics 17:358–367
Peterson JA, Ode PJ, Oliveira-Hofman C, Harwood JD (2016) Integration of plant defense traits with biological control of arthropod pests: challenges and opportunities. Front Plant Sci 7:1794
Prabhu M, Natarajan S, Veeraraghavathatham D, Pugalendhi L (2009) The biochemical basis of shoot and fruit borer resistance in interspecific progenies of brinjal (Solanum melongena). EurAsian J BioSci 3:50–57
Ramesh K, Sandeep K, Dharminder K, Gupta RK (2014) Characterization of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) genotypes through principle component and regression analyses. Indian J Agric Sci 84:765–769
Rohlf FJ (2005) NTSYS-PC: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, Version 2.2. Exeter Software, Setauket.
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot 2012:1–26
Sheoran, O.P; Tonk, D.S; Kaushik, L.S; Hasija, R.C and Pannu, R.S (1998). Statistical Software Package for Agricultural Research Workers. Recent Advances in information theory, Statistics & Computer Applications by D.S. Hooda& R.C. Hasija Department of Mathematics Statistics, CCS HAU, Hisar, 139-143
Showket AD, Wani AR, Bashir A, Rather KAA (2017) Biochemical basis of resistance in brinjal genotypes against shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee). Chem Sci Rev Lett 6:1931–1940
Singh BD (1983) Breeding for resistance to biotic stresses II. Insect resistance In: Plant breeding principles and methods. Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana, p 494
Singh AK, Singh M, Singh AK, Singh R, Kumar S, Kalloo G (2005) Genetic diversity within the genus Solanum (Solanaceae) as revealed by RAPD markers. Curr Sci 90:711–714
Sparks TC, Nauen R (2014) IRAC: mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 121:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.11.014
Srinivasan R (2008) Integrated Pest management for eggplant fruit and shoot borer (Leucinodes orbonalis) in south and Southeast Asia: past, present and future. J Biopesticides 1:105–112
Tiwari SK, Karihaloo JL, Hameed N, Gaikwad AB (2009) Molecular characterization of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) cultivars using RAPD and ISSR markers. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 18:189–195
Verma M, Rathi S, Munshi AD, Kumar A, Arya L, Bhat KV, Kumar R (2012) Genetic diversity of Indian eggplant revealed by RAPD and SSR markers. Indian J Hortic 69:517–522
Wagh SS, Pawara DB, Chandel EAG and Ukey NS (2012) Biophysical mechanisms of resistance to brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee in brinjal. Pest Management in Horticultural Ecosystems 18:54–59
War AR, Sharma HC, Paulraj MG, War MY, Ignacimuthu S (2011) Herbivore induced plant volatiles: their role in plant defense for pest management. Plant Signal Behav 6:1973–1978
War AR, Paulraj MG, Ahmad T, Buhroo AA, Hussain B, Ignacimuthu S, Sharma HC (2012) Mechanisms of plant defense against insect herbivores. Plant Signal Behav 7:1306–1320
Zhao LY, Chen JL, Cheng DF, Sun JR, Liu Y, Tian Z (2009) Biochemical and molecular characterizations of Sitobion avenae-induced wheat defense responses. Crop Protection 28:435–442
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Director, National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources, New Delhi, India, and the Professor and Head, Department of Vegetable Science, Dr. Y S Parmar University of Horticulture and Forestry, Nauni, Solan, H.P. India, for their help in providing the eggplant germplasm to carry out these studies. A special note of thanks to Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India, for providing Inspire fellowship.
Funding
This study was funded by the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India (Grant number IF170391).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Mohinder Singh was the major advisor of my Ph.D. research who guided me during the entire research period and thesis writing; Dr. Ramesh Kumar Bharadwaj was my advisory member who helped in procuring the brinjal genotypes used in the study; Gaikwad Mahesh Balaso helped me with evaluation of the biochemical compounds analysis in the laboratory; Priyanka Thakur helped me in the interpretation and analysis of my research data. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals (vertebrates).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Edited by Eugenio E de Oliveira
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 43.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Challa, N., Singh, M., Bharadwaj, R.K. et al. Characterization of Eggplant Genotypes for Different Resistance Mechanisms Against Leucinodes orbonalis. Neotrop Entomol 50, 643–653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-021-00888-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-021-00888-w