Abstract
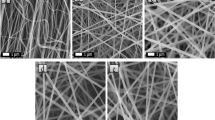
Dibenzo-18-crown-6 (DB18C6) as a host compound was doped into polyacrylonitrile (PAN) solution. The composite nanofibers (DB18C6/PAN) were prepared by the electrospinning. The morphology, chemical structure and thermal stability of nanofibers were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), respectively. The composite nanofibers with good morphology were obtained by controlling the weight percent of DB18C6 and electrospinning parameters. The static adsorption behavior of alkali metal ions and alkaline earth metal ions of different proportional DB18C6/PAN nanofibers were studied. DB18C6/PAN nanofibers have adsorptive selectivity about alkali metal ions: K+ > Na+ > > Cs+ > Li+. The 15wt%DB18C6/PAN nanofibers have the highest adsorption capacity. The adsorption kinetics of 15wt%DB18C6/PAN nanofibers for Na+ and K+ were accorded with the first-order equation, and the adsorption rate constants were 9.5 × 10–3 min−1 and 1.5 × 10–2 min−1, respectively. At 25 °C, the isotherm adsorption of the DB18C6/PAN nanofibers for Na+ and K+ was confirmed to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, and the maximum adsorption quantities of 15wt%DB18C6/PAN nanofibers were 11.9 mg g−1 and 24.8 mg g−1, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao Y, Loh CH, Tian M, Wang R, Fane AG (2018) Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: fabrication, modification and applications. Prog Polym Sci 77:69–94
Xue JJ, Xie JW, Liu WY, Xia YN (2017) Electrospun nanofibers: new concepts, materials, and applications. Acc Chem Res 50:1976–1987
Gök ZG, Inal M, Bozkaya O, Yiğitoğlu M, Vargel I (2020) Production of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-g-poly (ethylene terephthalate) nanofibers by electrospinning and evaluation of the properties of the obtained nanofibers. J Appl Polym Sci 137:e49257
Bozkaya O, Günay K, Arslan M, Gök ZG (2021) Removal of anionic dyes with glycidyl methacrylate-grafted polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibers modified with ethylenediamine. Res Chem Intermediat 47:2075–2093
Günay K, Arslan M, Bozkaya O, Aluç Y, Gök ZG (2019) Elimination of carcinogenic bromate ions from aqueous environment with 4-vinyl pyridine-g-poly(ethylene terephthalate) fibers. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:31644–31653
Ma WJ, Zhang MJ, Liu ZC, Kang MM, Huang CB, Fu GD (2019) Fabrication of highly durable and robust superhydrophobic-superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes based on a fluorine-free system for efficient oil/water separation. J Membr Sci 570:303–313
Zhang BA, Kang FY, Tarascon JM, Kim JK (2016) Recent advances in electrospun carbon nanofibers and their application in electrochemical energy storage. Prog Mater Sci 76:319–380
Zhang CL, Lu BR, Cao FH, Wu ZY, Zhang W, Cong HP, Yu SH (2019) Electrospun metal-organic framework nanoparticle fibers and their derived electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 55:226–233
Sridhar R, Lakshminarayanan R, Madhaiyan K, Barathi VA, Limh KHC, Ramakrishna S (2015) Electrosprayed nanoparticles and electrospun nanofibers based on natural materials: applications in tissue regeneration, drug delivery and pharmaceuticals. Chem Soc Rev 44:790–814
Topuz F, Uyar T (2019) Electrospinning of cyclodextrin functional nanofibers for drug delivery applications. Pharmaceutics 11:35
Uyar T, Havelund R, Hacaloglu J, Besenbacher F, Kingshott P (2010) Functional electrospun polystyrene nanofibers incorporating alpha-, beta-, and gamma-cyclodextrins: comparison of molecular filter performance. ACS Nano 4:5121–5130
Zhang W, Chen M, Diao GW (2011) Electrospinning beta-cyclodextrin/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membrane for molecular capture. Carbohydr Polym 86:1410–1416
Celebioglu A, Uyar T (2012) Electrospinning of nanofibers from non-polymeric systems: polymer-free nanofibers from cyclodextrin derivatives. Nanoscale 4:621–631
Zhang W, Chen M, Zha BB, Diao GW (2012) Correlation of polymer-like solution behaviors with electrospun fiber formation of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin and the adsorption study on the fiber. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:9729–9737
Chen ML, Nielsen SR, Uyar T, Zhang S, Zafar A, Dong MD, Besenbacher F (2013) Electrospun UV-responsive supramolecular nanofibers from a cyclodextrin-azobenzene inclusion complex. J Mater Chem C 1:850–855
Aytac Z, Yildiz ZI, Kayaci-Senirmak F, Keskin NOS, Kusku SI, Durgun E, Tekinay T, Uyar T (2016) Fast-dissolving, prolonged release, and antibacterial cyclodextrin/limonene-inclusion complex nanofibrous webs via polymer-free electrospinning. J Agric Food Chem 64:7325–7334
Celebioglu A, Yildiz ZI, Uyar T (2018) Thymol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibrous webs: enhanced water solubility, high thermal stability and antioxidant property of thymol. Food Res Int 106:280–290
Chen M, Wang CJ, Fang W, Wang J, Zhang W, Jin G, Diao GW (2013) Electrospinning of calixarene-functionalized polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes and application as an adsorbent and catalyst support. Langmuir 29:11858–11867
Bayrakci M, Ozcan F, Ertul S (2015) Synthesis of calixamide nanofibers by electrospinning and toxic anion binding to the fiber structures. Tetrahedron 71:3404–3410
Rodriguez JD, Vaden TD, Lisy JM (2009) Infrared spectroscopy of ionophore-model systems: hydrated alkali metal ion 18-crown-6 ether complexes. J Am Chem Soc 131:17277–17285
Boda A, Ali SM, Shenoi MRK, Rao H, Ghosh SK (2011) DFT modeling on the suitable crown ether architecture for complexation with Cs+ and Sr2+ metal ions. J Mol Model 17:1091–1108
Torrejos REC, Nisola GM, Song HS, Limjuco LA, Lawagon CP, Parohinog KJ, Koo S, Han JW, Chung WJ (2017) Design of lithium selective crown ethers: synthesis, extraction and theoretical binding studies. Chem Eng J 326:921–933
Atta NF, Galal A, Ahmed YM (2019) Highly conductive crown ether/ionic liquid crystal-carbon nanotubes composite based electrochemical sensor for chiral recognition of tyrosine enantiomers. J Electrochem Soc 166:B623–B630
Huang Y, Wang R (2018) An efficient lithium ion imprinted adsorbent using multi-wall carbon nanotubes as support to recover lithium from water. J Clean Prod 205:201–209
Mihandoost G, Zahedi MM, Ziyaadini M (2019) Transport of K+ from Seawater Using Dibenzo-18-crown-6 via Carbon Nanotube Based Pseudo Supported Liquid Membrane. Anal Bioanal Chem Res 6:241–251
Pan LT, Zhai GZ, Yang XR, Yu HR, Cheng CJ (2019) Thermosensitive microgels-decorated magnetic graphene oxides for specific recognition and adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. ACS Omega 4:3933–3945
Nisola GM, Parohinog KJ, Cho MK, Burnea FKB, Lee JY, Seo JG, Lee SP, Chung WJ (2020) Covalently decorated crown ethers on magnetic graphene oxides as bi-functional adsorbents with tailorable ion recognition properties for selective metal ion capture in water. Chem Eng J 389:12
Zhang EH, Liu WF, Liang Q, Liu XG, Zhao ZB, Yang YZ (2020) Selective recovery of Li+ in acidic environment based on one novel electroactive Li+-imprinted graphene-based hybrid aerogel. Chem Eng J 385:13
Liu Z, Zhou YQ, Guo M, Lv BL, Wu ZJ, Zhou WZ (2019) Experimental and theoretical investigations of Cs+ adsorption on crown ethers modified magnetic adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 371:712–720
Ibrahim BM, Fakhre NA (2019) Crown ether modification of starch for adsorption of heavy metals from synthetic wastewater. Int J Biol Macromol 123:70–80
Buriac O, Ciopec M, Duteanu N, Negrea A, Negrea P, Grozav I (2020) Platinum (IV) recovery from waste solutions by adsorption onto dibenzo-30-crown-10 ether immobilized on amberlite XAD7 resin-factorial design analysis. Molecules 25:23
Deb AKS, Sahu P, Boda A, Ali SM, Shenoy KT, Upadhyay D (2020) DFT and MD simulation supplemented experiments for isotopic fractionation of zinc compounds using a macrocyclic crown ether appended polymeric resin. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22:14682–14693
Limjuco LA, Nisola GM, Torrejos REC, Han JW, Song HS, Parohinog KJ, Koo S, Lee SP, Chung WJ (2017) Aerosol cross-linked crown ether diols melded with poly(vinyl alcohol) as specialized microfibrous Li+ adsorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:42862–42874
Chen LQ, Zhu XH, Huang DN, Xu Z, Shen J, Zhang WQ (2017) Polystyrene/poly(dibenzo-18-crown-6) composite nanofibers for the selective adsorption of plasma catecholamines. RSC Adv 7:13263–13271
Tas S, Kaynan O, Ozden-Yenigun E, Nijmeijer K (2016) Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)/crown ether composite nanofibers for the selective adsorption of cations. RSC Adv 6:3608–3616
Nisola GM, Parohinog KJ, Torrejos REC, Koo S, Lee SP, Kim H, Chung WJ (2020) Crown ethers “clicked” on fibrous polyglycidyl methacrylate for selective Li+ retrieval from aqueous sources. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp 596:13
Chen M, Chen Y, Diao GW (2010) Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue onto p-tert-butyl-calix 4,6,8 arene-bonded silica gel. J Chem Eng Data 55:5109–5116
Jia SY, Tang DY, Peng J, Yang X, Sun ZJ (2020) Crosslinked electrospinning fibers with tunable swelling behaviors: A novel and effective adsorbent for Methylene Blue. Chem Eng J 390:13
Papaphilippou PC, Karamanis P, Stavrinou K, Krasia-Christoforou T (2020) Functionalized electrospun fibrous membranes as effective adsorbents for benzoic acid from aqueous media. ChemistrySelect 5:9017–9021
Chen M, Cui L, Li CH, Diao GW (2009) Adsorption, desorption and condensation of nitrobenzene solution from active carbon: A comparison of two cyclodextrins and two surfactants. J Hazard Mater 162:23–28
Chen M, Shang T, Fang W, Diao GW (2011) Study on adsorption and desorption properties of the starch grafted p-tert-butyl-calix n arene for butyl Rhodamine B solution. J Hazard Mater 185:914–921
Chen M, Ding WH, Wang J, Diao GW (2013) Removal of Azo dyes from water by combined techniques of adsorption, desorption, and electrolysis based on a supramolecular sorbent. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:2403–2411
Surgutskaia NS, Di Martino A, Zednik J, Ozaltin K, Lovecka L, Bergerova ED, Kimmer D, Svoboda J, Sedlarik V (2020) Efficient Cu2+, Pb2+ and Ni2+ ion removal from wastewater using electrospun DTPA-modified chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers. Sep Purif Technol 247:12
Yu JY, Hu TJ, Du C, Zhang Y, Chu ZY, Li YH, Cao J (2020) Facile synthesis of a BCN nanofiber and its ultrafast adsorption performance. RSC Adv 10:25200–25208
Zhang XX, Li ZW, Lin SJ, Theato P (2020) Fibrous materials based on polymeric salicyl active esters as efficient adsorbents for selective removal of anionic dye. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:21100–21113
Acknowledgements
The funding support from the “Qinglan project” of Jiangsu Province (2018-12) and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, Y., Wang, J., Qian, C. et al. Dibenzo-18-crown-6/Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers for metal ions adsorption: adsorption studies for Na+ and K+. Polym. Bull. 79, 6275–6288 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03806-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03806-7