Abstract
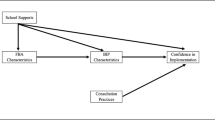
Behavior intervention plans (BIPs) are intended to help educators systematically support students with behavioral problems at school. Previous research confirms that the effectiveness of a BIP depends on the degree to which the plan is technically adequate and implemented with integrity. What remains unclear from the literature is how professional experience and environmental variables impact technical adequacy, treatment integrity, and student outcomes. The purpose of this study was to explore these relationships using data collected from a survey of members’ experiences with the BIP implementation team. The researchers collected BIPs from local school districts and then surveyed members of the implementation team regarding their professional qualifications, training, involvement in the BIP development process, treatment integrity, and perceived impact on student outcomes. Results from two multiple regression models predicting treatment integrity and student outcomes suggest that practitioners’ perceptions of BIP quality significantly predicted treatment integrity. Additionally, training, BIP quality, and treatment integrity significantly predicted student outcomes. These findings suggest that practitioners’ perceptions of BIP quality may play an important role in predicting treatment integrity but improving student outcomes requires technical adequacy and targeted professional development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benazzi, L., Horner, R. H., & Good, R. H. (2006). Effects of behavior support team composition on the technical adequacy and contextual fit of behavior support plans. The Journal of Special Education, 40(3), 160–170. https://doi.org/10.1177/00224669060400030401
Bertram, R. M., Blasé, K. A., & Fixsen, D. L. (2015). Improving programs and outcomes: Implementation frameworks and organizational change. Research on Social Work Practice, 25(4), 477–487. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731514537687
Billingsley, B., & Bettini, E. (2019). Special education teacher attrition and retention: A review of the literature. Review of Educational Research, 89(5), 697–744. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654319862495.
Blood, E., & Neel, R. S. (2007). From FBA to implementation: A look at what is actually being delivered. Education and Treatment of Children, 30(4), 67–80.
Browning-Wright, D. B., Mayer, G. R., Cook, C. R., Crews, S. D., Kraemer, B. R., & Gale, B. (2007). A preliminary study on the effects of training using behavior support plan quality evaluation guide (BSP-QE) to improve positive behavioral support plans. Education and Treatment of Children, 30(3), 89–106. https://doi.org/10.1353/etc.2007.0017
Browning-Wright, D., Mayer, R., & Saren, D. (2013). Behavior intervention plan quality evaluation scoring guide II: To evaluate behavior intervention plans (See www.pent.ca.gov). California Department of Education. http://www.pent.ca.gov/beh/qe/bipscoringrubric.pdf
Cochrane, W. S., & Laux, J. M. (2007). Investigating school psychologists’ perceptions of treatment integrity in school-based interventions for children with academic and behavior concerns. Preventing School Failure, 51(4), 29–34. https://doi.org/10.3200/PSFL.51.4.29-34
Cochrane, W. S., & Laux, J. M. (2008). A survey investigating school psychologists’ measurement of treatment integrity in school-based interventions and their beliefs about its importance. Psychology in the Schools, 45(6), 499–507. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20319
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Cook, C. R., Mayer, G. R., Wright, D. B., Kraemer, B., Wallace, M. D., Dart, E., et al. (2012). Exploring the link among behavior intervention plans, treatment integrity, and student outcomes under natural educational conditions. The Journal of Special Education, 46(1), 3–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466910369941
Fixsen, D. L., Naoom, S. F., Blasé, K. A., Friedman, R. M., & Wallace, F. (2005). Implementation Research: A Synthesis of the Literature. University of South Florida, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, The National Implementation Research Network (FMHI Publication #231). https://nirn.fpg.unc.edu/sites/nirn.fpg.unc.edu/files/resources/NIRN-MonographFull-01-2005.pdf
Glass, G. V., Peckham, P. D., & Sanders, J. R. (1972). Consequences of failure to meet assumptions underlying the fixed effects analyses of variance and covariance. Review of Educational Research, 42(3), 237–288. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543042003237
Gresham, F. M., Dart, E. H., & Collins, T. A. (2017). Generalizability of multiple measures of treatment integrity: Comparisons among direct observation, permanent products, and self-report. School Psychology Review, 46(1), 108–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.2017.12087606
Horner, R. H., Carr, E. G., Strain, P. S., Todd, A. W., & Reed, H. K. (2002). Problem behavior interventions for young children with autism: A research synthesis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32(5), 423–446. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020593922901
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, 20 U.S.C. §1401-1485 (1997).
Ingram, K., Lewis-Palmer, T., & Sugai, G. (2005). Function-based intervention planning: Comparing the effectiveness of FBA function-based and non-function-based intervention plans. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 7(4), 224–236. https://doi.org/10.1177/10983007050070040401
Iovannone, R., & Romer, N. (2017). The FBA/BIP technical adequacy tool for evaluation (TATE): Improving practice. Paper session presented at the meeting of the National Association of School Psychologists, Texas.
Kraemer, B. R., Cook, C. R., Browning-Wright, D., Mayer, G. R., & Wallace, M. D. (2008). Effects of training on the use of the behavior support plan quality evaluation guide with autism educators: A preliminary investigation examining positive behavior support plans. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 10(3), 179–189. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300708318796
Lubke, G. H., & Muthén, B. O. (2004). Applying multigroup confirmatory factor models for continuous outcomes to likert scale data complicates meaningful group comparisons. Structural Equation Modeling, 11(4), 514–534. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328007sem1104_2
Marcus, R. F. (2017). Normative aggression and violence. In The development of aggression and violence in adolescence (pp. 27–62). Palgrave Macmillan.
McKenna, J. W., Flower, A., & Adamson, R. (2015). A systematic review of function-based replacement behavior interventions for students with and at risk for emotional and behavioral disorders. Behavior Modification, 40(5), 678–712. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145445515621489
Medley, N. S., Little, S. G., & Akin-Little, A. (2008). Comparing individual behavior plans from schools with and without schoolwide positive behavior support: A preliminary study. Journal of Behavioral Education, 17(1), 93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-007-9053-y
National Implementation Research Network (2021, April). Active implementation hub: Module 2 implementation drivers. https://nirn.fpg.unc.edu/module-2/implementation-drivers
Noell, G. H., Gansle, K. A., Mevers, J. L., Knox, R. M., Mintz, J. C., & Dahir, A. (2014). Improving treatment plan implementation in schools: A meta-analysis of single subject design studies. Journal of Behavioral Education, 23(1), 168–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-013-9177-1
Ntinas, K. M., Neila, A., Nikolaidou, E., Papadimitriou, S., Papadopoulou, I., Fasoulas, A., & Hatzikonstantinidis, C. (2006). Inclusion and challenging behaviors: Greek general educators’ perspectives. The Behavior Analyst Today, 7(1), 84–95. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0100146
Owens, J. S., Coles, E. K., Evans, S. W., Himawan, L. K., Girio-Herrera, E., Holdaway, A. S., et al. (2017). Using multi-component consultation to increase the integrity with which teachers implement behavioral classroom interventions: A pilot study. School Mental Health, 9(3), 235–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-017-9225-4
Lloyd, B. P., Barton, E. E., Pokorski, E. A., Ledbetter-Cho, K., & Pennington, B. (2019). Function-based interventions in K-8 general education settings: A focus on teacher implementation. The Elementary School Journal, 119(4), 601–628. https://doi.org/10.1086/703114
Perepletchikova, F., & Kazdin, A. E. (2006). Treatment integrity and therapeutic change: Issues and research recommendations. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 12(4), 365–383. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy.bpi045
Pinkelman, S. E., & Horner, R. H. (2017). Improving implementation of function-based interventions: Self-monitoring, data collection, and data review. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 19(4), 228–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300716683634
Richardson, M., Caldarella, P., Young, B., and Young, E. L. (2007). Adapting the SSBD for secondary school PBS interventions: Student and parent correlates. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Teacher Educators for Children with Behavior Disorders, Tempe, AZ. http://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/facpub/1272
Strickland-Cohen, K., & Horner, R. (2015). Typical school personnel developing and implementing basic behavior support plans. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 17(2), 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300714554714
Rutherford, R. B., Jr., & Nelson, C. M. (1995). Management of aggressive and violent behavior in the schools. Focus on Exceptional Children, 27(6), 1–15.
U.S. Department of Education (2019). EDFacts data warehouse (EDW): IDEA Part B Child count and educational environments collection. https://www2.ed.gov/programs/osepidea/618-data/static-tables/index.html
U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, What Works Clearinghouse. (2016, December). Children Identified with or At Risk for an Emotional Disturbance topic area intervention report: Functional Behavioral Assessment-based Interventions. http://whatworks.ed.gov
Walker, H., Colvin, G., & Ramsey, E. (1996). Antisocial behavior in school: Strategies and best practices. Behavioral Disorders, 21(3), 253–255. https://doi.org/10.1177/019874299602100307
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude for the school district administrators and employees who made this possible throughout the state of Utah. Thank you for your dedication to the field and remarkable contributions to our children.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
All procedures and research materials used in the study were reviewed and approved by the university. Institutional Review Board. In addition, all participating districts reviewed IRB approvals and provided district approval for the recruitment of research participants and the collection of de-identified data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charlton, C.T., Rigby, D.M.G., Moulton, S.E. et al. Implementing Behavior Intervention Plans in Schools: A Pilot Study of the Complex Relationship Between Technical Adequacy, Treatment Integrity, and Student Outcomes. J Behav Educ 32, 382–403 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-021-09448-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-021-09448-z