Abstract
Purpose
The implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is the therapy of choice for the prevention of sudden cardiac death. The number of elderly patients receiving ICDs is increasing. This study aimed to assess the outcome of patients according to their age at the time of implantation, and to identify variables potentially associated with patient survival.
Methods
Between June 2009 and December 2019, we retrospectively enrolled all consecutive patients in whom ICD implantation had been performed for primary or secondary prevention at our center.
Results
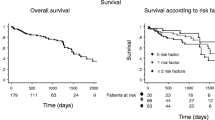
During the study period, 670 patients underwent ICD implantation. We stratified the population into four age-classes: Class 1 (23%) (pts aged less than 60 years), Class 2 (28%) (pts aged between 60 and 70 years), Class 3 (39%) (pts aged between 70 and 80 years) and Class 4 (9%) (pts aged 80 years or older). Over a median follow-up of 42 months, the rate of deaths in Class 4 was higher than in Classes 1 and 2 (log-rank test, P < 0.01), but was comparable to that in Class 3 (P = 0.407). With increasing age, we observed more complications at the time of implantation and during follow-up. On multivariate analysis, higher NYHA class, creatinine level and CHA2DS2-VASc score were identified as independent predictors of death, while age was not associated with worse prognosis. Higher body mass index, higher NYHA class and CHA2DS2-VASc score were also confirmed as independent predictors of hospitalizations or death due to any cause.
Conclusion
This study showed good survival in ICD patients in all age-groups, including those aged ≥80 years. The CHA2DS2-VASc score seems to be a stronger predictor of death than age.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raatikainen MJP, Arnar DO, Merkely B, Nielsen JC, Hindricks G, Heidbuchel H, et al. A decade of information on the use of cardiac implantable electronic devices and interventional electrophysiological procedures in the European Society of Cardiology Countries: 2017 report from the European heart rhythm association. Europace. 2017;19:ii1–ii90.
Russo AM, Stainback RF, Bailey SR, Epstein AE, Heidenreich PA, Jessup M, et al. ACCF/HRS/AHA/ASE/HFSA/SCAI/SCCT/SCMR 2013 appropriate use criteria for implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization therapy: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation appropriate use criteria task force, Heart Rhythm Society, American Heart Association, American Society of Echocardiography, Heart Failure Society of America, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1318–68.
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, et al. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: the task force for the Management of Patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Europace. 2015;17:1601–87.
Connolly SJ, Hallstrom AP, Cappato R, Schron EB, Kuck KH, Zipes DP, et al. Meta-analysis of the implantable cardioverter defibrillator secondary prevention trials. AVID, CASH and CIDS studies. Antiarrhythmics vs implantable defibrillator study. Cardiac arrest study Hamburg. Canadian implantable defibrillator study. Eur Heart J. 2000;21:2071–8.
Proclemer A, Zecchin M, D'Onofrio A, Boriani G, Ricci RP, Rebellato L, et al. Registro Italiano pacemaker e Defibrillatori - Bollettino Periodico 2018. Associazione Italiana di Aritmologia e Cardiostimolazione [the pacemaker and implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator registry of the Italian Association of Arrhythmology and Cardiac Pacing - annual report 2018]. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2020;21:157–69.
Bogle BM, Ning H, Mehrotra S, Goldberger JJ, Lloyd-Jones DM. Lifetime risk for sudden cardiac death in the community. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e002398.
Koplan BA, Epstein LM, Albert CM, Stevenson WG. Survival in octogenarians receiving implantable defibrillators. Am Heart J. 2006;152:714–9.
Kong MH, Al-Khatib SM, Sanders GD, Hasselblad V, Peterson ED. Use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators for primary prevention in older patients: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Cardiol J. 2011;18:503–14.
Pellegrini CN, Lee K, Olgin JE, Turakhia MP, Tseng ZH, Lee R, et al. Impact of advanced age on survival in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Europace. 2008;10:1296–301.
Provincia Autonoma di Trento Home Page. http://www.statistica.provincia.tn.it (accessed on Sept 2019).
Barra S, Providência R, Paiva L, Heck P, Agarwal S. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in the elderly: rationale and specific age-related considerations. Europace. 2015;17:174–86.
Goldenberg I, Vyas AK, Hall WJ, Moss AJ, Wang H, He H, et al. Risk stratification for primary implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:288–96.
Anné W, Theuns DA, Schaer B, Van Belle Y, Szili-Torok T, Smith T, et al. ICDs at higher age and clinical risk factors. Neth Heart J. 2014;22:279–85.
Kraaier K, Scholten MF, Tijssen JG, Theuns DA, Jordaens LJ, Wilde AA, et al. Early mortality in prophylactic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator recipients: development and validation of a clinical risk score. Europace. 2014;16:40–6.
Ferretto S, Zorzi A, Dalla Valle C, Migliore F, Leoni L, De Lazzari M, et al. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in the elderly: predictors of appropriate interventions and mortality at 12-month follow-up. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2017;40:1368–73.
Naccarelli GV, Panaccio MP, Cummins G, Tu N. CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc risk factors to predict first cardiovascular hospitalization among atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter patients. Am J Cardiol. 2012;109:1526–33.
Lahewala S, Arora S, Patel P, Kumar V, Patel N, Tripathi B, et al. Atrial fibrillation: utility of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores as predictors of readmission, mortality and resource utilization. Int J Cardiol. 2017;245:162–7.
Huang FY, Huang BT, Pu XB, Yang Y, Chen SJ, Xia TL, et al. CHADS2, CHA2DS2-VASc and R2CHADS2 scores predict mortality in patients with coronary artery disease. Intern Emerg Med. 2017;12:479–86.
Botto GL, Forleo GB, Capucci A, Solimene F, Vado A, Bertero G, et al. The Italian subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator survey: S-ICD, why not? Europace. 2017;19:1826–32.
Saxon LA, Hayes DL, Gilliam FR, Heidenreich PA, Day J, Seth M, et al. Long-term outcome after ICD and CRT implantation and influence of remote device follow-up: the ALTITUDE survival study. Circulation. 2010;122:2359–67.
Di Biase L, Gasparini M, Lunati M, Santini M, Landolina M, Boriani G, et al. Antiarrhythmic effect of reverse ventricular remodeling induced by cardiac resynchronization therapy: the InSync ICD (implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator) Italian registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1442–9.
Tsai V, Goldstein MK, Hsia HH, Wang Y, Curtis J, Heidenreich PA, et al. Influence of age on perioperative complications among patients undergoing implantable cardioverter-defibrillators for primary prevention in the United States. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2011;4:549–56.
Reynolds MR, Cohen DJ, Kugelmass AD, Brown PP, Becker ER, Culler SD, et al. The frequency and incremental cost of major complications among medicare beneficiaries receiving implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:2493–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Massimiliano Marini: conception and design of the research, drafting of the manuscript.
Marta Martin, Mattia Strazzanti, Silvia Quintarelli, Fabrizio Guarracini, Alessio Coser: acquisition of data, critical revision of the manuscript.
Sergio Valsecchi: statistical analysis.
Roberto Bonmassari: supervision.
All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S. Valsecchi is an employee of Boston Scientific, Inc. No other conflicts of interest exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marini, M., Martin, M., Strazzanti, M. et al. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in elderly patients: outcome and predictors of mortality. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 64, 573–580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-01017-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-01017-8