Abstract
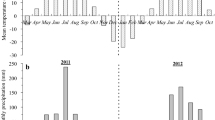
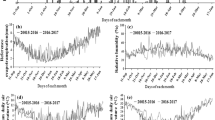
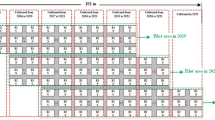
In arid and semi- arid regions selecting the appropriate planting method and irrigation regime along with optimum plant density are three critical factors that affect the yield and physiological characteristics of sugar beet. Therefore, in order to find the optimum field managements in sugar beet cultivation the split-split plot arrangement was used to examine the effects of three irrigation regimes as 100, 75 and 50% of full irrigation (FI), four plant densities as 180,000, 135,000, 90,000, and 45,000 plants ha−1 and two planting methods as direct seeding and transplanting on physiological growth and gas exchange of sugar beet for two growing seasons at experimental field of Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran located in a semi-arid environment. Results showed that the mean values of leaf and root dry matter decreased by 41% and 26% from 100%FI to 50%FI, respectively. Transplanting method has more tolerance to water stress than direct seeding and increased the average root dry matter and crop water productivity (WUEET) as 7% and 45%, respectively. The highest value of photosynthesis rate (An), transpiration rate (Tr) and stomata conductance (gs) were obtained in transplanting method under the density of 90,000 plant ha−1 and 100%FI, with no significant difference between I100 and I75 for An and Tr. The highest value of transpiration efficiency (WUEt) and intrinsic water use efficiency (WUEi) were obtained in 75%FI and 50%FI, respectively in density of 90,000 plant ha−1. Therefore, the transplanting method due to alleviating the adverse effects of water stress on yield and physiological response of sugar beet along with plant density of 90,000 plant ha−1 under moderate deficit irrigation (75%FI) can be suggested as an efficient field management in sugar beet cultivation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, Z., Shah, P., Kakar, K. M., El-Sharkawi, H., Gama, P. B. S., Khan, E. A., Honna, T., & Yamamoto, S. (2010). Sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) response to different planting methods and row geometries II: effect on plant growth and quality. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 8(2), 785–791.
Antonietta, M., Fanello, D. D., Acciaresi, H. A., & Guiamet, J. J. (2014). Senescence and yield responses to plant density in stay green and earlier-senescing maize hybrids from Argentina. Field Crop Research, 155, 111–119.
Aram, S., Weisany, W., Daliri, M. S., & Mousavi Mirkalaie, S. A. A. (2021). Phenology, physiology, and fatty acid profile of canola (Brassica napus L.) under agronomic management practices (Direct Seeding and Transplanting) and zinc foliar application. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00475-3
Azizian, A., & Sepaskhah, A. (2014). Maize response to water, salinity and nitrogen levels: physiological growth parameters and gas exchange. International Plant Production., 8, 131–162.
Baigy, M. J., Sahebi, F. G., Pourkhiz, I., Asgari, A., & Ejlali, F. (2012). Effect of deficit-irrigation management on components and yield of sugar beet. International Journal of Agronomy and Plant Production, 3, 781–787.
Barnabás, B., Jäger, K., & Fehér, A. (2008). The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant Cell & Environment., 31, 11–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01727.x
Bezerra, A. A. C., Neves, A. C., Rocha, M. M., & Brlto, L. C. R. (2017). Morpho-physiological and productive biometry in semi-erect cultivars of the cowpea under different plant populations. Revista Ciência Agronômica, 48, 625–630.
Bloch, D., Hoffmann, C. M., & Marlander, B. (2006). Impact of water supply on photosynthesis, water use and carbon isotope discrimination of sugar beet genotypes. European Journal of Agronomy, 24, 218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2005.08.004
Bresson, J., Vasseur, F., Dauzat, M., Koch, G., Granier, C., & Vile, D. (2015). Quantifying spatial heterogeneity of chlorophyll fluorescence during plant growth and in response to water stress. Plant Methods, 11, 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-015-0067-5
Brown, M., Perez, J., & Miles, A. (2015). Teaching organic farming and gardening, center for agro ecology and sustainable food systems (3rd ed.). University of California.
Çakmakçi, R., Oral, E., & Kantar, F. (1998). Root yield and quality of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) in relation to plant population. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 180, 45–52.
Chaudhary, D. R., Patel, A. P., Patel, V. P., Desai, L. J., Patel, J. V., & Tandel, D. H. (2015). Effect of age of seedlings and fertilizer management on yield, nutrient content and uptake of rice (Oryza Sataiva L.). The Bioscan., 10(1), 351–353.
Chaves, M. M. (1991). Effects of water deficits on carbon assimilation. Journal of Experimental Botany., 42, 1–16.
Chen, M., Zhang, Y., Liang, F., Tang, J., Ma, P., Tian, J., Jiang, C. H., & Zhang, W. (2021). The net photosynthetic rate of the cotton boll-leaf system determines boll weight under various plant densities. European Journal of Agronomy, 125, 126251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2021.126251
Clark, E. A., & Loomis, R. (1978). Dynamics of leaf growth and development in sugar beets. Journal of the American Society of Sugar Beet Technologists, 20, 97–112.
Cui, N. B., Du, T. S., Kang, S. Z., Li, F. S., Hu, X. T., Wang, M. X., & Li, Z. J. (2009). Relationship between stable carbon isotope discrimination and water use efficiency under regulated deficit irrigation of pear-jujube tree. Agricultural Water Management., 96, 1615–1622.
Dastrang, M., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2019). Response of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) to irrigation water salinity, irrigation regime and planting method: physiological growth and gas exchange. Scientia Horticulture, 257, 108714.
Dehqani, M., Jafaraghaei, M., & Mohammadikia, S. (2015). Effect of cotton transplanting on its yield and water use efficiency. Journal of Water Research in Agriculture., 28(2), 307–314.
Dillon, M. A., McCaslin, B. D., & Schemhl, W. R. (1972). Effect of transplanting and cover on growth of sugar beet. Agronomy Journal, 64, 183–186.
Dong, H. Z., Li, W. J., Tang, W., Li, Z. H., & Zhang, D. M. (2006). Effects of genotypes and plant density on yield, yield components and photosynthesis in Bt transgenic cotton. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science., 192, 132–139.
Draycott, A. P. (2006). Sugar beet (1st ed.). Blackwell Publishing.
Du, T., Kang, S., Zhang, J., Li, F., & Hu, X. (2006). Yield and physiological responses of cotton to partial root-zone irrigation in the oasis field of northwest China. Agricultural Water Management, 84(1–2), 41–52.
El-Hendawy, S. E., Abd El-Lattief, E. A., Ahmed, M. S., & Schmidhalter, U. (2008). Irrigation rate and plant density effects on yield and water use efficiency of drip-irrigated corn. Agricultural Water Management, 95, 836–844.
Erice, G., Aranjuelo, I., Irigoyen, J. J., & Sa´nchez-Dı´az, M. . (2007). Effect of elevated CO2, temperature and limited water supply on antioxidant status during regrowth of no dulated alfalfa. Physiologia Plantarum., 130, 33–45.
Ertek, A., & Kanber, R. (2003). Effects of different drip irrigation programs on the boll number and shedding percentage and yield of cotton. Agricultural Water Management., 60, 1–11.
Ertek, A., Sensoy, S., Gedik, I., & Kucukyumuk, C. (2006). Irrigation scheduling based on pan evaporation values for cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) grown under field conditions. Agricultural Water Management., 81(1–2), 159–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2005.03.008
Fabeiro, C., Olalla, F. M. D. S., López, R., & DomıŃ guez, A. (2003). Production and quality of the sugar beet (beta vulgaris, l.) cultivated under controlled deficit irrigation conditions in a semi-arid climate. Agricultural Water Management., 62, 215–227.
Fang, X., Li, Y., Nie, J., Wang, C., Huang, K., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., She, H., Liu, X., Ruan, R., Yuan, X., & Yi, Z. (2018a). Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and planting density on the leaf photosynthetic characteristics, agronomic traits and grain yield in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum M.). Field Crops Research., 219, 160–168.
Fang, X. M., She, H. Z., Wang, C., Liu, X. B., Li, Y. S., Nie, J., Ruan, R. W., Wang, T., & Yi, Z. L. (2018b). Effects of fertilizer application rate and planting density on photosynthetic characteristics, yield and yield components in waxy wheat. Cereal Research Communications, 46(1), 169–179.
Fernandez, J. E., Alcon, F., Diaz-Espejo, A., Hernandez-Santana, V., & Cuevas, M. V. (2020). Water use indicators and economic analysis for on-farm irrigation decision: a case study of a super high density olive tree orchard. Agricultural Water Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106074
Ghamarnia, H., Arji, I., Sepehri, S., Norozpour, S., & Khodaei, E. (2012). Evaluation and comparison of drip and conventional irrigation methods on sugar beets in a semi-arid region. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering., 138, 90–97. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR(1943-4774.0000362)
Haghighikhah, M., Khajeh-Hosseini, M., Nassiri-Mahallat, M., & Khavari-Khorasan, S. (2017). The effect of seed priming and transplanting on morphological characteristics, yield and yield components of super sweet corn. Journal of Agroecology., 8(4), 628–643.
Haghverdi, A., Yonts, C. D., Reichert, D. L., & Irmak, S. (2017). Impact of irrigation, surface residue cover and plant population on sugar beet growth and yield, irrigation water use efficiency and soil water dynamics. Agricultural Water Management., 180, 1–12.
Hashem, M. S., El-Abedin, T. Z., & Al-Ghobari, H. M. (2018). Assessing effects of deficit irrigation techniques on water productivity of tomato for subsurface drip irrigation system. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering., 11, 156–167.
Hernandez-Santana, V., Fernández, J. E., Cuevas, M. V., Perez-Martin, A., & Diaz- Espejo, A. (2017). Photosynthetic limitations by water deficit: effect on fruit and olive oil yield, leaf area and trunk diameter and its potential use to control vegetative growth of super high density olive orchards. Agricultural Water Management., 184, 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.12.016
Kamali, H. R., Zand-Parsa, Sh., & Zare, M. (2017). Estimating canopy cover, leaf area index and nitrogen status of sugar beet using color digital camera. Journal of Sugar Beet Research., 32(2), 123–133.
Kang, Y. H., Wang, R. S., Wan, S. Q., Hu, W., Jiang, S. F., & Liu, S. P. (2012). Effects of different water levels on cotton growth and water use through drip irrigation in an arid region with saline ground water of Northwest China. Agricultural Water Management., 109, 117–126.
Kazemeini, S. A., Mohamadi, S., & Pirasteh-Anosheh, H. (2015). Growth and photosynthesis responses of safflower cultivars to water stress at two developmental stages. Biological Forum., 7(2), 923–929.
Khozaei, M., Kamgar Haghighi, A. A., Sepaskhah, A. R., Zand Parsa, Sh., Razzaghi, F., Yousef Abadi, V. A., & Emam, Y. (2020). Evaluation of direct seeding and transplanting in sugar beet for water productivity, yield and quality under different irrigation regimes and planting densities. Agricultural Water Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106230
Leufen, G., Noga, G., & Hunsche, M. (2016). Drought stress memory in sugar beet: mismatch between 544 biochemical and physiological parameters. Journal of Plant Growth and Regulation, 35, 680–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9571-8
Li, Y., Liu, N., Fan, H., Su, J., Fei, C., Wang, K., Ma, F., & Kisekka, I. (2019). Effects of deficit irrigation on photosynthesis, photosynthate allocation and water use efficiency of sugar beet. Agricultural Water Management, 223, 105701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105701
Liu, T., Gu, L., Dong, S., Zhang, J., Liu, P., & Zhao, B. (2015). Optimum leaf removal increases canopy apparent photosynthesis: 13C-photosynthate distribution and grain yield of maize crops grown at high density. Field Crops Research., 170, 32–39.
Liu, W., Zhang, J. W., Lü, P., Yang, J. S., Liu, P., Dong, S. T., Li, D. H., & Sun, Q. Q. (2011). Effect of plant density on grain yield dry matter accumulation and partitioning in summer maize cultivar Denghai 661. Acta Agronomica Sinica., 37, 1301–1307.
Ma, S. C., Duan, A. W., Wang, R., Guan, Z. M., Yang, S. J., Ma, S. T., & Shao, Y. (2015). Root-sourced signal and photosynthetic traits dry matter accumulation and remobilization, and yield stability in winter wheat as affected by regulated deficit irrigation. Agricultural Water Management, 148, 123–129.
Mahbod, M., Zand-Parsa, Sh., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2015). Modification of maize simulation model for predicting growth and yield of winter wheat under different applied water and nitrogen. Agricultural Water Management., 150, 18–34.
Marchiori, P. E. R., Machado, E. C., & Ribeiro, R. V. (2014). Photosynthetic limitations imposed by self-shading in field-grown sugarcane varieties. Field Crops Research., 155, 30–37.
Mehrabi, F., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2019). Partial root zone drying irrigation, planting methods and nitrogen fertilization influence on physiologic and agronomic parameters of winter wheat. Agricultural Water Management, 223, 105688.
Meinke, H., Goudriaan, J., Hammer, G.L., & Keating, B.A. (1996). Light interception in spring wheat: the extinction coefficient during early growth. In Fourth Congress of the European Society for Agronomy, Veldhoven- Wageningen, 7–11 July 1996, p. 184–185
Miyashita, K., Tanakamaru, S., Maitani, T., & Kimura, K. (2005). Recovery responses of photosynthesis, transpiration, and stomatal conductance in kidney bean following drought stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany., 53, 205–214.
Monti, A., Barbanti, L., & Venturi, G. (2010). Photosynthesis on individual leaves of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) during the ontogeny at variable water regimes. Annals of Applied Biology, 151, 155–165.
Nasri, R., Kashani, A., Paknejad, F., Sadeghi, S. M., & Ghorbani, S. (2012). Correlation and path analysis of qualitative and quantitative yield in sugar beet in transplant and direct cultivation method in saline lands. Iranian Journal of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, 8(1), 213–223.
Nelson, J. M. (1978). Influence of planting date, nitrogen rate, and harvest date on yield and sucrose concentration of fall-planted sugar beets in central Arizona. Journal of the American Society of Sugar Beet Technologists, 20, 25–32.
Nyakudya, I. W., & Stroosnijder, L. (2014). Effect of rooting depth, plant density and planting date on maize (Zea mays L.) yield and water use efficiency in semi-arid Zimbabwe: modelling with AquaCrop. Agricultural Water Management., 146, 280–296.
Pasandi Pour, A. P., & Farahbakhsh, H. (2018). Growth and photosynthesis of three henna (Lowsonia inermis L.) ecotypes at different planting densities. Indian Crop Production, 123, 363–371.
Raes, D., Steduto, P., Hsiao, T. C., & Fereres, E. (2016). Aqua crop plug-in program version 5.0 reference manual. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Rahnema, A., & Bakhshande, A. (2005). Effect of sowing dates and direct seeding and transplanting methods on agronomic characteristics, and grain yield of canola under Ahvaz conditions. International Journal of Agriculture Crop Science., 7(4), 324–332. (In Persian with English abstract).
Rattin, J., di Benedetto, A., & Gornatti, T. (2010). The effects of transplant in sweet maize (Zea mays L.). I. Growth and yield. International Journal of Agricultural Research, 6, 403–412.
Rezazadeh, S., Aghayari, F., Paknejad, F., & Rezaee, M. (2019). The physiological and biochemical responses of directly seeded and transplanted maize (zea mays L) supplied with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) under water stress. Plant Physiology, 10(1), 3009–3021.
Richter, G. M., Jaggard, K. W., & Mitchell, R. A. (2001). Modelling radiation interception and radiation use efficiency for sugar beet under variable climatic stress. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 109(1), 13–25.
Rouhi, V., Samson, R., Lemeur, R., & Damme, P. V. (2007). Photosynthetic gas exchange characteristics in three different almond species during drought stress and subsequent recovery. Environmental Experimental Botany, 59, 117–129.
Rytter, R. M. (2005). Water use efficiency, carbon isotope discrimination and biomass production of two sugar beet varieties under well-watered and dry conditions. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 191, 426–438.
Safi, S. Z., Kamgar-Haghighi, A. A., Zand-Parsa, Sh., Emam, Y., & Honar, T. (2018). Evaluation of yield, actual crop evapotranspiration and water productivity of two canola cultivars as influenced by transplanting and seeding and deficit irrigation. International Journal of Plant Production, 13, 23–33.
Scott, R. K., & Jaggard, K. W. (1993). Crop physiology and agronomy. In D. A. Cooke & R. K. Scott (Eds.), The sugar beet crop: science into practice (pp. 179–237). Chapman & Hall.
Sepaskhah, A. R., & Ahmadi, S. H. (2012). A review on partial root-zone drying irrigation. International Journal of Plant Production, 4, 241–258.
Shabani, A., Kamgar-Haghighi, A. A., Sepaskhah, A. R., Emam, Y., & Honar, T. (2010). Effect of water stress on grain yield, yield components and quality of rapeseed (Brasicanapus L.) cv. Licord. Iranian Journal of Crop Sciences, 12(4), 409–421.
Shabani, A., Sepaskhah, A. R., & Kamgar-Haghighi, A. A. (2013). Growth and physiologic response of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to deficit irrigation, water salinity and planting method. International Journal of Plant Production, 7, 569–596.
Shahrokhnia, M. H., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2017). Physiologic and agronomic traits in safflower under various irrigation strategies, planting methods and nitrogen fertilization. Indian Crops Production, 95, 126–139.
Shrestha, N., Geerts, S., Raes, D., Horemans, S., Soentjens, S., & Maupas, F. (2010). Yield response of sugar beets to water stress under western European conditions. Agricultural Water Management, 97, 346–350.
Souza, C. R., Maroco, J., Santos, T., Rodrigues, M. L., Lopes, C. M., Pereira, J. S., & Chaves, M. M. (2005). Impact of deficit irrigation on water use efficiency and carbon isotope composition (d13C) of field-grown grapevines under Mediterranean climate. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 2163–2172.
Szeicz, G. (1974). Solar radiation in crop canopies. Journal of Applied Ecology, 11(3), 1117–1156.
Talebnejad, R., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2016). Physiological characteristics, gas exchange, and plant ion relations of quinoa to different saline groundwater depths and water salinity. Archive of Agronomy and Soil Science, 62, 1347–1367.
Topak, R., Suhert, S., & Acar, B. (2011). Effect of different drip irrigation regimes on sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) yield, quality and water use efficiency in middle Anatolian Turkey. Irrigation Science, 29, 79–89.
Vishwakarma, A., Singh, J. K., Sen, A., Bohra, J. S., & Singh, S. (2016). Effect of transplanting date and age of seedlings on growth, yield and quality of hybrids under system of rice (oryza sativa) intensification and their effect on soil fertility. Indian Journal of Agricultural Science, 86(5), 679–685.
Wang, Sh., Wang, E., Wang, F., & Tang, L. (2012). Phonological development and grain yield of canola as affected by sowing date and climate variation in the Yangtze River Basin of China. Crop Pasture Science, 63(5), 478–488.
Wanjura, D. F., Upchurch, D. R., Mahan, J. R., & Burke, J. J. (2002). Cotton yield and applied water relationships under drip irrigation. Agricultural Water Management, 55, 217–237.
Watanabe, S., Nakano, Y., & Okano, K. (2003). Effect of planting density on fruit size: light interception and photosynthetic activity of vertically trained watermelon (Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. et Nakai) plants. Journal of the Japanese Society for Horticultural Science, 72, 497–503.
Will, R. E., Narahari, N. V., Shiver, B. D., & Teskey, R. O. (2005). Effects of planting density on canopy dynamics and stem growth for intensively managed loblolly pine stands. Forest Ecology and Management, 205, 29–41.
Yan, W., Zhong, Y., & Shangguan, Z. (2016). A meta-analysis of leaf gas exchange and water status responses to drought. Scientific Reports, 6, 1–9.
Yan, Zh., Zhou, Q., Teng, M., Ji, H., Zhang, J., He, W., Ye, Y., Wang, B., & Wang, P. (2019). High planting density and leaf area index of masson pine forest reduce crown transmittance of photosynthetically active radiation. Global Ecology and Conservation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00759
Yarami, N., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2015). Physiological growth and gas exchange response of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) to irrigation water salinity, manure application and planting method. Agricultural Water Management, 154, 43–51.
Yonts, D., & Smith, J. (1997). Effects of plant population and row width on yield of sugar beet. Journal of Sugar Beet Research, 34, 21–30.
Zand-Parsa, Sh. (2006). Improved soil hydraulic conductivity function based on specific liquid-vapor interfacial area around the soil particles. Geoderma, 132, 20–30.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to appreciate the Center of Excellence for on-Farm Water Management and the Center of Drought Research, Shiraz University and the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF). Also we would like to acknowledge Dr. Davar Khalili and Yasmine Kamgar Haghighi for their help to English editing the manuscript, Dr. Ali Reza Yazdani for his help to prepare the sugar beet seedlings, Dr Mohsen Bazrafshan for his help to prepare the seed of sugar beet and also help to determine the yield quality parameter. This research did not receive any specific funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khozaei, M., Kamgar Haghighi, A.A., Zand Parsa, S. et al. Effects of Plant Densities and Irrigation Regimes on Yield, Physiological Parameters and Gas Exchange of Sugar Beet Under Transplanting and Direct Seeding Methods. Int. J. Plant Prod. 15, 635–653 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-021-00147-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-021-00147-3