Abstract
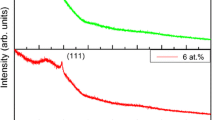
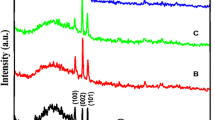
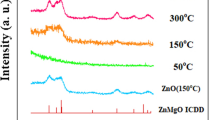
Thin films of Zn1–xMnxO (x = 1–4 at %) were applied onto a glass substrate by low-cost chemical bath deposition (CBD). The films were characterized by XRD, UV–VIS absorption spectra, SEM, and vibrating sample magnetometry—with special emphasis on the influence of dopant concentration x. Structural and optical properties of deposited films imply that the Mn2+ ions substituted Zn2+ ions without changing the wurtzite structure of ZnO. No impurity phases were detected in XRD patterns. The band gap in ZnO was found to increase with increasing x. Magnetic measurements showed that Mn-doped ZnO samples exhibited ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature, which tentatively was associated with the replacement of Zn2+ ions by Mn2+ ions in the ZnO lattice.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kazakova, O., van der Meulen, M.I., Petkov, N., and Holmes, J.D., Magnetic properties of single crystalline Ge1–xMnx nanowires, IEEE Trans. Magn., 2009, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 4085–4088. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2009.2023073
Nasir, A., Vijaya, A.R., Zahir, A.K., Tarafder, K., Kumar, A., Wadhwa, M.K., Singh, B., and Ghosh, S., Ferromagnetism from non-magnetic ions: Ag-doped ZnO, Sci. Rep., 2019, vol. 9, 20039. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56568-8
Shatnawi, M., Alsmadi, A.M., Bsoul, I., Salameh, B., Mathai, M., Alnawashi, G., Alzoubi, G.M., Al-Dweri, F., and Bawa’aneh, M.S., Influence of Mn doping on the magnetic and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystalline particles, Res. Phys., 2016, vol. 6, pp. 1064–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.11.041
Yuan, K., Yu, Q.X., Gao, Q.Q., Wang, J., and Zhang, X.T., A threshold of Vo+/Vo++ to room temperature ferromagnetism of hydrogenated Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, vol. 258, no. 8, pp. 3350–3353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.08.080
Vinod, R., Junaid Bushiri, M., Sajan, P., Achary, S.R., and Sanjose, V.M., Mn2+-induced room-temperature ferromagnetism and spin-glass behavior in hydrothermally grown Mn-doped ZnO nanorods, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2014, vol. 211, no. 5, pp. 1155–1161. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201330394
Wojnarowicz, J., Omelchenko, M., Szczytko, J., Chudoba, T., Gierlotka, S., Majhofer, A., Twardowski, A., and Lojkowski, W., Structural and magnetic properties of Co‒Mn codoped ZnO nanoparticles obtained by microwave solvothermal synthesis, Crystals, 2018, vol. 8, no. 11, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8110410
Yan, H.L., Zhong, X.L., Wang, J.B., Huang, G.J., Ding, S.L., Zhou, G.C., and Zhou, Y.C., Cathodoluminescence and room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanorod arrays grown by chemical vapor deposition, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, vol. 90, no. 8, 082503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2460297
Droubay, T.C., Keavney, D.J., Kaspar, T.C., Heald, S.M., Wang, C.M., Johnson, C.A., Whitaker, M., Gamelin, D.R., and Chambers, S.A., Correlated substitution in paramagnetic Mn2+-doped ZnO epitaxial films, Phys. Rev. B, 2009, vol. 79, no. 15, pp.155203–155208. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.79.155203
Kluth, O., Schope, G., Hupkes, J., Agashe, C., Muller, J., and Rech, B., Modified Thornton model for magnetron sputtered zinc oxide: Film structure and etching behavior, Thin Solid Films, 2003, vol. 442, nos. 1–2, pp. 80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(03)00949-0
Huang M.H., Mao S., Feick H., Yan H., Wu Y., Kind H., Weber E., Russo R., and Yang P., Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers, Science, 2001, vol. 292, no. 5523, pp. 1897–1899, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060367
Maiti, U.N., Ghosh, P.K., Nandy, S., and Chattopadhyay, K.K., Effect of Mn doping on the optical and structural properties of ZnO nano/micro-fibrous thin film synthesized by sol–gel technique, Physica B: Condens. Matter, 2007, vol. 387, nos. 1–2, pp. 103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2006.03.090
Lu, J.G., Huang, K., Zhu, J.B., Chen, X.M., Song, X.P., and Sun, Z.Q., Preparation and characterization of Na-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method, Physica B, 2010, vol. 405, no. 15, pp. 3167–3171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.04.045
Yılmaz, S., McGlynn, E., Bacaksız, E., Ozcan, Ş., Byrne, D., Henry, M.O., and Chellappan, R.K., Effects of Cu diffusion-doping on structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO nanorod arrays grown by vapor phase transport method, Appl. Phys., 2012, vol. 111, no. 1, pp. 013903-013905. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3673861
Yılmaz, S., Bacaksız, E., McGlynn, E., Polat, İ., and Ozcan, Ş., Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1–xMnxO micro-rod arrays synthesized by spray pyrolysis method, Thin Solid Films, 2012, vol. 520, no. 16, pp. 5172–5178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2012.04.002
Yan, X., Ho, D., Li, H., Li, L., Chong, X., and Wang, Y., Nanostructure and optical properties of M doped ZnO (M = Ni, Mn) thin films prepared by sol–gel process, Physica B: Condens. Matter, 2011, vol. 406, no. 20, pp. 3956–3962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.07.037
Yang, S. and Zhang, Y., Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2013, vol. 334, pp. 52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.01.026
Lee, J.H., Ko, K.H., and Park, B.O., Electrical and optical properties of ZnO transparent conducting films by the sol–gel method, J. Cryst. Growth, 2003, vol. 247, nos. 1–2, pp. 119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(02)01907-3
Deka, S. and Joy, P.A., Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn doped ZnO nanowires, Solid State Commun., 2007, vol. 142, no. 4, pp. 190–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2007.02.017
Hao, Y.M., Lou, S.Y., Zhou, S.M., Yuan, R.J., Zhu, G.Y., and Hao, N.L., Fabrication and characterization of Mn-doped CuO thin films by the SILAR method, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2012, vol. 7, p. 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-100
Gulen, Y., Bayansal, F., Sahin, B., Cetinkara, H.A., and Guder, H.S., Fabrication and characterization of Mn-doped CuO thin films by the SILAR method, Ceram. Int., 2013, vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 6475–6480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.01.077
Kharroubi, B., Baghdad, R., Abdiche, A., Bousmaha, M., Bousquet, M., Zeinert, A., Marssi, M.E., Zellama, K., and Hamzaoui, S., Mn doping effect on the structural properties of ZnO-nanostructured films deposited by the ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method, Phys. Scr., 2007, vol. 86, no. 1, 015805. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/86/01/015805
Sakai, K., Kakeno, T., Ikari, A., Shirakata, S., Sakemi, T., Awai, K., and Yamamoto, T., Defect centers and optical absorption edge of degenerated semiconductor ZnO thin films grown by a reactive plasma deposition by means of piezoelectric photothermal spectroscopy, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, vol. 99, no. 4, 043508. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2173040
Rekha, K., Nirmala, M., Nair, M., and Anukaliani, A., Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles, Physica B, 2010, vol. 405, no. 15, pp. 3180–3185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.04.042
Arvind, A., Jayara, M.K., Kumar, M., and Chandra, R., Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Mn doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2012, vol. 177, no. 13, pp. 1017–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2012.05.005
Diaconu, M., Schmidt, H., Hochmuth, H., Lorenz, M., Benndorf, G., Lenzer, J., Spemann, D., Setzer, A., Nielsen, K.W., Esquinazi, P., and Grundmann, M., UV optical properties of ferromagnetic Mn-doped ZnO thin films grown by PLD, Thin Solid Films, 2005, vol. 486, nos. 1–2, pp. 117–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2004.11.211
Theodoropoulou, N., Misra, V., Philip, J., Leclair, P., Berera, G.P., Moodera, J.S., Satpati, B., and Som, T., High-temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1–xMnxO semiconductor thin films, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2006, vol. 300, no. 2, pp. 407–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.05.039
Sharma, P., Gupta, A., Rao, K.V., Owens, F.J., Sharma, R., Ahuja, R., Guillen, J.M.O., Johansson, B., and Gehring, G.A., Ferromagnetism above room temperature in bulk and transparent thin films of Mn-doped ZnO, Nat. Mater., 2003, vol. 2, pp. 673–677. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat984
Baik, J.M. and Lee, J.L., Fabrication of vertically well-aligned (Zn,Mn)O nanorods with room temperature ferromagnetism, Adv. Mater., 2005, vol. 17, no. 22, pp. 2745–2748. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200500776
Ruderman, M.A. and Kittel, C., Indirect exchange coupling of nuclear magnetic moments by conduction electrons, Phys. Rev., 1954, vol. 96, pp. 99–102. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.96.99
Lin, Y.B., Xu, J.P., Zou, W.Q., Lu, L.Y., Lu, Z.H., Zhang, F.M., Du, Y.W., Huang, Z.G., and Zheng, J.G., Effects of annealing and hydrogenation on the properties of ZnMnO polycrystalline films synthesized by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2007, vol. 40, no. 12, 3674. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/12/019
Theodoropoulou, N., Misra, V., Philip, J., Leclair, P., Berera, G.P., Moodera, J.S., Satpati, B., and Som, T., High-temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1 − xMnxO semiconductor thin films, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2006, vol. 300, no. 2, pp. 407–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.05.039
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, G.R., Shelar, M.B., Kambale, N.J. et al. Thin Zn1 – xMnxO Films (x = 1–4 at %) by Chemical Bath Deposition: Influence of Dopant Concentration. Int. J Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth. 30, 100–105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386221020096
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386221020096