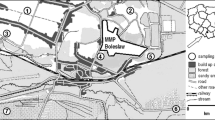
Abstract
Species of macrofungi were collected from extremely polluted sampling spots in the vicinity of abandoned antimony mines in Slovakia. Concentrations of potentially toxic elements in plants and fungi were determined by ICP-MS and in soils and sediments by both ICP-MS and ICP-ES. Of the edible species the highest values of arsenic and cadmium were recorded in Agaricus arvensis, lead in Imleria badia, and species of the genera Boletus, Leccinum, and Suillus accumulated high levels of mercury. Suillus species also accumulated high levels of antimony and chromium. Bioconcentration factors were calculated for selected species and antimony, cadmium, and mercury were accumulated by most of the sampled species. Based on our results, Cardamine amara belongs to accumulators of potentially toxic elements. We do not recommend the consumption of edible mushrooms and medicinal plants from the studied localities, as they may pose a risk of intoxication for humans.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ababneh FA (2017) The hazard content of cadmium, lead, and other trace elements in some medicinal herbs and their water infusions. Int J Anal Chem 2017:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6971916
Abreu CA, Cantoni M, Coscione AR, Paz-Ferreiro J (2012) Organic matter and barium absorption by plant species grown in an area polluted with scrap metal residue. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2012:476821. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/476821
Ahmad MSA, Ashraf M (2011) Essential roles and hazardous effects of nickel in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 214:125–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0668-6_6
Akgul A, Akgul A (2018) Mycoremediation of copper: exploring the metal tolerance of brown rot fungi. BioResour 13(3):7155–7171
Alonso J, García MA, Pérez-López M, Melgar MJ (2003) The concentrations and bioconcentration factors of copper and zinc in edible mushrooms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44(2):180–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2051-0
Amjad M, Raza H, Murtaza B, Abbas G, Imran M, Shahid M, Naeem MA, Zakir A, Iqbal MM (2019) Nickel toxicity induced changes in nutrient dynamics and antioxidant profiling in two maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids. Plants 9(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010005
Andresen E, Küpper H (2013) Cadmium toxicity in plants. In: Sigel A, Sigel H, Sigel RKO (eds) Cadmium: from toxicity to essentiality. Metal ions in life sciences 11:395-413. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5179-8_13
Annan K, Dickson RA, Amponsah IK, Nooni IK (2013) The heavy metal contents of some selected medicinal plants sampled from different geographical locations. Pharm Res 5(2):103–108. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8490.110539
Antosiewicz DM, Escudĕ-Duran C, Wierzbowska E, Skłodowska A (2008) Indigenous plant species with the potential for the phytoremediation of arsenic and metals contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 193(1–4):197–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9683-2
Árvay J, Tomáš J, Hauptvogl M, Kopernická M, Kováčik A, Bajčan D, Massányi P (2014) Contamination of wild-grown edible mushrooms by heavy metals in a former mercury-mining area. J Environ Sci Health B 49(11):815–827. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2014.938550
Árvay J, Tomáš J, Hauptvogl M, Massányi P, Harangozo Ľ, Tóth T, Stanovič S, Bryndzová Š, Bumbalová M (2015) Human exposure to heavy metals and possible public health risks via consumption of wild edible mushrooms from Slovak paradise National Park, Slovakia. J Environ Sci Health, B 50(11):833–843. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2015.1058107
Arvensis M, Tupý P, Kupcová Z, Fodorová V, Mudráková M, Čechovská K, Čamaj P, Klačan J (1994) Dúbrava – impoundments, preliminary research. Geol. Surv. Spišská Nová Ves. 188 p, (in Slovak)
Azevedo R, Rodriguez E (2012) Phytotoxicity of mercury in plants: a review. J Bot 2012:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/848614
Baroni F, Boscagli A, Protano G, Riccobono F (2000) Antimony accumulation in Achillea ageratum, Plantago lanceolata and Silene vulgaris growing in an old Sb-mining area. Environ Pollut 109(2):347–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(99)00240-7
Baroni F, Boscagli A, Di Lella LA, Protano G, Riccobono F (2004) Arsenic in soil and vegetation of contaminated areas in southern Tuscany (Italy). J Geochem Explor 81(1–3):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0375-6742(03)00208-5
Baumhardt GR, Welch LF (1972) Lead uptake and corn growth with soil-applied lead. J Environ Qual 1(1):92–93. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1972.00472425000100010022x
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17(1):21–34. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-04202005000100003
Borovička J (2004) Nová lokalita baňky velkokališné (A new site for Sarcosphaera coronaria (Jacq.) J. Schröt) Mykologický Sborník 81(3):97–100
Borovička J, Řanda Z (2007) Distribution of iron, cobalt, zinc and selenium in macrofungi. Mycol Prog 6(4):249–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-007-0544-y
Borovička J, Řanda Z, Jelínek E (2005) Gold content of ectomycorrhizal and saprobic macrofungi from non-auriferous and unpolluted areas. Mycol Res 109(8):951–955. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095375620500328X
Borovička J, Řanda Z, Jelínek E (2006) Antimony content of macrofungi from clean and polluted areas. Chemosphere 64(11):1837–1844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.060
Borovička J, Dunn CE, Gryndler M, Mihaljevič M, Jelínek E, Rohovec J, Rohošková M, Řanda Z (2010) Bioaccumulation of gold in macrofungi and ectomycorrhizae from the vicinity of the Mokrsko gold deposit, Czech Republic. Soil Biol Biochem 42(1):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.10.003
Brooks RR (1972) Geobotany and biogeochemistry in mineral exploration. Harper and Row Publishers, 290 p. ISBN 006040969X
Brooks RR (1980) Accumulation of nickel by terrestrial plants. In: Nriagu JO (ed) Nickel in the environment. John Wiley And Sons, New York, Chichester, Brisbane, Toronto, pp 407–429
Broyer TC, Johnson CM, Paull RE (1972) Some aspects of lead in plant nutrition. Plant Soil 36(1–3):301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01373485
Burger A, Lichtscheidl I (2019) Strontium in the environment: review about reactions of plants towards stable and radioactive strontium isotopes. Sci Total Environ 653:1458–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.312
Cejpková J, Gryndler M, Hršelová H, Kotrba P, Řanda Z, Synková I, Borovička J (2016) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals, metalloids, and chlorine in ectomycorrhizae from smelter-polluted area. Environ Pollut 218:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.009
Chaudhry FM, Wallace A, Mueller RT (1977) Barium toxicity in plants. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 8(9):795–797. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103627709366776
Chen C, Huang D, Liu J (2009) Functions and toxicity of nickel in plants: recent advances and future prospects. CLEAN Soil Air Water 37(4–5):304–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200800199
Chovan M, Háber M, Jeleň S, Rojkovič I, Andráš P, Antal B (1994) Ore textures in the Western Carpathians. Slovak Academic Press, Bratislava, 219 pp
Cipollini ML, Pickering JL (1986) Determination of the phytotoxicity of barium in leach-field disposal of gas well brines. Plant Soil 92(2):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02372630
Clarkson DT, Hanson JB (1980) The mineral nutrition of higher plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 31(1):239–298. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.001323
Connolly EL, Guerinot ML (2002) Iron stress in plants. Genome Biol 3(8):reviews1024.1. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-8-reviews1024
Das P, Samantaray S, Rout GR (1997) Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environ Pollut 98(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(97)00110-3
DesMarias TL, Costa M (2019) Mechanisms of chromium-induced toxicity. Curr Opin Toxicol 14:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2019.05.003
Dogan HH, Sanda MA, Uyanöz R, Öztürk C, Çetin Ü (2006) Contents of metals in some wild mushrooms: its impact in human health. Biol Trace Elem Res 110(1):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1385/bter:110:1:79
Ducic T, Polle A (2005) Transport and detoxification of manganese and copper in plants. Brazilian J Plant Physiol 17(1):103–112. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-04202005000100009
ECHA (2021): Antimony https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.028.314. Accessed 7 Mar 2021
EFSA (2009) Scientific opinion on arsenic in food. EFSA J 7(10):1351. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1351
EFSA (2014) Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of chromium in food and drinking water. EFSA J 12(3):3595. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3595
El-Jaoual T, Cox DA (1998) Manganese toxicity in plants. J Plant Nutr 21(2):353–386. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169809365409
EU (2006) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. DO L 364/8
EU (2008) Commission Regulation (EC) No 629/2008 of 2 July 2008 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Office J European Union 372008L173/6–9
Falandysz J (2008) Selenium in edible mushrooms. J Environ Sci Health C 26(3):256–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590500802350086
Falandysz J, Bielawski L (2007) Mercury and its bioconcentration factors in Brown Birch Scaber stalk (Leccinum scabrum) from various sites in Poland. Food Chem 105(2):635–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.04.024
Falandysz J, Borovička J (2013) Macro and trace mineral constituents and radionuclides in mushrooms: health benefits and risks. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(2):477–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4552-8
Falandysz J, Gucia M (2008) Bioconcentration factors of mercury by parasol mushroom (Macrolepiota procera). Environ Geochem Health 30:121–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-008-9133-5
Falandysz J, Rizal LM (2016) Arsenic and its compounds in mushrooms: a review. J Environ Sci Health, C 34(4):217–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2016.1235935
Falandysz J, Bona H, Danisiewicz D (1994) Silver content of wild-grown mushrooms from northern Poland. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 199(3):222–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01193449
Falandysz J, Szymczyk K, Ichihashi H, Bielawski L, Gucia M, Frankowska A, Yamasaki SI (2001) ICP/MS and ICP/AES elemental analysis (38 elements) of edible wild mushrooms growing in Poland. Food Addit Contam 18(6):503–513. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030119625
Falandysz J, Frankowska A, Mazur A (2007) Mercury and its bioconcentration factors in King Bolete (Boletus edulis) Bull. Fr. J Environ Sci Health A 42(14):2089–2095. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520701627058
Falandysz J, Krasińska G, Pankavec S, Nnorom IC (2014) Mercury in certain boletus mushrooms from Poland and Belarus. J Environ Sci Health B 49(9):690–695. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2014.922853
Falandysz J, Chudzińska M, Barałkiewicz D, Drewnowska M, Hanć A (2017) Toxic elements and bio-metals in Cantharellus mushrooms from Poland and China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(12):11472–11482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8554-z
Fayez KA, El-Deeb BA, Mostafa NY (2017) Toxicity of biosynthetic silver nanoparticles on the growth, cell ultrastructure and physiological activities of barley plant. Acta Physiol Plant 39(7):155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2452-3
Feng R, Wei C, Tu S, Ding Y, Wang R, Guo J (2013) The uptake and detoxification of antimony by plants: a review. Environ Exp Bot 96:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.08.006
Figueiredo E, Soares ME, Baptista P, Castro M, Bastos ML (2007) Validation of an electrothermal atomization atomic absorption spectrometry method for quantification of total chromium and chromium(vi) in wild mushrooms and underlying soils. J Agric Food Chem 55(17):7192–7198. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0710027
Filella M, Belzile N, Chen YW (2002) Antimony in the environment: a review focused on natural waters. Earth-Sci Rev 57(1–2):125–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-8252(01)00070-8
Filella M, Williams PA, Belzile N (2009) Antimony in the environment: knowns and unknowns. Environ Chem 6(2):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1071/en09007
Finnegan PM, Chen W (2012) Arsenic toxicity: the effects on plant metabolism. Front Physiol 3:182. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00182
Foy CD, Scott BJ, Fisher JA (1988) Genetic differences in plant tolerance to manganese toxicity. In: Graham RD, Hannam RJ, Uren NC (eds) Manganese in soils and plants. Dev Plant Soil Sci 33:293-307, Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-2817-6_20
FSANZ (2021) Antimony. Food standards for Australia and new Zealand. https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/publications/pages/20thaustraliantotaldietsurveyjanuary2003/20thaustraliantotaldietsurveyfullreport/partb20thatds/partbmetals.aspx. Accessed 8 Mar 2021
Gadd GM (1993) Tansley review no. 47. Interactions of fungi with toxic metals. New Phytol 124(1):25–60.https://www.jstor.org/stable/2558069. Accessed 8 March 2021
García MÁ, Alonso J, Melgar MJ (2009) Lead in edible mushrooms: levels and bioaccumulation factors. J Haz Mat 167(1–3):777–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.058
García MA, Alonso J, Melgar MJ (2013) Bioconcentration of chromium in edible mushrooms: influence of environmental and genetic factors. Food Chem Toxicol 58:249–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.04.049
Garg N, Singla P (2011) Arsenic toxicity in crop plants: physiological effects and tolerance mechanisms. Environ Chem Lett 9(3):303–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-011-0313-7
Grecula P, Abonyi A, Abonyiová M, Antaš J, Bartalský B, Bartalský J, Dianiška I, Drzík E, Ďuďa R, Gargulák M, Gazdočko Ľ, Hudáček J, Kobulský J, Lörinz L, Macko J, Návesňák D, Németh Z, Novotný L, Radvanec M, Rojkovič I, Rozložník L, Rozložník O, Varček C, Zlocha J (1995) Mineral deposits of the Slovenské Rudohorie Mts. 1. Geokomplex, Bratislava, Slovakia, 834p. (In Sovak)
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53(366):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.366.1
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Hakeem KR, Öztürk M, Fujita M (2015) Arsenic toxicity in plants and possible remediation. Soil Remediat Plants 2015:433–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-799937-1.00016-4
Hassan MU, Chattha MU, Khan I, Chattha MB, Aamer M, Nawaz M, Ali A, Khan MAU, Khan TA (2019) Nickel toxicity in plants: reasons, toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and remediation possibilities—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(13):12673–12688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04892-x
Hernández-Baranda Y, Rodríguez-Hernández P, Peña-Icart M, Meriño-Hernández Y, Cartaya-Rubio O (2019) Toxicity of cadmium in plants and strategies to reduce its effects. Case study: the tomato. Cultivos Tropicales 40(3):e10
Hettick BE, Cañas-Carrell JE, French AD, Klein DM (2015) Arsenic: a review of the element’s toxicity, plant interactions, and potential methods of remediation. J Agric Food Chem 63(32):7097–7107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02487
Horst WJ (1988) The physiology of manganese toxicity. In: Graham RD, Hannam RJ, Uren NC (eds) Manganese in soils and plants. Dev Plant Soil Sci 33:175-188. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-2817-6_13
Isermann K (1981) Uptake of stable strontium by plants and effects on plant growth. In: Skoryna SC (ed) Handbook of stable strontium. Springer, Boston, pp. 65–86. 10.1007/978-1-4684-3698-3_5
Jacobs K, Büschelberger F, Plaschkies K (2016) K. Virulenz von holzzerstörenden Pilzen in Prüfverfahren zur Bestimmung der Wirksamkeit von Holzschutzmitteln und der Dauerhaftigkeit von Holz und Holzwerkstoffen. Conference paper, Deutsche Holzschutztagung - organisiert vom Institut für Holztechnologie Dresden gemeinnützige GmbH. Dresden, 22. und 23. September 2016. Dresden 2016. Institut für Holztechnologie (ihd) 2016:144–158
JECFA (2010) Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. Seventy-second meeting. Rome, 16–25 February 2010. Summary and conclusions. JECFA/72/SC. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations World Health Organization. Issued 16th March 2010
Kabata A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kalač P (2010) Trace element contents in European species of wild growing edible mushrooms: a review for the period 2000–2009. Food Chem 122(1):2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.045
Kalač P (2013) A review of chemical composition and nutritional value of wild-growing and cultivated mushrooms. J Sci Food Agric 93(2):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.5960
Kalač P, Svoboda L (2000) A review of trace element concentrations in edible mushrooms. Food Chem 69(3):273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0308-8146(99)00264-2
Kautmanová I, Červenka J, Szabóová D, Lalinská-Voleková B, Šottník P (2020) Diversity of macromycetes in the areas affected by Sb mining in Slovakia. Acta Rerum Naturalium Museil Nationalis Slovaci (in press)
Kavčič A, Mikuš K, Debeljak M, Teun van Elteren J, Arčon I, Kodre A, Kump P, Karydas AG, Migliori A, Czyzycki M, Vogel-Mikuš K (2019) Localization, ligand environment, bioavailability and toxicity of mercury in Boletus spp. and Scutiger pes-caprae mushrooms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109623
Klimko T, Chovan M, Huraiová M (2009) Hydrothermal mineralization of the stibnite veins in the Spišskogemerské rudohorie Mts. Mineralia Slovaca 41:115–132 (in Slovak)
Koděra M, Andrusovová-Vlčeková G, Belešová O, Briatková D, Dávidová Š, Fejdiová V, Hurai V, Chovan M, Nelišerová E, Ženiš P (1990) Topografic mineralogy of Slovakia II. Veda, Bratislava
Komárek M, Chrastný V, Štíchová J (2007) Metal/metalloid contamination and isotopic composition of lead in edible mushrooms and forest soils originating from a smelting area. Environ Int 33(5):677–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.02.001
Krasińska G, Falandysz J (2015) Mercury in Orange Birch Bolete Leccinum versipelle and soil substratum: bioconcentration by mushroom and probable dietary intake by consumers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(1):860–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5331-8
Krupa P, Kozdrój J (2004) Accumulation of heavy metals by ectomycorrhizal fungi colonizing birch trees growing in an industrial desert soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(4):427–430. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:wibi.0000033067.64061.f3
Kumar V, Suryakant SP, Kumar S, Kumar N (2016) Effect of chromium toxicity on plants: a review. Agriways 4(1):107–120
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Kumar V, Pandita S, Sidhu GPS, Sharma A, Khanna K, Kaur P, Bali AS, Setia R (2020) Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 262:127810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127810
Küpper H, Gotz B, Mijovilovich A, Kűpper FC, Meyer-Klaucke W (2009) Complexation and toxicity of copper in higher plants. I. Characterization of copper accumulation, speciation, and toxicity in Crassula helmsii as a new copper accumulator. Plant Physiol 151(2):702–714. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.139717
Lalinská B, Chovan M (2006) Hydrothermal mineralization in the Medzibrod deposit and the Sopotnická dolina valley. Mineralia Slovaca 38:261–272
Lalinská-Voleková B, Majzlan J, Klimko T, Chovan M, Kučerová G, Michňová J, Hovorič R, Göttlicher J, Steininger R (2012) Mineralogy of weathering products of Fe-as-Sb mine wastes and soils at several Sb deposits in Slovakia. Can Mineral 50(2):481–500. https://doi.org/10.3749/canmin.50.2.481
Lalotra P, Gupta D, Yangdol R, Sharma YP, Gupta SK (2016) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the sporocarps of some wild mushrooms. Curr Res Environ Appl Mycol 6(3):159–165. https://doi.org/10.5943/cream/6/3/2
Larsen EH, Hansen M, Gössler W (1998) Speciation and health risk consideration of arsenic in the edible mushroom Laccaria amethystine collected from contaminated and uncontaminated locations. Appl Organomet Chemy 12(4):285–291
Lei Y, Korpelainen H, Li C (2007) Physiological and biochemical responses to high Mn concentrations in two contrasting Populus cathayana populations. Chemosphere 68(4):686–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.01.066
Lenka M, Panda KK, Panda BB (1992) Monitoring and assessment of mercury pollution in the vicinity of a chloralkali plant. IV. Bioconcentration of mercury in in situ aquatic and terrestrial plants at Ganjam, India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22(2):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00213285
Li R, Wu H, Ding J, Fu W, Gan L, Li Y (2017) Mercury pollution in vegetables, grains and soils from areas surrounding coal-fired power plants. Sci Rep 7:46545. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46545
Liu Y, Wang Q, Zhuang W, Yuan Y, Yuan Y, Jiao K, Wang M, Chen Q (2018) Calculation of thallium’s toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index: a case study. Chemosphere 194:562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.002
Llugany M, Poschenrieder C, Barceló J (2000) Assessment of barium toxicity in bush beans. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39(4):440–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010125
López-Millán AF, Sagardoy R, Solanas M, Abadía A, Abadía J (2009) Cadmium toxicity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) plants grown in hydroponics. Environ Exp Bot 65(2–3):376–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.11.010
Malinowska E, Szefer P, Falandysz J (2004) Metals bioaccumulation by bay bolete, Xerocomus badius, from selected sites in Poland. Food Chem 84(3):405–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0308-8146(03)00250-4
Maresca V, Heydari M, Basile A (2020) Antimony and plants: accumulation, toxic effects, and plants’ defense systems. Metalloids in Plants: Advances and Future Prospects 275–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119487210.ch14
Marhold K, Hindák F (eds) (1998) Checklist of non-vascular and vascular plants of Slovakia. VEDA, Bratislava. 688 p. ISBN: 8022405264
Marschner H (1986) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. New York, London, Academic Press. Springer-Verlag, chapter 7, 245–300. ISBN: 9780124735439
Melgar MJ, Alonso J, García MA (2009) Mercury in edible mushrooms and underlying soil: bioconcentration factors and toxicological risk. Sci Total Environ 407(20):5328–5334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.07.001
Melo LCA, Alleoni LRF, Carvalho G, Azevedo RA (2011) Cadmium- and barium-toxicity effects on growth and antioxidant capacity of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants, grown in two soil types with different physicochemical properties. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(5):847–859. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201000250
Mench M, Vangronsveld J, Didier V, Clijsters H (1994) Evaluation of metal mobility, plant availability and immobilization by chemical agents in a limed-silty soil. Environ Pollut 86(3):279–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(94)90168-6
Mendez MO, Maier RM (2008) Phytostabilization of mine tailings in arid and semiarid environments—an emerging remediation technology. Environ Health Perspect 116(3). https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10608
Mendil D, Uluözlü ÖD, Hasdemir E, Çaǧlar A (2004) Determination of trace elements on some wild edible mushroom samples from Kastamonu, Turkey. Food Chem 88(2):281–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.01.039
Millaleo R, Reyes-Diaz M, Ivanov AG, Mora ML, Alberdi M (2010) Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10(4):470–481. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-95162010000200008
Mirończuk-Chodakowska I, Socha K, Zujk ME, Terlikowsk KM, Borawsk MH, Witkowsk AM (2019) Copper, manganese, selenium and zinc in wild-growing edible mushrooms from the eastern territory of "green lungs of Poland": nutritional and toxicological implications. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(19):3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193614
Mirshekali H, Hadi H, Amirnia R, Khodaverdiloo H (2012) Effect of zinc toxicity on plant productivity, chlorophyll and Zn contents of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and common lambsquarter (Chenopodium album). Int J Agric Res Rev 2(3):247–254
Mitchell RL (1963) Soil aspects of trace element problems in plants and animals. J R Agric Soc England 124:75–86
Müller M, Anke M, Illing-Günther H (1997) Aluminium in wild mushrooms and cultivated Agaricus bisporus. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch A 205(3):242–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170050159
Nikolic M, Pavlovic J (2018) Chapter 3 - plant responses to iron deficiency and toxicity and iron use efficiency in plants. Plant Micronutrient Use Efficiency 2018:55–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-812104-7.00004-6
Orvošová M, Majzlan J, Chovan M (1998) Hydrothermal alteration of granitoid rocks and gneisses in the Dúbrava Sb–Au deposit, Western Carpathians. Geol Carpath 49:377–387
Patra M, Sharma A (2000) Mercury toxicity in plants. Bot Rev 66(3):379–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02868923
Petkovšek SAS, Pokorny B (2013) Lead and cadmium in mushrooms from the vicinity of two large emission sources in Slovenia. Sci Total Environ 443:944–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.007
Pratas J, Prasad MNV, Freitas H, Conde L (2005) Plants growing in abandoned mines of Portugal are useful for biogeochemical exploration of arsenic, antimony, tungsten and mine reclamation. J Geochem Explor 85(3):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2004.11.003
Qian H, Peng X, Han X, Ren J, Sun L, Fu Z (2013) Comparison of the toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on the growth of terrestrial plant model Arabidopsis thaliana. J Environ Sci 25(9):1947–1956. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(12)60301-5
Ragsdale SW (1998) Nickel biochemistry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2(2):208–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-5931(98)80062-8
Rizwan M, Ali S, ur Rehman MZ, Maqbool A (2019) A critical review on the effects of zinc at toxic levels of cadmium in plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:6279–6289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04174-6
Rout GR, Das P (2009) Effect of metal toxicity on plant growth and metabolism: I. Zinc Sustainable Agric:873–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2666-8_53
Saba M, Falandysz J, Nnorom IC (2016) Mercury bioaccumulation by Suillus bovinus mushroom and probable dietary intake with the mushroom meal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(14):14549–14559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6558-8
Sabo-Attwood T, Unrine JM, Stone JW, Murphy CJ, Ghoshroy S, Blom D, Bertsch PM, Newman LA (2011) Uptake, distribution and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in tobacco (Nicotiana xanthi) seedlings. Nanotoxicology 6(4):353–360. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.579631
Santos EF, Santini JMK, Paixão AP, Júnior EF, Lavres J, Campos M, dos Reis AR (2017) Physiological highlights of manganese toxicity symptoms in soybean plants: Mn toxicity responses. Plant Physiol Biochem 113:6–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.01.022
Sasmaz M, Sasmaz A (2017) The accumulation of strontium by native plants grown on Gumuskoy mining soils. J Geochem Explor 181:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.08.001
Sasmaz M, Akgül B, Yıldırım D, Sasmaz A (2016) Mercury uptake and phytotoxicity in terrestrial plants grown naturally in the Gumuskoy (Kutahya) mining area, Turkey. Int J Phytoremediat 18(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2015.1058334
Schmidt W, Thomine S, Buckhout TJ (2020) Iron nutrition and interactions in plants. Front Plant Sci 10:1670. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01670
Shacklette HT, Lakin HW, Hubert AE, Curtin GC (1970) Absorption of gold by plants. Bulletin 1314-B. US Department of the Interior. https://doi.org/10.3133/b1314B
Shanker A, Cervantes C, Lozatavera H, Avudainayagam S (2005) Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ Int 31(5):739–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.02.003
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Lead toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17(1):35–52. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-04202005000100004
Sharma A, Kapoor D, Wang J, Shahzad B, Kumar V, Bali AS, Jasrotia S, Zheng B, Yuan H, Yan D (2020) Chromium bioaccumulation and its impacts on plants: an overview. Plants 9(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010100
Sheldon AR, Menzies NW (2005) The effect of copper toxicity on the growth and root morphology of Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Knuth.) in resin buffered solution culture. Plant Soil 278(1):341–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-8815-3
Shtangeeva I, Steinnes E, Lierhagen S (2012) Uptake of different forms of antimony by wheat and rye seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(2):502–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0589-y
Singh HP, Mahajan P, Kaur S, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2013) Chromium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Environ Chem Lett 11(3):229–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0407-5
Slávik M, Tóth T, Harangozo Ľ, Árvay J, Stanovič R, Miššík J (2013) The content of mercury in edible mushrooms from middle Spiš area. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci 2(1):2115–2124. https://www.jmbfs.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/114_jmbs_slavik_fbp_f.pdf. Accessed 7 March 2021
Slávik M, Tóth T, Árvay J, Harangozo Ľ, Kopernická M (2016) The heavy metals content in wild growing mushrooms from burdened Spiš area. Potravinarstvo Slovak J Food Sci 10(1):232–236. https://doi.org/10.5219/564
Sowa I, Wójciak-Kosior M, Strzemski M, Dresler S, Szwerc W, Blicharski T, Szymczak G, Kocjan R (2014) Biofortification of soy (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with strontium ions. J Agric Chem 62(23):5248–5252. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf501257r
Suwa R, Jayachandran K, Nguyen NT, Boulenouar A, Fujita K, Saneoka H (2008) Barium toxicity effects in soybean plants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55(3):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9132-7
Svoboda L, Zimmermannová K, Kalač P (2000) Concentrations of mercury, cadmium, lead and copper in fruiting bodies of edible mushrooms in an emission area of a copper smelter and a mercury smelter. Sci Total Environ 246(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00411-8
Świsłowski P, Dołhańczuk-Śródka A, Rajfur M (2020) Bibliometric analysis of European publications between 2001 and 2016 on concentrations of selected elements in mushrooms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:22235–22250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08693-5
Taylor AF, Rylott EL, Anderson CWN, Bruce NC (2014) Investigating the toxicity, uptake, nanoparticle formation and genetic response of plants to gold. PLoS One 9(4):e93793. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093793
Thiel H, Finck A (1973) Determination of limiting values of optimum copper supply of oat and barley plants. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 134(2):107–125. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.19731340204
Tripathi DK, Tripathi A, Shweta SS, Singh Y, Vishwakarma K, Yadav G, Sharma S, Singh VK, Mishra RK, Upadhyay RG, Dubey NK, Lee Y, Chauhan DK (2017) Uptake, accumulation and toxicity of silver nanoparticle in autotrophic plants, and heterotrophic microbes: a concentric review. Front Microbiol 08. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00007
U.S. EPA (1991) Antimony. Integrated risk information system (IRIS). Environmental criteria and assessment office, Office of health and environmental assessment, Cincinnati, OH
Vaculík M, Jurkovič Ľ, Matejkovič P, Molnárová M, Lux A (2013) Potential risk of arsenic and antimony accumulation by medicinal plants naturally growing on old mining sites. Water Air Soil Pollut 224(5):1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1546-9
Van Assche F, Cardinaels C, Clijsters H (1988) Induction of enzyme capacity in plants as a result of heavy metal toxicity: dose-response relations in Phaseolus vulgaris L., treated with zinc and cadmium. Environ Pollut 52(2):103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(88)90084-x
Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (1992) A biological test system for the evaluation of metal phytotoxicity and immobilization by additives in metal-contaminated soils. In: Merian E, Haerdi W (eds) . Interrelation between chemistry and biology, Northwood Sci Technol Lett, pp 117–125
Veresoglou DS, Barbayiannis N, Matsi T, Anagnostopoulos C, Zalidis GC (1996) Shoot Sr concentrations in relation to shoot Ca concentrations and to soil properties. Plant Soil 178(1):95–100
Wang P, Lombi E, Sun S, Scheckel KG, Malysheva A, McKenna BA, Menzies NW, Zhao FJ, Kopittke PM (2017) Characterizing the uptake, accumulation and toxicity of silver sulfide nanoparticles in plants. Environ Sci Nano 4(2):448–460. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6en00489j
Warren HV, Delavault RE (1962) Lead in some food crops and trees. J Sci Food Agric 13(2):96–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740130206
Wei Y, Chen Z, Wu F, Hou H, Li J, Shangguan Y, Zhang J, Li F, Zeng Q (2015) Molecular diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at a large-scale antimony mining area in southern China. J Environ Sci 29:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.10.002
Wheeler BD, Al-Farraj MM, Cook RED (1985) Iron toxicity to plants in base-rich wetlands: comparative effects on the distribution and growth of Epilobium Hirsutum L. and Juncus Subnodulosus Schrank. New Phytol 100(4):653–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1469-8137.1985.tb02810.x
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee SJWT, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protocols: a guide to methods and applications 18(1):315–322
WHO (World Health Organization) (2000) Safety evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. WHO Food Additives Series 44: Lead. Available at http://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v44jec12.htm. Accessed 7 March 2021
Wójciak-Kosior M, Sowa I, Blicharski T, Strzemski M, Dresler S, Szymczak G, Wnorowski A, Kocjan R, Świeboda R (2016) The stimulatory effect of strontium ions on phytoestrogens content in Glycine max (L.) Merr. Molecules 21(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21010090
Wong JWC, Ip CM, Wong MH (1998) Acid-forming capacity of lead–zinc mine tailings and its implications for mine rehabilitation. Environ Geochem Health 20:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006589124204
Yah CS (2013) The toxicity of gold nanoparticles in relation to their physiochemical properties. Biomed Res 24(3):400–413
Yamaç M, Yıldız D, Sarıkürkcü C, Çelikkollu M, Solak MH (2007) Heavy metals in some edible mushrooms from the Central Anatolia, Turkey. Food Chem 103(2):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.041
Ye ZH, Shu WS, Zhang ZQ, Lan CY, Wong MH (2002) Evaluation of major constraints to revegetation of lead/zinc mine tailings using bioassay techniques. Chemosphere 47(10):1103–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00054-1
Záhorcová Z, Árvay J, Hauptvogl M, Tomáš J, Harangozo Ľ (2016) Heavy metals determination in edible wild mushrooms growing in former mining area - Slovakia: health risk assessment. Potravinarstvo Slovak J Food Sci 10(1):37–46. https://doi.org/10.5219/528
Zhang W, Lin K, Zhou J, Zhang W, Liu L, Han X (2013) Spatial distribution and toxicity of cadmium in the joint presence of sulfur in rice seedling. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(3):1235–1241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.10.007
Zhou X, Sun C, Zhu P, Liu F (2018) Effects of antimony stress on photosynthesis and growth of acorus calamus. Front Plant Sci 9:579. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00579
Zhu F, Qu L, Fan W, Qiao M, Hao H, Wang X (2011) Assessment of heavy metals in some wild edible mushrooms collected from Yunnan Province, China. Environ Monit Assess 179(1–4):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1728-5
Zimmermannová K, Svoboda L, Kalač P (2001) Mercury, cadmium, lead and copper contents in fruiting bodies of selected edible mushrooms in contaminated middle Spiš region, Slovakia. Ekológia (Bratislava) 20(4):440–446. http://147.213.211.222/node/2850
Funding
This work was supported by the Grant Agency for Research and Development with project number APVV-17-0317 and the Operational Program of Research and Innovations and co-financed with the European Fund for Regional Development (EFRD) ITMS2014 + 313021 W683: “DNA barcoding of Slovakia (SK-BOL), as a part of international initiative International Barcode of Life (iBOL)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in writing this article equally. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kautmanová, I., Brachtýr, O., Gbúrová Štubňová, E. et al. Potentially toxic elements in macromycetes and plants from areas affected by antimony mining. Biologia 76, 2133–2159 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00788-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00788-9