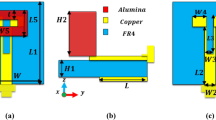
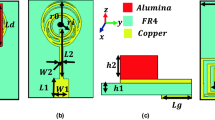
Abstract
Sensor design using ultra-wideband (UWB) technology is considered powerful emerging technique to extract information about the state of biological and physiological conditions of human organs for diagnostic purposes. Recently, UWB radio sensor technology is being proposed for early stage breast cancer detection in view of some superior characteristics or bio-markers over current methods. In this paper, a RDRA is designed, leading to develop the smart data acquisition system. A novel RDRA structure is simulated, which operates in the range of 3.7–7.4 GHz (67% bandwidth) which lies in the lower European UWB frequency band. The positive gain of the proposed antenna is stable across the active bandwidth and the peak value is 2.5 dB, which makes the RDRA structure highly suitable for body centric applications, especially for early detection of breast cancer. Thus, the proposed RDRA antenna structure can be integrated for early stage breast cancer detection application as well.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. (2020). WHO report on cancer: setting priorities, investing wisely and providing care for all. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330745
A. C. Society, Cancer Facts & Figures, The Society, New York, NY, USA, 2016. https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2016.html
K. B. C. Society, Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2014,Korean Breast Cancer Society, Seoul, South Korea, 2014. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28382089/
A.L.Siu,“ Screening for breast cancer:U.S. Preventive ser- vices task force recommendation statement,” Annals of Internal Medicine,vol.164, pp.279–296,2016
D. R. Hooley, “Mammographic Images Showing How Cancer Looks in Each of the Breast Density Categories,” Dense Breast info, http://densebreast-info.org/faqs-for-health-professionals .aspx.
P. M. Meaney, M. W. Fanning, T. Zhou, A. Golnabi, S. D. Geimer, and K. D. Paulsen, “Clinical microwave breast imaging—2D results and the evolution to 3D,” In: Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA’09), pp. 881–884, Torino, Italy, September 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEAA.2009.5297356.
P. M. Meaney, M. W. Fanning, D. Li, S. P. Poplack, and K. D. Paulsen, “A clinical prototype for active microwave imaging of the breast,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 48, pp. 1841–1853, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1109/22.883861
M. Grzegorczyk, P. M. Meaney, P. A. Kaufman, R. M. Diflorio-Alexander, and K. D. Paulsen, “Fast 3-D tomographic microwave imaging for breast cancer detection,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,vol.31,pp. 1584–1592, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tmi.2012.2197218
K.-J. Lee, J.-Y. Kim, S.-H. Son, J. Lee, and S. Jeon, “Sensing probe for 3–6 GHz microwave imaging systems,” Electronics Letters, vol.50, pp. 1049-1050,2014. https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2014.1923
E. Porter, E. Kirshin, A. Santorelli, M. Coates, and M. Popovı,“Time-domain multistatic radar system for microwave breast screening,” IEEEAntennas andWireless Propagation Letters,vol. 12, pp. 229–232, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2013.2247374
E.C.Fear, P.M.Meaney, andM.A.Stuchly,“Microwaves for breast cancer detection?” IEEE Potentials,vol.22,pp. 12– 18, 2003. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/Mp.2003.1180933
M. Klemm, J. A. Leendertz, D. Gibbins, I. J. Craddock, A. Preece, andR. Benjamin, “Microwave radar-based breast cancer detection: imaging in inhomogeneous breast phantoms,” IEEE Antennas andWireless Propagation Letters,vol.8,pp. 1349–1352, 2009.https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2009.2036748
J. Bourqui, J. Garrett, and E. Fear, “Measurement and analysis of microwave frequency signals transmitted through the breast,” International Journal of Biomedical Imaging,vol.2012, Article ID 562563, 11 pages, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/562563
R. C. Conceicao, H. Medeiros, M. O’Halloran, D. Rodriguez- Herrera, D. Flores-Tapia, and S. Pistorius, “Initial classification of breast tumour phantoms using a UWB radar prototype,” in Proceedings ofthe 15th International Conference on Electromag- netics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA ’13), pp. 720–723, IEEE, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEAA.2013.6632339
P. M. Meaney, S. A. Pendergrass, M. W. Fanning, and K. D. Paulsen, “Importance of using a reduced contrast coupling medium in 2D microwave breast imaging,” Journal of Electro- magnetic Waves and Applications,vol.17,pp.333–355, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1163/156939303322235851
S. S. Chaudhary, R. K. Mishra, A. Swarup, and J. M. Thomas,“Dielectric properties of normal & malignant human breast tissues at radiowave & microwave frequencies,” Indian Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics,vol.21,pp. 76–79, 1984. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6490065/
L. Wang, “Microwave sensors for breast cancer detection,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 1–17, 2018, https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020655
R. Cicchetti, E. Miozzi, and O. Testa, “Wideband and UWB antennas for wireless applications: A comprehensive review,” Int. J. Antennas Propag., vol. 2017, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2390808.
T. Uno and S. Adachi, “Inverse scattering method for one-dimensional inhomogeneous layered media,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 1456–1466, 1987, https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.1987.1144033
R. K. Mongia, P. Bhartia, C. L. Larose, and S. R. Mishra, “Accurate Measurement of Q-Factors of Isolated Dielectric Resonators,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 42, no. 8, pp. 1463–1467, 1994, https://doi.org/10.1109/22.297807
T. Jun Cui and C. Hong Liang, “Inverse Scattering Method for One-Dimensional Inhomogeneous Lossy Medium by Using a Microwave Networking Technique,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 43, no. 8, pp. 1773–1781, 1995, https://doi.org/10.1109/22.402259.
O. P. Profiles, V. a Mikhnev, and P. Vainikainen, “Two-Step Inverse Scattering Method for,” vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 293–298, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1109/8.833079
D. Franceschini, M. Donell, G. Franceschini, and A. Massa, “Iterative image reconstruction of two-dimensional scatterers illuminated by TE waves,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 1484–1494, 2006, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2006.871921
J. M. Geffrin, P. Sabouroux, and C. Eyraud, “Free space experimental scattering database continuation: Experimental set-up and measurement precision,” Inverse Probl., vol. 21, no. 6, 2005, https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/21/6/S09.
W. Huang and A. A. Kishk, “Compact dielectric resonator antenna for microwave breast cancer detection,” IET Microwaves, Antennas Propag., vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 638–644, 2009, https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2008.0170
S. M. Salvador, E. C. Fear, M. Okoniewski, and J. R. Matyas, “Exploring joint tissues with microwave imaging,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 58, no. 8, pp. 2307–2313, 2010, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2010.2052662
T. Kikkawa and T. Sugitani, “Planar UWB antenna array for breast cancer detection,” 2013 7th Eur. Conf. Antennas Propagation, EuCAP 2013, vol. 2, pp. 339–343, 2013. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6546278
S. Kwon and S. Lee, “Instantaneous microwave imaging with time-domain measurements for breast cancer detection,” Electron. Lett., vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 653–654, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2013.0248
E. Porter, E. Kirshin, A. Santorelli, M. Coates, and M. Popoví, “Time-domain multistatic radar system for microwave breast screening,” IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 12, pp. 229–232, 201https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2013.2247374
A. Sabouni and A. A. Kishk, “Dual-polarized, broadside, thin dielectric resonator antenna for microwave imaging,” IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., vol. 12, pp. 380–383, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2013.2252142
B. J. Mohammed, A. M. Abbosh, S. Mustafa, and D. Ireland, “Microwave system for head imaging,” IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 63, no. 1, pp. 117–123, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2013.2277562
E. Porter, H. Bahrami, A. Santorelli, B. Gosselin, L. A. Rusch, and M. Popovic, “A Wearable Microwave Antenna Array for Time-Domain Breast Tumor Screening,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1501–1509, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2518489
Z. Xu, S. Zhu, R. Wang, and R. Xie, “An H-shape dielectric resonator antenna with U-slot on the patch,” 2016 Prog. Electromagn. Res. Symp. PIERS 2016 - Proc., pp. 4447–4450, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1109/PIERS.2016.7735647.
V. Selvaraj, D. Baskaran, P. H. Rao, P. Srinivasan, and R. Krishnan, “Breast Tissue Tumor Analysis Using Wideband Antenna and Microwave Scattering,” IETE J. Res., vol. 0, no. 0, pp. 1–11, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2018.1531067
W. Shao, A. Edalati, T. R. McCollough, and W. J. McCollough, “A Time-Domain Measurement System for UWB Microwave Imaging,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 66, no. 5, pp. 2265–2275, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2018.2801862
M. Z. Mahmud, M. T. Islam, N. Misran, S. Kibria, and M. Samsuzzaman, “Microwave imaging for breast tumor detection using uniplanar AMC Based CPW-fed microstrip antenna,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, no. c, pp. 44763–44775, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2859434.
M. T. Islam, M. Z. Mahmud, M. T. Islam, S. Kibria, and M. Samsuzzaman, “A Low Cost and Portable Microwave Imaging System for Breast Tumor Detection Using UWB Directional Antenna array,” Sci. Rep., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1–13, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51620-z
S. S. Singhwal, B. K. Kanaujia, A. Singh, and J. Kishor, “Novel circularly polarized dielectric resonator antenna for microwave image sensing application,” Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 1821–1827, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.31830
G. Kaur and A. Kaur, “ Breast tissue tumor detection using ‘ S ’ parameter analysis with an UWB stacked aperture coupled microstrip patch antenna having a ‘ + ’ shaped defected ground structure ,” Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol., pp. 1–17, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1017/s1759078719001442.
G. Kaur and A. Kaur, “Monostatic radar-based microwave imaging of breast tumor detection using a compact cubical dielectric resonator antenna,” Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., no. January, pp. 1–9, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.32557 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/mop.32557.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, T., Vashishath , M., Vasisht, P. et al. A Versatile Ultra-Wideband Radio Sensor for Early Stage Detection of Breast Cancer. MAPAN 36, 891–901 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-021-00473-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-021-00473-x