Abstract
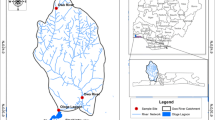
Metal contamination is one of the crucial global problems in aquatic ecosystems that can be hazardous for public health. Due to the living of the benthic fish like large-scale tongue sole (Cynoglossus arel) on the seafloor, toxicants are more accumulated in their bodies. Therefore, the accumulation of some heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb, and Zn) was determined in the edible tissues of this fish species captured from Chabahar Bay located in the northern shores of the Gulf of Oman, as well as in the sediment of their environment. For this purpose, thirty fish samples and sediment from five stations were collected during wet and dry seasons. The preparation of samples was done based on standard procedures, and the concentration of metals was measured by a flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Besides conventional statistical analysis, Muller's index (Igeo) for the classification of contamination and the biota–sediment accumulation factor (BSAF) were calculated. Results showed that the sediment of Chabahar Bay was classified as moderately contaminated in terms of Ni (Igeo = 1.271) and Pb (Igeo = 1.019). A significant correlation was found between the levels of Ni (18.1 µg∙g−1) in sediments and bio-concentration of Cu (4.85 µg∙g−1), Ni, (0.591 µg∙g−1) and Pb (1.2 µg∙g−1) in fish tissues (p < 0.05). In conclusion, Pb content accumulated in fish or sediment was the most important from the health view.
Highlights
-
The measured Cd and Cu in the sediments of the western cape in winter was significantly higher than in summer (dry season). .
-
A significant correlation was between the levels of Ni in sediments and bio-concentration of Cu, Ni, and Pb in fish tissues.
-
A significant correlation was between the sampling stations and heavy metals in sediments (except Fe and Zn) (p < 0.05).
-
A significant correlation was between the bioaccumulation of Ni in fish tissues and the concentration of Cr in sediments (p < 0.05).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agah H, Hashtroudi MS, Baeyens W (2012) Trace metals and major elements in sediments of the Northern Persian Gulf. J Persian Gulf (marine Sci) 3(7):45–58
Ahmed F, Fakhruddin ANM, Toufick Imam MD, Khan N, Ahmed Khan T, Mahfuzur Rahman M, Mohammad Abdullah AT (2016) Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metal pollution in roadside surface soil: a study of Dhaka Aricha highway, Bangladesh. Ecol Process 5(2):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-016-0045-5
Aliko V, Hajdaraj G, Caci A, Faggio C (2015) Copper induced lysosomal membrane destabilisation in haemolymph cells of Mediterranean Green Crab (Carcinus Aestuarii, Nardo, 1847) from the Narta Lagoon (Albania). Braz Arch Biol and Technol 58(5):750–756. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132015050244
Arulkumar A, Paramasivam S, Rajaram R (2017) Toxic heavy metals in commercially important food fishes collected from Palk Bay, Southeastern India. Mar Pollut Bull 119(1):454–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.03.045
Atabak N, Savari A, Dehghan Madise S (2011) Food regime of commercial juvenile Cynoglossus arel fishes in the Khuzestan Coastal Waters. Oceanography 2(6):23–30 (in Persian)
Aytekin T, Kargın D, Çoğun HY, Temiz Ö, Varkal HS, Kargın F (2019) Accumulation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in tissues of the shrimp and fish species from the Yumurtalik coast of Iskenderun Gulf, Turkey. Heliyon 5(8):e02131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02131
Bazzi AO (2014) Heavy metals in sea water, sediments and marine organisms in the Gulf of Chabahar, Oman Sea. J Oceanogr Mar Sci 5(3):20–29. https://doi.org/10.5897/JOMS2014.0110
Bone Q, Moore RH (2008) Biology of fishes, 3rd edn. Taylor and Francis Group, New York
Burkhard L (2009) Estimation of biota sediment accumulation factor (BSAF) from paired observations of chemical concentrations in biota and sediment (final report). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center, Cincinnati. EPA/600/R-06/047
Capillo G, Silvestro S, Sanfilippo M, Fiorino E, Giangrosso G, Ferrantelli V, Faggio C (2018) Assessment of electrolytes and metals profile of the Faro Lake (Capo Peloro Lagoon, Sicily, Italy) and its impact on Mytilus galloprovincialis. J Chem Biodivers 15(5):1800044. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201800044
Chen Y, Liu Q, Xu M, Wang Z (2020) Inter-annual variability of heavy metals pollution in surface sediments of Jiangsu coastal region, China: case study of the Dafeng Port. Mar Pollut Bull 150:110720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110720
Cheung KC, Wong MH (2006) Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in shrimp farming in Mai Po Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Environ Geochem Health 28(1–2):27–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-9008-y
De Mora S, Fowler SW, Wyse E, Azemard S (2004) Distribution of heavy metals in marine bivalves, fish and coastal sediments in the Gulf and Gulf of Oman. Mar Pollut Bull 49:410–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.02.029
Djikanović V, Skorić S, Spasić S, Naunovic Z, Lenhardt M (2018) Ecological risk assessment for different macrophytes and fish species in reservoirs using biota-sediment accumulation factors as a useful tool. Environ Pollut 241:1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.054 (Epub 2018 Jun 21)
FAO (2014) Species Fact Sheets, No. 123. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (Fisheries and Aquaculture Department), Rome
Fazio F, Piccione G, Tribulato K, Ferrantelli V, Giangrosso G, Arfuso F, Faggio C (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two Italian lakes. J Aquat Animal Health 26(4):278–284. https://doi.org/10.1080/08997659.2014.938872
Gu YG, Lin Q, Huang HH, Wang LG, Ning JJ, Du FY (2017) Heavy metals in fish tissues/stomach contents in four marine wild commercially valuable fish species from the western continental shelf of South China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 114:1125–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.040
Janadeleh H, Jahangiri S (2016) Risk assessment and heavy metal contamination in fish (Otolithes ruber) and sediments in Persian Gulf. J Commun Health Res 5(3):169–181
Kadhum SA, Ishak MY, Zulkifli SZ, Hashim RB (2015) Evaluation of the status and distributions of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Langat River Basin in Selangor Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 101:391–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.012
Kwok CK, Liang Y, Leung SY, Wang H, Dong YH, Young L, Giesy JP, Wong MH (2013) Biota–sediment accumulation factor (BSAF), bioaccumulation factor (BAF), and contaminant levels in prey fish to indicate the extent of PAHs and OCPs contamination in eggs of waterbirds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8425–8434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1809-4
Liu R, Jiang W, Li F, Pan Y, Wang C, Tian H (2020) Occurrence, partition, and risk of seven heavy metals in sediments, seawater, and organisms from the eastern sea area of Shandong Peninsula, Yellow Sea, China. J Environ Manage 279:111771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111771
Makedonski L, Peycheva K, Stancheva M (2017) Determination of heavy metals in selected black sea fish species. Food Control 72:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.08.024
Moyson S, Liew HJ, Fazio A, Van Dooren N, Delcroix A, Faggio C, Blust R, De Boeck G (2016) Kidney activity increases in copper exposed goldfish (Carassius auratus). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol 190:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.08.003
Müller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins, Verän- derungen seit 1971. Umschau 79:778–783
Nascimento JR, Sabadini-Santos E, Carvalho C, Keunecke KA, César R, Bidone ED (2017) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by shrimp (Litopenaeus schmitti): a dose–response approach for coastal resources management. Mar Pollut Bull 114(2):1007–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.11.013
Nasehi F, Monavari M, Naderi G, Vaezi MA, Madani F (2013) Investigation of heavy metals accumulation in the sediment and body of carp fish in Aras River, Iran. J Fish Sci 12(2):398–410
Olmedo P, Pla A, Hernandez AF, Barbier F, Ayouni L, Gill F (2013) Determination of toxic elements (mercury, cadmium, lead, tin and arsenic) in fish and shellfish samples. Risk assessment for the consumers. Environ Int 59:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.05.005
Pilehvarian AA, Malekirad AA, Rezaei BNS, M, (2015) Heavy metal bioaccumulation in different fish species in the coast of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Toxin Rev 34(4):215–219. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569543.2015.1135959
Rajeshkumar S, Li X (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species from the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Toxicol Rep 5:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.01.007
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ravikumar B, Bai G, Li X (2018) Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 191:626–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.078
Sadatipour SMT, Raghavan BR, Karimkhani Bahador A, Deepthi T (2010) Heavy metal scenario in the gulf of Chabahar-Oman Sea. Int J Earth Sci Eng 3(3):316–322
Shakouri A, Gheytasi H (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in oyster (Saccostrea cucullata) from Chabahar bay coast in Oman Sea: regional, seasonal and size-dependent variations. Mar Poll Bull 126:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.012
Simionov IA, Cristea V, Petrea SM, Mogodan A, Nicoara M, Baltag ES, Strungaru SA, Faggio C (2020) Bioconcentration of essential and nonessential elements in black sea turbot (Psetta Maxima Maeotica Linnaeus, 1758) in relation to fish gender. J Mar Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120466
Stewart RH (2006) Introduction to physical oceanography. University of Florida Press. ISBN-10: 1616100451
Torre A, Trischitta F, Faggio C (2013) Effect of CdCl2 on regulatory volume decrease (Rvd) in Mytilus Galloprovincialis digestive cells. Toxicol in Vitro 27:1260–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2013.02.017
Tudhope AW, Lea DW, Shimmield GB, Chilcott CP, Head S (1996) Monsoon climate and Arabian Sea coastal upwelling recorded in massive corals from Southern Oman. Palaios 11(4):347–361. https://doi.org/10.2307/3515245
Türkmen M, Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Töre Y, Ates A (2009) Determination of metals in fish species from Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Food Chem 113:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.071
Velusamy A, Satheesh Kumar P, Ram A, Chinnadurai S (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in commercially important marine fishes from Mumbai Harbor, India. Mar Pollut Bull 81:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.049
Vinagre C, França S, Costa MJ, Cabral HN (2005) Accumulation of heavy metals by flounder, Platichthys flesus (Linnaeus 1758), in a heterogeneously contaminated nursery area. Mar Pollut Bull 49(11–12):1109–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.08.021
WHO (1989) Heavy metals-environmental aspects, Environment Health Criteria, No. 85. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wright D, Welbourn P (2002) Environment toxicology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Yap CK, Ismail A, Tan SG, Omar H (2002) Correlations between speciation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in sediment and their concentrations in total soft tissue of green-lipped mussel Perna viridis from the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Environ Int 28:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00015-6
Zafarzadeh A, Bay A, Fakhri Y, Keramati H, Hosseini Pouya R (2018) Heavy metal (Pb, Cu, Zn, and Cd) concentrations in the water and muscle of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fish and associated non-carcinogenic risk assessment: alagol wetland in the Golestan, Iran. Toxin Rev 37(2):154–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2017.1386684
Zarezadeh R, Rezaee P, Lak R, Masoode M, Ghorbani M (2017) Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in sediments of the northern part of mangrove in hara biosphere reserve, Qeshm Island (Persian Gulf). Soil Water Res 12(2):86–95
Zhang M, He P, Qiao G, Huang J, Yuan X, Li Q (2019) Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shoal, China: spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk. Chemosphere 223:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.058
Ziyaadini M, Yousefiyanpour Z, Ghasemzadeh J, Zahedi MM (2017) Biota-sediment accumulation factor and concentration of heavy metals (Hg, Cd, As, Ni, Pb and Cu) in sediments and tissues of Chiton lamyi (Mollusca: Polyplacophora: Chitonidae) in Chabahar Bay, Iran. Iran J Fish Sci 16(4):1123–1134
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the School of Veterinary Medicine, Shiraz University for their financial support and technical collaborations during the study period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiry, N., Derakhshesh, N., Gholamhosseini, A. et al. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Cynoglossus arel (Bloch & Schneider, 1801) and Sediment in the Chabahar Bay, Iran. Int J Environ Res 15, 773–784 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-021-00352-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-021-00352-y