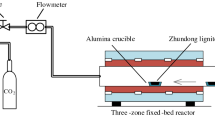
Abstract
Loy Yang lignite was pyrolyzed under nitrogen atmosphere in a tube furnace. The changes in physicochemical properties during low-temperature pyrolysis process and their effects on water re-adsorption capacity were investigated. All the samples were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, zeta potential, N2 adsorption–desorption analyzer, and scanning electron microscopy. Moreover, equilibrium water contents (EWCs) across a range of relative humidities (RHs) were measured. The results showed that oxygen-containing functional groups continuously decreased in the temperature range of 180–300°C; in contrast, pore volume increased mainly due to the release of volatiles. Note that the pore volume of the sample treated at 300°C increased substantially relative to those of the other samples. Furthermore, the EWCs of the treated samples decreased compared with that of raw lignite. For the microscopic description of the process, at low RHs the decrease in oxygen-containing functional groups corresponds to the decrease in EWC. At high RHs the competitive effects of the decrease in oxygen-containing functional groups and increase in pore volume account for the changes in EWC.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Nonaka, M. and Sasaki, K., Dry. Technol., 2016, vol. 34, no. 12, p. 1471.
Vyazova, N.G., Proidakov, A.G., Shaulina, L.P., and Shmid, A.F., Solid Fuel Chem., 2019, vol. 53, no. 3, p. 129.
Sakurovs, R., Lewis, C., and Wibberley, L., Fuel, 2016, vol. 172, p. 124.
Zhou, G.S., Huang, Q.X., Yu, B., Tong, H., Chi, Y., and Yan, J.H., Chinese J. Chem. Eng., 2017, vol. 26, no. 5, p. 1171.
Li, C.Z., Advances in the Science of Victorian Brown Coal, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2004.
Liu, X.C., Hirajima, T., Nonaka, M., and Sasaki, K., Mater. Trans., 2016, vol. 57, no. 6, p. 935.
Yu, J.L., Tahmasebi, A., Han, Y.N., Yin, F.K., and Li, X.C., Fuel Process. Technol., 2013, vol. 106, p. 9.
Yang, Y.L., Jing, X.X., Li, Z.Q., Liu, X., Zhang, Y.L., and Chang, L.P., Dry. Technol., 2013, vol. 31, no. 12, p. 1430.
Vogt, C., Wild, T., Bergins, C., Strauß, K., Hulston J., and Chaffee, A.L., Fuel, 2012, vol. 93, p. 433.
Ye, C.P., Huang, H.J., Li, X.H., Li, W.Y., and Feng, J., Fuel, 2017, vol. 207, p. 85.
Zhang Y.L., Jing, X.X., Jing, K.G., Chang, L.P., and Bao, W.R., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, vol. 324, p. 90.
Murray, J.B. and Evanst, D.G., Fuel, 1972, vol. 51, no. 4, p. 290.
Huang, H., Wang, Y.J., and Cannon, F.S., Fuel Process. Technol., 2009, vol. 90, no. 9, p. 1183.
Li, Y., Wang, Z.H., Huang, Z.Y., Liu, J.Z., Zhou, J.H., and Cen, K.F., Fuel Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 134, p. 52.
Salmas, C.E., Tsetsekou, A.H., Hatzilyberis, K.S., and Androutsopoulos, G.P., Dry. Technol., 2001, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 35.
Liu X.C., Yu, D.L., Zhao, Z.G., Xie, R.L., and Cui, P., Dry. Technol., 2019, vol. 37, no. 12, p. 1481.
Allardice, D.J., Clemow L.M., and Jackson, W.R., Fuel, 2003, vol. 82, no. 1, p. 35.
Feng, X.F., Zhang, C., Tan, P., Zhang, X.P., Fang, Q.Y., and Chen, G., Fuel, 2016, vol. 185, p. 112.
Ling, Q., Zhao, Z.G., Xie, R.L., Yu, D.L., Ke, Q.P., Lei, Z., and Cui, P., J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 2018, vol. 135, p. 319.
Simons, G.A., Combust. Flame, 1983, vol. 53, p. 83.
Liu, X.C., Hirajima, T., Nonaka, M., and Sasaki, K., J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2016, vol. 126, no. 3, p. 1925.
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Provincial Education Department (KJ2019A0076), the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2008085QB87), and Student Research Training Program of Anhui Province (S201910360204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Information
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, D., Pan, X., Tan, M. et al. Effects of Low-Temperature Pyrolysis in a Tube Furnace on Water Re-adsorption of Loy Yang Lignite and Microscopic Description of the Process. Solid Fuel Chem. 55, 200–206 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0361521921030125
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0361521921030125