Abstract
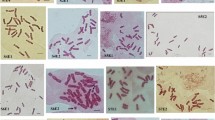
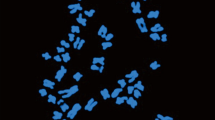
The purpose of this study was to investigate cytogenetic variations between the nine Haworthia species necessary for subsequent breeding. Flow cytometric analysis of H. badia ‘Murasaki’, H. splendens, H. truncata ‘Seiko’, H. cooperi var. obtusa, H. cymbiformis, H. mirabilis var. mundula, and H. retusa showed a wide range of DNA content from 10.17 to 12.17 pg/1C, whereas two tetraploids, H. limifolia and H. angustifolia var. baylisii, showed higher DNA content of 16.81 and 12.64 pg/1C, respectively. Seven diploid Haworthia expressed three karyotype formulas, whereas two tetraploid Haworthia each expressed a different karyotype formula. Secondary constriction was observed in H. truncata ‘Seiko’ and H. cooperi var. obtusa. Results of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) showed a major difference between the diploid and tetraploid Haworthia in the distribution of 5S and 18S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) loci. There were eight loci in two out of seven diploids and both tetraploid Haworthia, while H. cymbiformis and H. mirabilis var. mundula each showed seven 18S rDNA loci. H. badia ‘Murasaki’, H. splendens, and H. retusa had four, three, and five 18S rDNA loci, respectively. In addition, a single pair of 5S rDNA loci was observed in all diploid Haworthia except H. cooperi var. obtusa, which had four 5S rDNA loci. Each tetraploid Haworthia had four 5S rDNA loci, with two strong and two weak signals. All 5S and 18S rDNA loci were observed on the long arm, in the subtelomeric or telomeric region, while a significant variation in chromosome length was observed among the Haworthia. This cytological analysis provides the necessary genetic information to elucidate the genetic makeup of newly introduced Haworthia hybrids.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SP, Leitch IJ, Bennett MD, Chase MW, Leitch AR (2000) Ribosomal DNA evolution and phylogeny in Aloe (Asphodelaceae). Am J Bot 87:1578–1583. https://doi.org/10.2307/2656733
Bae S, Islam MM, Kim HY, Lim KB (2020) Induction of Tetraploidy in Watermelon with Oryzalin Treatments. Hortic Sci Technol 38:385–393. https://doi.org/10.7235/HORT.20200037
Bennett MD, Leitch IJ (2005) Genome size evolution in plants. The evolution of the genome. Academic Press. pp 89–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012301463-4/50004-8
Bennett MD, Bhandol P, Leitch IJ (2000) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms and their modern uses 807 new estimates. Ann Bot 86:859–909. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2000.1253
Brandham P (1969) Chromosome behaviour in the Aloineae. Chromosoma 27:201–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00326145
Brandham P (1971) The chromosomes of the Liliaceae: II: Polyploidy and karyotype variation in the Aloineae. Kew Bull 25:381–399. https://doi.org/10.2307/4103181
Brandham P, Doherty MJ (1998) Genome size variation in the Aloaceae, an angiosperm family displaying karyotypic orthoselection. Ann Bot 82:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1998.0742
Breuer I (2010) The genus Haworthia. Book 1. Alsterworthia International, London
Breuer I, Metzing D (1997) Types of names accepted in Haworthia (Aloaceae). Taxon, pp 3–14. https://doi.org/10.2307/1224286
Chen YM, Huang JZ, Hou TW, Pan IC (2019) Effects of light intensity and plant growth regulators on callus proliferation and shoot regeneration in the ornamental succulent Haworthia. Bot Stud 60:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-019-0257-y
Daru BH, Manning JC, Boatwright JS, Maurin O, Maclean N, Schaefer H, Kuzmina M, van der Bank M (2013) Molecular and morphological analysis of subfamily Alooideae (Asphodelaceae) and the inclusion of Chortolirion in Aloe. Taxon 62:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/tax.621006
Doležel J, Greilhuber J, Suda J (2007) Flow cytometry with plants: an overview. Flow Cytom Plant Cells Anal Genes Chromosom Genom. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527610921.ch3
Galbraith DW, Bartos J (2005) Flow cytometry and cell sorting in plant biotechnology. Flow Cytom Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780195183146.003.0021
He M, Pasquariello T, Steinhoff MJ, Morphology M (2016) Application of HER2 CISH pharmDX for DNA ploidy determination. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 24:465–469. https://doi.org/10.1097/pai.0000000000000220
Hwang YJ, Kim HH, Kim JB, Lim KB (2011) Karyotype analysis of Lilium tigrinum by FISH. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 52:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-011-0225-2
Islam MM, Yesmin R, Jung MJ, Kim HY, Kim CK, Lim KB (2020) Investigation of the morphological and cytogenetic variations of an intraspecific Asiatic lily hybrid using 5S and 18S rDNA probes. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 61:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00216-7
Jessy NS, Begum R, Khatun M, Alam SS (2005) Differential fluorescent chromosome banding of four species in Haworthia Duval (Aloaceae). Cytologia 70:435–440. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.70.435
Jiang J, Gill BS (2006) Current status and the future of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in plant genome research. Genome 49:1057–1068. https://doi.org/10.1139/g06-076
Jo YK, Mazharu IM, Kim CK, Kim HY, Lim KB (2019) Morphological characteristics and FISH analysis of Hibiscus F1 hybrids and parental lines. Hortic Sci Technol 37:630–639. https://doi.org/10.7235/HORT.20190063
Kim DH, Kang KW, Sivanesan I (2019) Influence of auxins on somatic embryogenesis in Haworthia retusa Duval. Biologia 74:25–33. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-018-0151-1
Lee YS, Park HM, Kim NH, Waminal NE, Kim YJ, Lim KB, Baek JH, Kim HH, Yang TJ (2016) Phylogenetic relationship of 40 species of genus Aloe L. and the origin of an allodiploid species revealed by nucleotide sequence variation in chloroplast intergenic space and cytogenetic in situ hybridization. Genet Resour Crop Evol 63:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-015-0243-5
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1964.tb01953.x
Lim KB, Wennekes J, Jong JHd, Jacobsen E, Van Tuyl JM (2001) Karyotype analysis of Lilium longiflorum and Lilium rubellum by chromosome banding and fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Genome 44:911–918. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-44-5-911
Lim KB, De Jong H, Yang TJ, Park JY, Kwon SJ, Kim JS, Lim MH, Kim JA, Jin M et al (2005) Characterization of rDNAs and tandem repeats in the heterochromatin of Brassica rapa. Mol Cells 19:436–444
Lim KB, Yang TJ, Hwang YJ, Kim JS, Park JY, Kwon SJ, Kim J, Choi BS, Lim MH et al (2007) Characterization of the centromere and peri-centromere retrotransposons in Brassica rapa and their distribution in related Brassica species. Plant J 49:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2006.02952.x
Marasek A, Hasterok R, Wiejacha K, Orlikowska T (2004) Determination by GISH and FISH of hybrid status in Lilium. Hereditas 140:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.2004.01721.x
Mazharul IM, Reshma Y, Jung JM, Mohammad DD, Lim KB (2019) Cytogenetic assessment of Lilium longiflorum × L. hansonii revealed by genomic in situ hybridization (GISH). Acta Hortic https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2019.1237.10
Nuzhyna NV, Gaydarzhy MM (2015) Comparative characteristics of anatomical and morphological adaptations of plants of two subgenera Haworthia Duval to arid environmental conditions. Acta Agrobot 68:23–31. https://doi.org/10.5586/aa.2015.006
Ogihara Y (1981) Tissue culture in Haworthia. Theor Appl Genet 60:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00264330
Oselebe H, Tenkouano A, Pillay M, Obi I, Uguru MJ (2006) Ploidy and genome segregation in Musa breeding populations assessed by flow cytometry and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 131:780–786. https://doi.org/10.21273/jashs.131.6.780
Parai P, Saha A, Mukherjee A (2012) Karyomorphology of three species of Haworthia Duval (Xanthorrhoeaceae). Nucleus 55:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-012-0070-4
Riley HP, Majumdar SK (1966) Chromosome studies of diploid and polyploid plants of Haworthia. Bot Gaz 127:239–242. https://doi.org/10.1086/336371
Riley HP, Majumdar S, Hammack R (1969) Meiosis in a triploid Haworthia With a Chromosomal Translocation. J Hered 60:255–259. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107985
Sato D (1942) Karyotype alteration and phylogeny V. Cytologia 12:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.12.170
Sattler MC, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2016) The polyploidy and its key role in plant breeding. Planta 243:281–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2450-x
Smith G, Van Wyk BE, Steyn E, Breuer I (2001) Infrageneric classification of Haworthia (Aloaceae): perspectives from nectar sugar analysis. Syst Geogr Pl. https://doi.org/10.2307/3668687
Stebbins GL (1971) Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. Addison-Wesley, Menlo Park
Suda J, Trávníček PJ (2006) Reliable DNA ploidy determination in dehydrated tissues of vascular plants by DAPI flow cytometry—new prospects for plant research. Cytometry A 69:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20253
Taylor WR (1925) Cytological studies on Gasteria. II. A comparison of the chromosomes of Gasteria, Aloe, and Haworthia. Am J Bot. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1925.tb05828.x
Tessadori F, van Driel R, Fransz P (2004) Cytogenetics as a tool to study gene regulation. Trends Plant Sci 9:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.01.008
Uitewaal A (1947) A first attempt to subdivide the genus Haworthia based on floral characters. Desert Plant Life 19:133–138
Vosa CG (2005) On chromosome uniformity, bimodality and evolution in the tribe Aloineae (Asphodelaceae). Caryologia 58:83–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2005.10589437
Vosa CG, Bayer M (1986) Chromosome studies in the southern African flora. 38–57: Haworthia. Caryologia 39:325–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.1986.10797794
Vosa CG, Bennett ST (1990) Chromosome studies in the southern African flora. 58–94. Chromosome evolution in the genus Gasteria Duval. Caryologia 43:235–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.1990.10797002
Zhou H, Zeng W, Yan H (2017) In vitro induction of tetraploids in cassava variety ‘Xinxuan 048’using colchicine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 128:723–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1141-z
Zhou J, Guo F, Fu J, Xiao Y, Wu J (2020) In vitro polyploid induction using colchicine for Zingiber Officinale Roscoe cv. ‘Fengtou’ginger. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 142:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01842-1
Zonneveld B (2015) Nuclear genome sizes of 343 accessions of wild collected Haworthia and Astroloba (Asphodelaceae, Alooideae), compared with the genome sizes of Chortolirion, Gasteria and 83 Aloe species. Plant Syst Evol 301:931–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-014-1127-4
Zonneveld B, Van Jaarsveld E (2005) Taxonomic implications of genome size for all species of the genus Gasteria Duval (Aloaceae). Plant Syst Evol 251:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-004-0244-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry (iPET) through an Agri-Bio industry Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (Grant No. IPET318021-4).
The research being report in this publication was supported by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs. I hereby disclose all of my conflicts of interest and other potentially conflicting interests, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology (HEAB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RY and MI designed the experimental structure and ideas. DMD, H-YK, C-KK, and LK-B verified the analytical methods. K-BL encouraged and supervised the findings of this work. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Jongyun Kim, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yesmin, R., Islam, M.M., Deepo, D.M. et al. Cytogenetic assessment of Haworthia using flow cytometry and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 63, 115–123 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00353-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00353-y