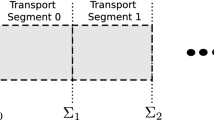
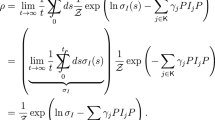Abstract
We propose the quantum field formalism as a new type of stochastic Markov process determined by local configuration. Our proposed Markov process is different with the classical one, in which the transition probability is determined by the state labels related to the character of state. In the new quantum Markov process, the transition probability is determined not only by the state character, but also by the occupation of the state. Due to the probability occupation of the state, the classical relation between the probability and condition probability at different times is no more valid. We have formulated the chain relation of successive transition for transition probability of the quantum Markov process instead of classical Chapman–Kolmogorov equation. The master equation is valid only in a classical Markov process. We have derived Euler-Lagrange equation in operator form as a characteristic equation of motion for the evolution of particle states as a Markov process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson, E.: Derivation of the Schrodinger equation from Newtonian mechanics. Phys. Rev. 150, 1079–1085 (1966)
Srinivas, M.D.: Quantum mechanics as a generalized stochastic theory in phase space. Phys. Rev. D 15, 2837–2849 (1977)
Grabert, H., Hanggi, P., Talkner, P.: Is quantum mechanics equivalent to a classical stochastic process. Phys. Rev. A 19, 2440–2445 (1979)
Guerra, F.: Structural aspects of Stochastic Mechanics and Stochastic field theory. Phys. Rep. 77, 263–312 (1981)
Siena, S.D., Guerra, F., Ruggiero, P.: Stochastic quantization of the vector-meson field. Phys. Rev. D 27, 2912–2915 (1983)
Werner, R.: A generalization of stochastic mechanics and its relation to quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. D 34, 463–469 (1986)
Wang, M.S.: Stochastic mechanics and Feynman path integrals. Phys. Rev. A 37, 1036–1039 (1988)
Roncadelli, M.: Langevin formulation of quantum mechanics. Il Nuovo Cimento 11, 73–99 (1989)
Gillespie, D.T.: Why quantum mechanics cannot be formulated as a Markov process. Phys. Rev. A 49, 1607–1612 (1994)
Skorobogatov, G.A., Svertilov, S.I.: Quantum mechanics can be formulated as a non-Markovian stochastic process. Phys. Rev. A 58, 3426–3432 (1998)
Olavo, L.S.F.: Foundations of quantum mechanics: connection with stochastic processes. Phys. Rev. A 61, 052109 (2000)
Skorobogatov, G.A.: Deduction of the Klein-Fock-Gordon equation from a non-Markovian Stochastic equation for real pure-jump process. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 88, 614–623 (2002)
Lan, B.L., Tan, Y.O.: A stochastic mechanics based on Bohm’s theory and its connection with quantum mechanics. Found. Phys. Lett. 19, 143–155 (2006)
Poulin, D.: Lieb-Robinson bound and locality for general Markovian quantum dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 190401 (2010)
Andrisani, A., Petroni, N.C.: Markov processes and generalized Schrödinger equations. J. Math. Phys. 52, 113509 (2011)
Durt, T.: Quantum mechanics and the role of time: are quantum systems markovian? Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 26, 1243005 (2012)
Allen, J.M.A., Barrett, J., Horsman, D.C., Lee, C.M., Spekkens, R.W.: Quantum common causes and quantum causal models. Phys. Rev. X 7, 031021 (2017)
Pollock, F.A., Rodriguez-Rosario, C., Frauenheim, T., Paternostro, M., Modi, K.: Operational Markov condition for quantum processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 040405 (2018)
Chiribella, G.: http://arxiv.org/1412.8539 (2018)
Greiner, W., Reinhardt, J.: Field Quantization. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Fetter, A.L., Walecka, J.D.: Quantum Theory of Many-Particle System. McGraw-Hill, New York (1971)
Ni, J.: Principles of Physics: From Quantum Field Theory to Classical Mechanics. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore (2017)
Gordon, W.D.: Der Comptoneffekt nach der Schrodingerschen Theorie. Z. Phys. 40, 117–133 (1926)
Klein, O.: Elektrodynamik und Wellenmechanik vom Standpunkt des Korrespondenz prinzips. Z. Phys. 41, 407–422 (1927)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grants No. 2016YFB0700102, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 11774195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, J. Quantum Field Theory Formulated as a Markov Process Determined by Local Configuration. Found Phys 51, 74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10701-021-00481-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10701-021-00481-6