Abstract
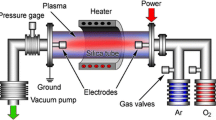
Zinc oxide (ZnO), a wide direct band gap (3.37 eV) II-VI semiconductor, is a fascinating technological material capable of exhibiting both semiconducting and piezoelectric characteristics and distinguished performance in photonics and optoelectronics. We report the synthesis of ZnO thin films composed of randomly oriented, 1-dimensional (1-D) and multipod (tripod and tetrapod)-like nanostructures of varying diameters by thermal evaporation technique. ZnO films of 150 nm thickness were grown for various deposition rates on room temperature Si and pyrex substrates by evaporating catalyst-free ZnO powder. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the films confirmed polycrystalline nature of wurtzite ZnO nanostructures with lattice constants of a = b = 3.24 Å and c = 5.2 Å. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) analysis revealed a strong influence of film deposition rate on the morphology of nanostructures. For a typical deposition rate of 0.04 nm/sec, aligned 1-D vertically oriented ZnO nanowires of 50–60 nm diameter having lattice spacing of 5.2 Å with [0001] facet were grown. Energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS) has confirmed spatially uniform high quality ZnO nanostructures growth. Micro-Raman spectra of the films confirmed appearance of characteristic longitudinal optical (LO) and transverse optical (TO) modes of wurtzite ZnO dependent on the deposition rate. The nanostructure formation is via a multiphase polytypic growth process depending on precursor growth to deposition ratio, thus promoting a particular growth facet by the crystal growth kinetics under those conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.L. Wang, J. Phys, Condens. Mater. 16, R829 (2004)
R. Yang, Y. Qin, L. Dai, Z.L. Wang, Nature Nanotechnol. Lett. 4, 34 (2009)
Z.L. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 3553 (2008)
Z.W. Pan, Z.R. Dai, Z.L. Wang, Science 291, 1947 (2001)
X.Y. Kong, Z.L. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 975 (2004)
X.Y. Kong, Y. Ding, R. Yang, Z.L. Wang, Science 303, 1384 (2004)
P.X. Gao, Y. Ding, W. Mai, W.L. Hughes, C.S. Lao, Z.L. Wang, Science 309, 1700 (2005)
F. Liu, P.J. Cao, H.R. Zhang, J.Q. Li, H.J. Gao, Nanotechnology 15, 949 (2004)
X.D. Wang, C.J. Summers, Z.L. Wang, Nano Lett. 4, 423 (2004)
Y. Wu, X.H. Zhang, F. Xu, L.S. Zhang, J. Kang, Nanotechnology 20(32), 325709 (2009)
Y. Kozuka, A. Tsukazaki, M. Kawasaki, Appl. Phys. Rev. 1, 011303 (2014)
J. He, X. Zheng, X. Hong, W. Wang, Y. Cao, T. Chen, L. Kong, Y. Wu, Z. Wu, J. Kang, Mater. Lett. 216, 182 (2018)
J. Zhou, Y. Gu, P. Fei, W. Mai, Y. Gao, R. Yang, G. Bao, Z.L. Wang, Nano Lett. 8(9), 3035 (2008)
J. Zhou, N. Xu, Z.L. Wang, Adv. Mater. 18, 2432 (2006)
V.P. Singh, K. Sandeep, H.S. Kushwaha, S. Powar, R. Vaish, Constr. Build. Mater. 158, 285 (2018)
X. Wang, J. Song, J. Liu, Z.L. Wang, Science 316, 102 (2007)
J. Liu, P. Fei, J. Zhou, R. Tummala, Z.L. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 173105 (2008)
Y. Qin, X. Wang, Z.L. Wang, Nature Lett. 451, 809 (2008)
Z.L. Wang, J.H. Song, Science 312, 242 (2006)
Y. Li, F. Qian, J. Xiang, C.M. Lieber, Mater. Today 9, 18 (2006)
G.F. Zheng, F. Patolsky, Y. Cui, W.U. Wang, C.M. Lieber, Nature Biotechnol. 23, 1294 (2005)
Z. Zhang, H. Yuan, Y. Gao, J. Wang, D. Liu, J. Shen, L. Liu, W. Zhou, S. Xie, X. Wang, X. Zhu, Y. Zhao, L. Sun, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 153116 (2007)
A.B. Djurisic, W.M. Kwok, Y.H. Leung, W.K. Chan, D.L. Phillips, M.S. Lin, S. Gwo, Nanotechnology 17(1), 244 (2006)
M.C. Newton, P.A. Warburton, Mater. Today 10, 50 (2007)
M. Erfan, L.M. Gnambodoe-Capochichi, F. Marty, Y.M. Sabry, T. Bourouina, Y. Leprince-Wang, Nanoscale 12, 1397 (2020)
Z.L. Wang, Mater. Today 10(5), 20 (2007)
Z.L. Wang, MRS Bull. 32, 109 (2007)
P.C. Chang, Z.Y. Fan, D.W. Wang, W.Y. Tseng, W.A. Chiou, J. Hong, J.G. Lu, Chem. Mater. 16, 5133 (2004)
W. Lee, M. Jeong, J. Myoung, Acta Mater. 52, 3949 (2004)
R.B.M. Cross, M.M. De. Souza, E.M.S. Narayanan, Nanotechnology 16, 2188 (2005)
B.D. Yao, Y.F. Chan, N. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 757 (2002)
S. Xu, Y. Wei, M. Kirkham, J. Liu, W. Mai, D. Davidovic, R.L. Snyder, Z.L. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(45), 14958 (2008)
E. Mosquera, M.J. Morel, J.E. Diosa, Appl. Phys. A 125(9), 613 (2019)
D. Yuvaraj, M. Sathyanarayanan, K.N. Rao, Appl. Nanosci. 4, 801 (2014)
V. Bilgin, S. Kose, F. Atay, I. Akyuz, Mater. Chem. Phys. 94, 103 (2005)
Y.F. Gao, Z.L. Wang, Nano Lett. 7(8), 2499 (2007)
Y. Ding, X.Y. Kong, Z.L. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 306 (2004)
U. Ozgur, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Dogan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, H. Morkoc, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005)
J. Serrano, F.J. Manjon, A.H. Romero, A. Ivanov, R. Lauck, M. Cardona, M. Krisch, Phys. Status Solidi b 244, 1478 (2007)
H. Gao, F. Yan, J. Li, Y. Zeng, J. Wang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 3654 (2007)
G.S. Wu, T. Xie, X.Y. Yuan, Y. Li, L. Yang, Y.H. Xiao, L.D. Zhang, Solid State Commun. 134(7), 485 (2005)
A.P. de Moura, R.C. Lima, M.L. Moreira, D.P. Volanti, J.W.M. Espinosa, M.O. Orlandi, P.S. Pizani, J.A. Varela, E. Longo, Solid State Ion. 181(15–16), 775 (2010)
Z.R. Dai, Z.W. Pan, Z.L. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 13, 9 (2003)
G.Z. Shen, Y.S. Bando, B.D. Liu, D. Golberg, C.J. Lee, Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 410 (2006)
C. Huang, M. Wang, Y. Cao, Q. Liu, Z. Huang, Y. Liu, W. Guo, Q. Huang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42, 165306 (2009)
G.J. Jiang, H.R. Zhuang, J. Zhang, M.L. Ruan, W.L. Li, F.Y. Wu, B.L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 35, 63 (2000)
W. Seo, K. Koumoto, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1777 (1996)
Z.L. Wang, X.Y. Kong, J.M. Zuo, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 185502 (2003)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Institute of Education/ Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, for AcRF grant RI 7/08 RSR to conduct this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M., Jiaji, L., Lee, P. et al. Catalyst free growth of ZnO thin film nanostructures on Si substrate by thermal evaporation. Appl. Phys. A 127, 553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04650-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04650-2