Abstract
The influences of Zr on the microstructures and impression creep behavior of A356–SiC composites were investigated. An optical microscope and a scanning electron microscopy were used to examine the microstructure. An impression creep test was conducted in a temperature range of 225–275 °C under a stress range of 350–450 MPa. The addition of 0.14 wt% Zr can significantly improve the creep resistance of the A356–SiC composite. The stress exponent (n) and creep activation energy (Q) reveal that the lattice diffusion climb-controlled creep is a dislocation climb in the A356–SiC composite, and with the addition of Zr in the A356–SiC composite, grain boundary sliding is the dominant creep mechanism. The activation energy for creep is obtained in a range of 112–173 kJ/mol, which is close to the value for the lattice self-diffusion of aluminum (142 kJ/mol). The addition of Zr alters the creep mechanism of the A356–SiC composite. The creep resistance of A356–SiC composites with added Zr higher than 0.14 wt% decreases due to grain boundary sliding.













Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
M. Mohammadpoura, R. Azari Khosroshahi, R. Taherzadeh Mousavian, D. Brabazon, Effect of interfacial active elements addition on the incorporation of micron-sized SiC particles in molten pure aluminum. Ceram. Int. 40(6), 8323–8332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.038
F. Akhlaghi, A. Lajevardi, H.M. Maghanaki, Effects of casting temperature on the microstructure and wear resistance of compocast A356/SiCp composites: a comparison between SS and SL routes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 155–156, 1874–1880 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.04.328
J.A. Garcia-Hinojosa, C.R. Gonzalez, J.A.I. Juarez, M.K. Surrapa, Effect of grain refinement treatment on the microstructure of cast Al–7Si–SiCp composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 386(1–2), 54–60 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.07.020
A.P. Kumar, D. Rohatgi, D. Weiss, 50 years of foundry-produced metal matrix composites and future opportunities. Inter. Metalcast. 14, 291–317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00375-4
F. Wang, D. Qiu, Z.L. Liu, J.A. Taylor, M.A. Easton, M.X. Zhang, The grain refinement mechanism of cast aluminium by zirconium. Acta Mater. 61(15), 5636–5645 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.05.044
B. Baradarani, R. Raiszadeh, Precipitation hardening of cast Zr-containing A356 aluminium alloy. Mater. Des. 32(2), 935–940 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.08.006
J. Hashim, L. Looney, M.S.J. Hashmi, The wettability of SiC particles by aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Pro. Technol. 119(1–3), 324–328 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355452
G.H. Garza-Elizondo, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, Effect of transition metals on the tensile properties of 354 alloy: role of precipitation hardening. Inter. Metalcast. 11, 413–427 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0074-y
K.E. Knipling, D.C. Dunand, Creep resistance of cast and aged Al–0.1Zr and Al–0.1Zr–0.1Ti (at.%) alloys at 300–400 °C. Scr. Mater. 59(4), 387–390 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.02.059
J.D. Robson, P.B. Prangnell, Dispersoid precipitation and process modelling in zirconium containing commercial aluminium alloys. Acta Mater. 49(4), 599–613 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(00)00351-7
J. Major, M. Hartlieb, Advances in aluminum foundry alloys for permanent and semi-permanent mold casting. Inter Metalcast 3, 43–53 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355452
K.E. Knipling, D.C. Dunand, D.N. Seidman, Precipitation evolution in Al–Zr and Al–Zr–Ti alloys during isothermal aging at 375–425°C. Acta Mater. 56(1), 114–127 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.09.004
Z. Lin, F.A. Mohamed, Creep and microstructure in powder metallurgy 15 vol.% SiCp–2009 Al composite. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 2975–2984 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-6131-2
Y. Li, T.G. Langdon, A comparison of the creep properties of an Al-6092 composite and the unreinforced matrix alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 29, 2523–2531 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-998-0224-9
A.B. Pandey, R.S. Mishra, Y.R. Mahajan, Steady state creep behaviour of silicon carbide particulate reinforced aluminium composites. Acta Metall. Mater. 40(8), 2045–2052 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(92)90190-P
J. Čadek, H. Oikawa, V. Šustek, Threshold creep behaviour of discontinuous aluminium and aluminium alloy matrix composites: an overview. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 190(1–2), 9–23 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(94)09605-V
S.N.G. Chu, J.C.M. Li, Impression creep; a new creep test. J. Mater. Sci. 12, 2200–2208 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00552241
V. Raman, R. Berriche, An investigation of the creep processes in tin and aluminum using a depth-sensing indentation technique. J. Mater. Res. 7(3), 627–638 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1992.0627
C. Panthglin, S. Boontein, J. Kajornchaiyakul, C. Limmaneevichitr, The Effects of Zr Addition on The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of A356–SiC Composites. Inter Metalcast 15, 169–181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00439-w
S. Rashno, B. Nami, S.M. Miresmaeili, Impression creep behavior of a cast MRI153 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 60, 289–294 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.03.072
F. Labib, R. Mahmudi, H.M. Ghasemi, Impression creep behavior of extruded Mg–SiCp composites. Mater. Sci. Eng .A 640, 91–97 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.05.090
S.M. Miresmaeili, B. Nami, Impression creep behavior of Al–1.9%Ni–1.6%Mn–1%Mg alloy. Mater. Des. 56, 286–290 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.011
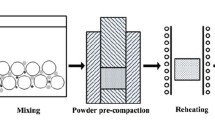
S. Soltani, R.A. Khosroshahi, R.T. Mousavian, Z.Y. Jiang, A.F. Boostani, D. Brabazon, Stir casting process for manufacture of Al–SiC composites. Rare Met. 36(7), 581–590 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0565-7
F. Xu, C.W. Lawrence, G. Han, Y. Tan, Compression creep behavior of high volume fraction of SiC particles reinforced Al composite fabricated by pressureless infiltration. Chinese J. Aero. 20(2), 115–119 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1000-9361(07)60016-8
H.J. Ryu, W.H. Sohn, S.H. Hong, Effect of SiC volume fraction on creep behavior of SiCp/2124Al metal matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Res. Int. 5(4), 280–284 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2472/jsms.48.12Appendix_280
F. Kahrıman, M. Zeren, The effect of Zr on aging kinetics and properties of as-cast AA6082 alloy. Int. J. Metal. 11, 216–222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0047-1
R. Gupta, B.S.S. Daniel, Impression creep behaviour of ultrasonically processed in-situ Al3Ti reinforced aluminium composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 733, 257–266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.017
B. Nami, H. Razavi, S. Mirdamadi, S.G. Shabestari, S.M. Miresmaeili, Effect of Ca and rare earth elements on impression creep properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41, 1973–1982 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0238-y
H. Liu, Y. Chen, Y. Tang, S. Wei, G. Niu, Tensile and indentation creep behavior of Mg-5% Sn and Mg-5% Sn-2% Di alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 464(1–2), 124–128 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.061
A. Viswanath, H. Dieringa, K.K. Ajith Kumar, U.T.S. Pillai, B.C. Pai, Investigation on mechanical properties and creep behavior of stir cast AZ91–SiCp composites. J. Magn. Alloys 3(1), 16–22 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2015.01.001
F. Ji, M.Z. Ma, A.J. Song, W.G. Zhang, H.T. Zong, S.X. Liang, Y. Osamu, R.P. Liu, Creep behavior of in situ TiCP/2618 aluminum matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 506, 58–62 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.11.010
S. Rashno, M. Reihanian, K. Ranjbar, Effect of rare earth Er on microstructure and creep behavior of Al–7Si–0.3Mg alloy. Metals Mater. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00562-2
J.A. Taylor, Iron-containing intermetallic phases in Al–Si based casting alloys. Pro. Mater. Sci. 1, 19–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2012.06.004
H.E. Evans, G. Knowles, Threshold stress for creep in dispersion-strengthened alloys. Metal Sci. 14(7), 262–266 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/030634580790426382
A.H. Clauer, N. Hansen, High temperature strength of oxide dispersion strengthened aluminium. Acta Metall. 32(2), 269–278 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(84)90055-5
A.E. Hammad, A.A. Ibrahiem, Enhancing the microstructure and tensile creep resistance of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy by reinforcing nano-sized ZnO particles. Micro. Relia. 75, 187–194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.07.034
O.D. Sherby, E.M. Taleff, Influence of grain size, solute atoms and second-phase particles on creep behavior of polycrystalline solids. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 322(1–2), 89–99 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01121-2
M. Cabibbo, Strengthening evaluation in a composite Mg-RE alloy using TEM. Mater. Sci. Forum 678, 75–84 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.678.75
S. Spigarelli, C. Paoletti, A new model for the description of creep behaviour of aluminium-based composites reinforced with nanosized particles. Com. Part A Appl. Sci. Manu. 112, 325–355 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.06.021
J.C. Gibeling, Mechanical Testing an Evaluation, A.S.M. Handbook, vol. 8, (American Society for Metals, Materials Park, 2003), pp. 789–798
S. Rashno, K. Ranjbar, M. Reihanian, Impression creep characterization of cast Al–7Si–0.3 Mg alloy. Mater. Res. Express 6(8), 0865e6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab251b
M. Reihanian, K. Ranjbar, S. Rashno, Microstructure and impression creep behavior of Al–7Si–0.3Mg alloy with Zr addition. Metals Mater. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00628-6
Acknowledgements
CP is grateful to Thailand Graduate Institute of Science and Technology (TGIST) No. TG-33-20-57-043D for her Ph.D. scholarship. This work was supported by a grant from Research Strengthening Project of the Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi and Mr. Chaow Niumsorn’s Commemorative Fund. The authors thank Ghit Laungsopapun at Thailand Institute of Scientific and Technological Research for his support of the SEM and EDS for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panthglin, C., Boontein, S., Kajornchaiyakul, J. et al. Microstructure and Impression Creep Characteristics of A356–SiC Composites Containing Zr. Inter Metalcast 16, 783–797 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00620-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00620-9